ATMEGA128-16AI Atmel, ATMEGA128-16AI Datasheet - Page 200

ATMEGA128-16AI
Manufacturer Part Number
ATMEGA128-16AI
Description
IC AVR MCU 128K 16MHZ 64-TQFP
Manufacturer
Atmel
Series
AVR® ATmegar
Specifications of ATMEGA128-16AI
Core Processor
AVR
Core Size
8-Bit
Speed
16MHz
Connectivity
EBI/EMI, I²C, SPI, UART/USART
Peripherals
Brown-out Detect/Reset, POR, PWM, WDT
Number Of I /o
53
Program Memory Size
128KB (64K x 16)
Program Memory Type
FLASH
Eeprom Size
4K x 8
Ram Size
4K x 8
Voltage - Supply (vcc/vdd)
4.5 V ~ 5.5 V
Data Converters
A/D 8x10b
Oscillator Type
Internal
Operating Temperature
-40°C ~ 85°C
Package / Case
64-TQFP, 64-VQFP
For Use With
ATSTK501 - ADAPTER KIT FOR 64PIN AVR MCU
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Contains lead / RoHS non-compliant
Other names
Q1167170A
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Company:
Part Number:
ATMEGA128-16AI
Manufacturer:
FSC
Quantity:
7 600
Part Number:
ATMEGA128-16AI
Manufacturer:
ATMEL/爱特梅尔
Quantity:
20 000
- Current page: 200 of 385
- Download datasheet (8Mb)
Combining Address
and Data Packets Into
a Transmission
Multi-master Bus
Systems,
Arbitration and
Synchronization
200
ATmega128
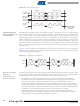
Figure 90. Data Packet Format
A transmission basically consists of a START condition, a SLA+R/W, one or more data packets
and a STOP condition. An empty message, consisting of a START followed by a STOP condi-
tion, is illegal. Note that the Wired-ANDing of the SCL line can be used to implement
handshaking between the master and the slave. The slave can extend the SCL low period by
pulling the SCL line low. This is useful if the clock speed set up by the master is too fast for the
slave, or the slave needs extra time for processing between the data transmissions. The slave
extending the SCL low period will not affect the SCL high period, which is determined by the
master. As a consequence, the slave can reduce the TWI data transfer speed by prolonging the
SCL duty cycle.
Figure 91
between the SLA+R/W and the STOP condition, depending on the software protocol imple-
mented by the application software.
Figure 91. Typical Data Transmission
The TWI protocol allows bus systems with several masters. Special concerns have been taken
in order to ensure that transmissions will proceed as normal, even if two or more masters initiate
a transmission at the same time. Two problems arise in multi-master systems:
•
•
An algorithm must be implemented allowing only one of the masters to complete the
transmission. All other masters should cease transmission when they discover that they
have lost the selection process. This selection process is called arbitration. When a
contending master discovers that it has lost the arbitration process, it should immediately
switch to slave mode to check whether it is being addressed by the winning master. The fact
that multiple masters have started transmission at the same time should not be detectable to
the slaves, i.e., the data being transferred on the bus must not be corrupted.
Different masters may use different SCL frequencies. A scheme must be devised to
synchronize the serial clocks from all masters, in order to let the transmission proceed in a
lockstep fashion. This will facilitate the arbitration process.
Transmitter
Aggregate
SDA
SCL
SDA from
SDA from
SCL from
Receiver
Master
SDA
START
SLA+R/W
shows a typical data transmission. Note that several data bytes can be transmitted
Addr MSB
1
2
Data MSB
SLA+R/W
1
Addr LSB
7
2
R/W
8
ACK
9
Data Byte
7
Data MSB
Data LSB
1
8
2
Data Byte
ACK
9
7
Data LSB
8
STOP, REPEATED
ACK
9
START or Next
Data Byte
2467V–AVR–02/11
STOP
Related parts for ATMEGA128-16AI
Image
Part Number
Description
Manufacturer
Datasheet
Request
R

Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Microcontroller with 128K bytes In-system programmable flash, 8 MHz, power supply =2.7 - 5.5V
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
IC AVR MCU 128K 16MHZ 5V 64TQFP
Manufacturer:
Atmel
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
IC AVR MCU 128K 16MHZ 5V 64-QFN
Manufacturer:
Atmel
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
IC AVR MCU 128K 16MHZ COM 64-QFN
Manufacturer:
Atmel
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
IC AVR MCU 128K 16MHZ 64-TQFP
Manufacturer:
Atmel
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
IC AVR MCU 128K 16MHZ IND 64-QFN
Manufacturer:
Atmel
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
MCU AVR 128KB FLASH 16MHZ 64TQFP
Manufacturer:
Atmel
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
MCU AVR 128KB FLASH 16MHZ 64QFN
Manufacturer:
Atmel
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
MCU AVR 128KB FLASH 16MHZ 64TQFP
Manufacturer:
Atmel
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
MCU AVR 128KB FLASH 16MHZ 64QFN
Manufacturer:
Atmel
Datasheet: