MC68F375BGMZP33 Freescale Semiconductor, MC68F375BGMZP33 Datasheet - Page 275
MC68F375BGMZP33
Manufacturer Part Number
MC68F375BGMZP33
Description
IC MPU 32BIT 33MHZ 217-PBGA
Manufacturer
Freescale Semiconductor
Datasheet
1.MC68F375BGMZP33.pdf
(616 pages)
Specifications of MC68F375BGMZP33
Processor Type
M683xx 32-Bit
Speed
33MHz
Voltage
5V
Mounting Type
Surface Mount
Package / Case
217-PBGA
Processor Series
M683xx
Core
CPU32
Data Bus Width
32 bit
Program Memory Type
Flash
Program Memory Size
256 KB
Data Ram Size
10 KB
Interface Type
SPI, SCI, CAN
Maximum Clock Frequency
16 MHz
Number Of Programmable I/os
48
Number Of Timers
16
Maximum Operating Temperature
+ 125 C
Mounting Style
SMD/SMT
Minimum Operating Temperature
- 40 C
On-chip Adc
10 bit, 16 Channel
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Contains lead / RoHS non-compliant
Features
-
Lead Free Status / Rohs Status
No
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Company:
Part Number:
MC68F375BGMZP33
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor
Quantity:
10 000
- Current page: 275 of 616
- Download datasheet (9Mb)
6.7.8 Mode Fault
6.8 Serial Communication Interface
MC68F375
REFERENCE MANUAL
mands are executed again. SPE is not cleared by the QSPI. New receive data
overwrites previously received data located in the receive data segment.
Wraparound mode is properly exited in two ways: a) The CPU may disable wrap-
around mode by clearing WREN. The next time end of the queue is reached, the QSPI
sets SPIF, clears SPE, and stops; and, b) The CPU sets HALT. This second method
halts the QSPI after the current transfer is completed, allowing the CPU to negate
SPE. The CPU can immediately stop the QSPI by clearing SPE; however, this method
is not recommended, as it causes the QSPI to abort a serial transfer in process.
MODF is asserted by the QSPI when the QSPI is the serial master (MSTR = 1) and
the slave select (PCS0/SS) input pin is pulled low by an external driver. This is possi-
ble only if the PCS0/SS pin is configured as input by QDDR. This low input to SS is not
a normal operating condition. It indicates that a multimaster system conflict may exist,
that another MCU is requesting to become the SPI network master, or simply that the
hardware is incorrectly affecting PCS0/SS. SPE in SPCR1 is cleared, disabling the
QSPI. The QSPI pins revert to control by QPDR. If MODF is set and HMIE in SPCR3
is asserted, the QSPI generates an interrupt to the CPU.
The CPU may clear MODF by reading SPSR with MODF asserted, followed by writing
SPSR with a zero in MODF. After correcting the mode fault problem, the QSPI can be
re-enabled by asserting SPE.
The PCS0/SS pin may be configured as a general-purpose output instead of input to
the QSPI. This inhibits the mode fault checking function. In this case, MODF is not
used by the QSPI.
The dual, independent, serial communication interface (DSCI) communicates with
external devices through an asynchronous serial bus. The two SCI modules are func-
tionally equivalent, except that the SCI1 also provides 16-deep queue capabilities for
the transmit and receive operations. The SCIs are fully compatible with other Motorola
SCI systems. The DSCI has all of the capabilities of previous SCI systems as well as
several significant new features.
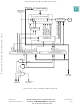
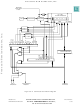
Figure 6-10
of the SCI receiver.
is a block diagram of the SCI transmitter.
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
QUEUED SERIAL MULTI-CHANNEL MODULE
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Rev. 25 June 03
Figure 6-11
is a block diagram
MOTOROLA
6-41
Related parts for MC68F375BGMZP33
Image
Part Number
Description
Manufacturer
Datasheet
Request
R
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet: