IPR-SDRAM/DDR2 Altera, IPR-SDRAM/DDR2 Datasheet - Page 23

IPR-SDRAM/DDR2
Manufacturer Part Number
IPR-SDRAM/DDR2
Description
IP CORE Renewal Of IP-SDRAM/DDR2
Manufacturer
Altera
Type
MegaCorer
Specifications of IPR-SDRAM/DDR2
Software Application
IP CORE, Memory Controllers, SDRAM
Supported Families
Cyclone, HardCopy, Stratix
Features
Data Mask Signals For Partial Write Operations, Bank Management Architecture
Core Architecture
FPGA
Core Sub-architecture
Cyclone, HardCopy, Stratix
Rohs Compliant
NA
Function
DDR2 SDRAM Controller
License
Renewal License
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
na
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
na
Chapter 2: Getting Started
MegaWizard Plug-In Manager Design Flow
© March 2009 Altera Corporation
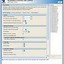
17. Enter the board trace delays. These delays are used by the timing analysis and to
18. Click Show Timing Estimates, at any time in the parameterize screen ), to see the
19. Click the Project Settings tab.
20. Enter the pin name of the clock driving the memory (+); enter the pin name of the
21. Ensure Update the example design file that instantiates the controller variation
22. Altera recommends that you turn on Automatically apply datapath-specific
23. Turn off Update the example design PLLs, if you have edited the PLL and you do
24. The constraints script analyzes and elaborates your design to automatically extract
1
configure the datapath.
1
results of the system timing analysis.
f
clock driving the memory (–). IP Toolbench suggests the name for the fed-back
clock input, but you can edit this name if you wish.
1
1
is turned on, for IP Toolbench to automatically update the example design and the
testbench.
contraints to the Quartus II project and Automatically verify datapath-specific
timing in the Quartus II project, so that the Quartus II software automatically
runs these scripts when you compile the example design.
not want the wizard to regenerate the PLL when you regenerate the variation.
the hierarchy to your variation. To prevent the constraints script analyzing and
elaborating your design, turn on Enable hierarchy control, and enter the correct
hierarchy path to your variation. The hierarchy path is the path to the datapath in
your DDR SDRAM controller, without the top-level name.
page 2–14
1
You must enter suitable values for the pin loading, because the values affect
timing. Unsuitable values may lead to inaccurate timing analysis.
You must accurately set the board trace delays for your system to work in
hardware.
The pin names must end in [0], even if you have more than one clock pair.
Only change the suggested clock pin names, if you have edited the clock
pin names in the top-level design file. Changing the clock pin names
changes the names of the clock outputs and fed-back clock in the example
top-level design.
The constraints apply to the datapath (rather than the controller) so that if
you replace the controller logic with your own controller, the add
constraints script is still valid. So, if you maintain the entity and instance
names, the Quartus II software will correctly add the constraints to your
design.
For more information on project settings, refer to
page
shows a system example.
3–40.
DDR and DDR2 SDRAM Controller Compiler User Guide
“Project Settings” on
Figure 2–1 on
2–13