MC68F375BGMZP33 Freescale Semiconductor, MC68F375BGMZP33 Datasheet - Page 184
MC68F375BGMZP33
Manufacturer Part Number
MC68F375BGMZP33
Description
IC MPU 32BIT 33MHZ 217-PBGA
Manufacturer
Freescale Semiconductor
Datasheet
1.MC68F375BGMZP33.pdf
(616 pages)
Specifications of MC68F375BGMZP33
Processor Type
M683xx 32-Bit
Speed
33MHz
Voltage
5V
Mounting Type
Surface Mount
Package / Case
217-PBGA
Processor Series
M683xx
Core
CPU32
Data Bus Width
32 bit
Program Memory Type
Flash
Program Memory Size
256 KB
Data Ram Size
10 KB
Interface Type
SPI, SCI, CAN
Maximum Clock Frequency
16 MHz
Number Of Programmable I/os
48
Number Of Timers
16
Maximum Operating Temperature
+ 125 C
Mounting Style
SMD/SMT
Minimum Operating Temperature
- 40 C
On-chip Adc
10 bit, 16 Channel
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Contains lead / RoHS non-compliant
Features
-
Lead Free Status / Rohs Status
No
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Company:
Part Number:
MC68F375BGMZP33
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor
Quantity:
10 000
- Current page: 184 of 616
- Download datasheet (9Mb)
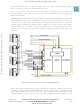
5.6 General-Purpose I/O Port Operation
5.6.1 Port Data Register
MC68F375
REFERENCE MANUAL
when the CPU is operating in supervisor mode. Assignable data space can have either
restricted to supervisor-only data space access or unrestricted supervisor and user
data space accesses. The SUPV bit in QADC64MCR designates the assignable
space as supervisor or unrestricted.
Attempts to read or write supervisor-only data space when the CPU is not in supervisor
mode cause the bus master to assert the internal transfer error acknowledge (TEA)
signal.
The supervisor-only data space segment contains the QADC64 global registers, which
include QADC64MCR and QADC64INT. The supervisor/unrestricted space designa-
tion for the CCW table, the result word table, and the remaining QADC64 registers is
programmable.
QADC64 port pins, when used as general-purpose input, are conditioned by a syn-
chronizer with an enable feature. The synchronizer is not enabled until the QADC64
decodes an IMB bus cycle which addresses the port data register to minimize the high-
current effect of mid-level signals on the inputs used for analog signals. Digital input
signals must meet the input low voltage (V
see
input pin does not meet the digital input pin specifications when a digital port read
operation occurs, an indeterminate state is read. To avoid reading inappropriate val-
ues on analog inputs, the user software should employ a “masking” operation.
During a port data register read, the actual value of the pin is reported when its corre-
sponding bit in the data direction register defines the pin to be an input (port A only).
When the data direction bit specifies the pin to be an output, the content of the port
data register is read. By reading the latch which drives the output pin, software instruc-
tions (like bit manipulation instructions) that read data, modify it, and write the result
work correctly.
There is one special case to consider for digital I/O port operation. When the MUX
(externally multiplexed) bit is set in QACR0, the data direction register settings are
ignored for the bits corresponding to PQA[2:0] and the three multiplexed address
MA[2:0] output pins. The MA[2:0] pins are forced to be digital outputs, regardless of
the data direction setting, and the multiplexed address outputs are driven. The data
returned during a port data register read is the value of the multiplexed address latches
which drive MA[2:0], regardless of the data direction setting.
QADC64 ports A and B are accessed through two 8-bit port data registers (PORTQA
and PORTQB). Port A pins are referred to as PQA when used as an 8-bit input/output
port. Port A can also be used for analog inputs AN[59:52] and external multiplexer
address outputs MA[2:0].
Table E-3
QUEUED ANALOG-TO-DIGITAL CONVERTER MODULE-64
in
APPENDIX E ELECTRICAL
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc.
For More Information On This Product,
Go to: www.freescale.com
Rev. 25 June 03
IL
) or input high voltage (V
CHARACTERISTICS. If an analog
IH
) requirements,
MOTOROLA
5-8
Related parts for MC68F375BGMZP33
Image
Part Number
Description
Manufacturer
Datasheet
Request
R
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet:
Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc
Datasheet: