MC68F375BGMZP33 Freescale Semiconductor, MC68F375BGMZP33 Datasheet - Page 73
MC68F375BGMZP33
Manufacturer Part Number
MC68F375BGMZP33
Description
IC MPU 32BIT 33MHZ 217-PBGA
Manufacturer
Freescale Semiconductor
Datasheet
1.MC68F375BGMZP33.pdf
(616 pages)
Specifications of MC68F375BGMZP33
Processor Type
M683xx 32-Bit
Speed
33MHz
Voltage
5V
Mounting Type
Surface Mount
Package / Case
217-PBGA
Processor Series
M683xx
Core
CPU32
Data Bus Width
32 bit
Program Memory Type
Flash
Program Memory Size
256 KB
Data Ram Size
10 KB
Interface Type
SPI, SCI, CAN
Maximum Clock Frequency
16 MHz
Number Of Programmable I/os
48
Number Of Timers
16
Maximum Operating Temperature
+ 125 C
Mounting Style
SMD/SMT
Minimum Operating Temperature
- 40 C
On-chip Adc
10 bit, 16 Channel
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Contains lead / RoHS non-compliant
Features
-
Lead Free Status / Rohs Status
No
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Company:
Part Number:
MC68F375BGMZP33
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor
Quantity:
10 000
- Current page: 73 of 616
- Download datasheet (9Mb)
3.10.1 M68000 Family Development Support
3.10.2 Background Debug Mode
MC68F375
REFERENCE MANUAL
All M68000 Family members include features to facilitate applications development.
These features include the following:
Trace on Instruction Execution — M68000 Family processors include an instruction-
by-instruction tracing facility as an aid to program development. The MC68020,
MC68030, MC68040, and CPU32 also allow tracing only of those instructions causing
a change in program flow. In the trace mode, a trace exception is generated after an
instruction is executed, allowing a debugger program to monitor the execution of a pro-
gram under test.
Breakpoint Instruction — An emulator may insert software breakpoints into the target
code to indicate when a breakpoint has occurred. On the MC68010, MC68020,
MC68030, and CPU32, this function is provided via illegal instructions, 0x4848–
0x484F, to serve as breakpoint instructions.
Unimplemented Instruction Emulation — During instruction execution, when an
attempt is made to execute an illegal instruction, an illegal instruction exception
occurs. Unimplemented instructions (F-line, A-line, . . .) utilize separate exception vec-
tors to permit efficient emulation of unimplemented instructions in software.
Microcomputer systems generally provide a debugger, implemented in software, for
system analysis at the lowest level. The background debug mode (BDM) on the
CPU32 is unique in that the debugger has been implemented in CPU microcode.
BDM incorporates a full set of debugging options: registers can be viewed or altered,
memory can be read or written to, and test features can be invoked.
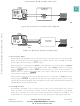
A resident debugger simplifies implementation of an in-circuit emulator. In a common
setup (refer to
A complex, expensive pod-and-cable interface provides a communication path
between the target system and the emulator.
By contrast, an integrated debugger supports use of a bus state analyzer (BSA) for
incircuit emulation. The processor remains in the target system (refer to
and the interface is simplified. The BSA monitors target processor operation and the
on-chip debugger controls the operating environment. Emulation is much “closer” to
target hardware, and many interfacing problems (for example, limitations on high-fre-
quency operation, AC and DC parametric mismatches, and restrictions on cable
length) are minimized.
• Hardware Breakpoints
Figure
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
For More Information On This Product,
3-8), emulator hardware replaces the target system processor.
CENTRAL PROCESSOR UNIT
Go to: www.freescale.com
Rev. 25 June 03
Figure
MOTOROLA
3-9)
3-19
Related parts for MC68F375BGMZP33
Image
Part Number
Description
Manufacturer
Datasheet
Request
R
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet: