MC68F375BGMZP33 Freescale Semiconductor, MC68F375BGMZP33 Datasheet - Page 240
MC68F375BGMZP33
Manufacturer Part Number
MC68F375BGMZP33
Description
IC MPU 32BIT 33MHZ 217-PBGA
Manufacturer
Freescale Semiconductor
Datasheet
1.MC68F375BGMZP33.pdf
(616 pages)
Specifications of MC68F375BGMZP33
Processor Type
M683xx 32-Bit
Speed
33MHz
Voltage
5V
Mounting Type
Surface Mount
Package / Case
217-PBGA
Processor Series
M683xx
Core
CPU32
Data Bus Width
32 bit
Program Memory Type
Flash
Program Memory Size
256 KB
Data Ram Size
10 KB
Interface Type
SPI, SCI, CAN
Maximum Clock Frequency
16 MHz
Number Of Programmable I/os
48
Number Of Timers
16
Maximum Operating Temperature
+ 125 C
Mounting Style
SMD/SMT
Minimum Operating Temperature
- 40 C
On-chip Adc
10 bit, 16 Channel
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Contains lead / RoHS non-compliant
Features
-
Lead Free Status / Rohs Status
No
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Company:
Part Number:
MC68F375BGMZP33
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor
Quantity:
10 000
- Current page: 240 of 616
- Download datasheet (9Mb)
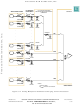
6.5.4 QSMCM Interrupts
6.5.5 QSMCM Configuration Register (QSMCMMCR)
MC68F375
REFERENCE MANUAL
Both the QSPI and SCI can generate interrupt requests. Each has a separate interrupt
request priority register. A single vector register is used to generate exception vector
numbers.
The values of the ILQSPI and ILSCI fields in QILR determine the priority of QSPI and
SCI interrupt requests. The values in these fields correspond to internal interrupt re-
quest signals IRQ[7:1]. A value of 0b111 causes IRQ7 to be asserted when a QSM
interrupt request is made. Lower field values cause correspondingly lower-numbered
interrupt request signals to be asserted. Setting the ILQSPI or ILSCI field values to
0b000 disables interrupts for the respective section. If ILQSPI and ILSCI have the
same non-zero value, and the QSPI and SCI make simultaneous interrupt requests,
the QSPI has priority.
When the CPU32 acknowledges an interrupt request, it places the value in the status
register interrupt priority (IP) mask on the address bus. The QSM compares the IP
mask value to the priority of the request to determine whether it should contend for ar-
bitration priority. Arbitration priority is determined by the value of the IARB field in
QSMCR. Each module that generates interrupts must have a non-zero IARB value. Ar-
bitration is performed by means of serial contention between values stored in individ-
ual module IARB fields.
When the QSM wins interrupt arbitration, it responds to the CPU32 interrupt acknowl-
edge cycle by placing an interrupt vector number on the data bus. The vector number
is used to calculate displacement into the CPU32 exception vector table. SCI and
QSPI vector numbers are generated from the value in the QIVR INTV field. The values
of bits INTV[7:1] are the same for QSPI and SCI. The value of INTV0 is supplied by
the QSM when an interrupt request is made. INTV0 = 0 for SCI interrupt requests;
INTV0 = 1 for QSPI interrupt requests.
At reset, INTV[7:0] is initialized to 0x0F, the uninitialized interrupt vector number. To
enable interrupt-driven serial communication, a user-defined vector number must be
written to QIVR, and interrupt handler routines must be located at the addresses point-
ed to by the corresponding vector. Writes to INTV0 have no effect. Reads of INTV0
return a value of one.
Refer to
INTEGRATION MODULE 2 (SCIM2E)
terrupts.
The QSMCMMCR contains parameters for interfacing to the CPU and the intermodule
bus. This register can be modified only when the CPU is in supervisor mode.
SECTION 3 CENTRAL PROCESSOR UNIT
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
QUEUED SERIAL MULTI-CHANNEL MODULE
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Rev. 25 June 03
for more information about exceptions and in-
and
SECTION 4 SINGLE-CHIP
MOTOROLA
6-6
Related parts for MC68F375BGMZP33
Image
Part Number
Description
Manufacturer
Datasheet
Request
R
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet: