ATMEGA128-16AU Atmel, ATMEGA128-16AU Datasheet - Page 225

ATMEGA128-16AU
Manufacturer Part Number
ATMEGA128-16AU
Description
IC AVR MCU 128K 16MHZ 5V 64TQFP
Manufacturer
Atmel
Series
AVR® ATmegar
Datasheets
1.ATMEGA128-16AU.pdf
(26 pages)
2.ATMEGA128-16AU.pdf
(385 pages)
3.ATMEGA128-16AU.pdf
(389 pages)
Specifications of ATMEGA128-16AU
Core Processor
AVR
Core Size
8-Bit
Speed
16MHz
Connectivity
EBI/EMI, I²C, SPI, UART/USART
Peripherals
Brown-out Detect/Reset, POR, PWM, WDT
Number Of I /o
53
Program Memory Size
128KB (64K x 16)
Program Memory Type
FLASH
Eeprom Size
4K x 8
Ram Size
4K x 8
Voltage - Supply (vcc/vdd)
4.5 V ~ 5.5 V
Data Converters
A/D 8x10b
Oscillator Type
Internal
Operating Temperature
-40°C ~ 85°C
Package / Case
64-TQFP, 64-VQFP
Processor Series
ATMEGA128x
Core
AVR8
Data Bus Width
8 bit
Data Ram Size
4 KB
Interface Type
2-Wire, JTAG, SPI, USART
Maximum Clock Frequency
16 MHz
Number Of Programmable I/os
53
Number Of Timers
4
Operating Supply Voltage
4.5 V to 5.5 V
Maximum Operating Temperature
+ 85 C
Mounting Style
SMD/SMT
3rd Party Development Tools
EWAVR, EWAVR-BL
Development Tools By Supplier
ATAVRDRAGON, ATSTK500, ATSTK600, ATAVRISP2, ATAVRONEKIT
Minimum Operating Temperature
- 40 C
On-chip Adc
10 bit, 8 Channel
Controller Family/series
AVR MEGA
No. Of I/o's
53
Eeprom Memory Size
4096Byte
Ram Memory Size
4KB
Cpu Speed
16MHz
Rohs Compliant
Yes
For Use With
ATSTK600-TQFP64 - STK600 SOCKET/ADAPTER 64-TQFP770-1007 - ISP 4PORT ATMEL AVR MCU SPI/JTAG770-1005 - ISP 4PORT FOR ATMEL AVR MCU JTAG770-1004 - ISP 4PORT FOR ATMEL AVR MCU SPIATAVRISP2 - PROGRAMMER AVR IN SYSTEMATJTAGICE2 - AVR ON-CHIP D-BUG SYSTEMATSTK501 - ADAPTER KIT FOR 64PIN AVR MCUATSTK500 - PROGRAMMER AVR STARTER KIT
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Lead free / RoHS Compliant
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Company:
Part Number:
ATMEGA128-16AU
Manufacturer:
MITSUBISHI
Quantity:
104
Company:
Part Number:
ATMEGA128-16AU
Manufacturer:
ATMEL
Quantity:
3 340
Part Number:
ATMEGA128-16AU
Manufacturer:
ATMEL/爱特梅尔
Quantity:
20 000
Miscellaneous States
Table 92. Miscellaneous States
Combining Several TWI
Modes
2467M–AVR–11/04
Status Code
(TWSR)
Prescaler Bits
are 0
$F8
$00
Status of the Two-wire Serial
Bus and Two-wire Serial Inter-
face Hardware
No relevant state information
available; TWINT = “0”
Bus error due to an illegal
START or STOP condition
There are two status codes that do not correspond to a defined TWI state, see Table 92.
Status $F8 indicates that no relevant information is available because the TWINT flag is
not set. This occurs between other states, and when the TWI is not involved in a serial
transfer.
Status $00 indicates that a bus error has occurred during a Two-wire Serial Bus trans-
fer. A bus error occurs when a START or STOP condition occurs at an illegal position in
the format frame. Examples of such illegal positions are during the serial transfer of an
address byte, a data byte, or an acknowledge bit. When a bus error occurs, TWINT is
set. To recover from a bus error, the TWSTO flag must set and TWINT must be cleared
by writing a logic one to it. This causes the TWI to enter the not addressed slave mode
and to clear the TWSTO flag (no other bits in TWCR are affected). The SDA and SCL
lines are released, and no STOP condition is transmitted.
In some cases, several TWI modes must be combined in order to complete the desired
action. Consider for example reading data from a serial EEPROM. Typically, such a
transfer involves the following steps:
1. The transfer must be initiated
2. The EEPROM must be instructed what location should be read
3. The reading must be performed
4. The transfer must be finished
Note that data is transmitted both from master to slave and vice versa. The master must
instruct the slave what location it wants to read, requiring the use of the MT mode. Sub-
sequently, data must be read from the slave, implying the use of the MR mode. Thus,
the transfer direction must be changed. The master must keep control of the bus during
all these steps, and the steps should be carried out as an atomical operation. If this prin-
ciple is violated in a multimaster system, another master can alter the data pointer in the
EEPROM between steps 2 and 3, and the master will read the wrong data location.
Such a change in transfer direction is accomplished by transmitting a REPEATED
START between the transmission of the address byte and reception of the data. After a
REPEATED START, the master keeps ownership of the bus. The following figure shows
the flow in this transfer.
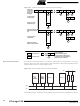
Figure 104. Combining Several TWI Modes to Access a Serial EEPROM
S
S = START
Application Software Response
To/from TWDR
No TWDR action
No TWDR action
Transmitted from master to slave
SLA+W
To TWCR
STA
No TWCR action
0
A
Master Transmitter
ADDRESS
STO
1
TWINT
1
A
TWEA
Rs = REPEATED START
X
Rs
Transmitted from slave to master
Wait or proceed current transfer
Only the internal hardware is affected, no STOP condi-
tion is sent on the bus. In all cases, the bus is released
and TWSTO is cleared.
SLA+R
Next Action Taken by TWI Hardware
A
ATmega128
Master Receiver
DATA
P = STOP
A
225
P