ATMEGA16-16PU Atmel, ATMEGA16-16PU Datasheet - Page 198

ATMEGA16-16PU
Manufacturer Part Number
ATMEGA16-16PU
Description
IC AVR MCU 16K 16MHZ 5V 40DIP
Manufacturer
Atmel
Series
AVR® ATmegar
Datasheets
1.ATMEGA16L-8MI.pdf
(26 pages)
2.ATMEGA16L-8MI.pdf
(357 pages)
3.ATMEGA16-16PU.pdf
(358 pages)
4.ATMEGA16-16PU.pdf
(351 pages)
Specifications of ATMEGA16-16PU
Core Processor
AVR
Core Size
8-Bit
Speed
16MHz
Connectivity
I²C, SPI, UART/USART
Peripherals
Brown-out Detect/Reset, POR, PWM, WDT
Number Of I /o
32
Program Memory Size
16KB (8K x 16)
Program Memory Type
FLASH
Eeprom Size
512 x 8
Ram Size
1K x 8
Voltage - Supply (vcc/vdd)
4.5 V ~ 5.5 V
Data Converters
A/D 8x10b
Oscillator Type
Internal
Operating Temperature
-40°C ~ 85°C
Package / Case
40-DIP (0.600", 15.24mm)
Package
40PDIP
Device Core
AVR
Family Name
ATmega
Maximum Speed
16 MHz
Operating Supply Voltage
5 V
Data Bus Width
8 Bit
Number Of Programmable I/os
32
Interface Type
TWI/SPI/USART
On-chip Adc
8-chx10-bit
Number Of Timers
3
Processor Series
ATMEGA16x
Core
AVR8
Data Ram Size
1 KB
Maximum Clock Frequency
16 MHz
Maximum Operating Temperature
+ 85 C
Mounting Style
Through Hole
3rd Party Development Tools
EWAVR, EWAVR-BL
Development Tools By Supplier
ATAVRDRAGON, ATSTK500, ATSTK600, ATAVRISP2, ATAVRONEKIT
Minimum Operating Temperature
- 40 C
A/d Inputs
8-Channel, 10-Bit
Cpu Speed
16 MIPS
Eeprom Memory
512 Bytes
Input Output
32
Interface
JTAG/SPI/UART
Memory Type
Flash
Number Of Bits
8
Package Type
44-pin PDIP
Programmable Memory
16K Bytes
Timers
2-8-bit, 1-16-bit
Voltage, Range
4.5-5.5 V
Controller Family/series
AVR MEGA
No. Of I/o's
32
Eeprom Memory Size
512Byte
Ram Memory Size
1KB
Rohs Compliant
Yes
For Use With
ATSTK600-TQFP44 - STK600 SOCKET/ADAPTER 44-TQFPATSTK600-DIP40 - STK600 SOCKET/ADAPTER 40-PDIP770-1007 - ISP 4PORT ATMEL AVR MCU SPI/JTAGATAVRISP2 - PROGRAMMER AVR IN SYSTEMATJTAGICE2 - AVR ON-CHIP D-BUG SYSTEMATSTK500 - PROGRAMMER AVR STARTER KIT
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Lead free / RoHS Compliant
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Company:
Part Number:
ATMEGA16-16PU
Manufacturer:
Atmel
Quantity:
140
- ATMEGA16L-8MI PDF datasheet
- ATMEGA16L-8MI PDF datasheet #2
- ATMEGA16-16PU PDF datasheet #3
- ATMEGA16-16PU PDF datasheet #4
- Current page: 198 of 351
- Download datasheet (3Mb)
198
ATmega16(L)
Several different scenarios may arise during arbitration, as described below:
•
•
•
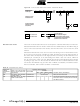
This is summarized in Figure 96. Possible status values are given in circles.
Figure 96. Possible Status Codes Caused by Arbitration
START
Two or more Masters are performing identical communication with the same Slave.
In this case, neither the Slave nor any of the Masters will know about the bus
contention.
Two or more Masters are accessing the same Slave with different data or direction
bit. In this case, arbitration will occur, either in the READ/WRITE bit or in the data
bits. The Masters trying to output a one on SDA while another Master outputs a zero
will lose the arbitration. Losing Masters will switch to not addressed Slave mode or
wait until the bus is free and transmit a new START condition, depending on
application software action.
Two or more Masters are accessing different Slaves. In this case, arbitration will
occur in the SLA bits. Masters trying to output a one on SDA while another Master
outputs a zero will lose the arbitration. Masters losing arbitration in SLA will switch to
Slave mode to check if they are being addressed by the winning Master. If
addressed, they will switch to SR or ST mode, depending on the value of the
READ/WRITE bit. If they are not being addressed, they will switch to not addressed
Slave mode or wait until the bus is free and transmit a new START condition,
depending on application software action.
Address / General Call
received
Direction
Own
Yes
Arbitration lost in SLA
SLA
Read
Write
No
68/78
38
B0
Arbitration lost in Data
TWI bus will be released and not addressed slave mode will be entered
A START condition will be transmitted when the bus becomes free
Data byte will be received and NOT ACK will be returned
Data byte will be received and ACK will be returned
Last data byte will be transmitted and NOT ACK should be received
Data byte will be transmitted and ACK should be received
Data
2466J–AVR–10/04
STOP
Related parts for ATMEGA16-16PU
Image
Part Number
Description
Manufacturer
Datasheet
Request
R

Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Atmel Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
IC AVR MCU 16K 16MHZ 5V 44TQFP
Manufacturer:
Atmel
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
IC AVR MCU 16K 16MHZ 5V 44-QFN
Manufacturer:
Atmel
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
MCU AVR 16K FLASH 16MHZ 44-QFN
Manufacturer:
Atmel
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
IC AVR MCU 16K 16MHZ COM 40-DIP
Manufacturer:
Atmel
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
IC AVR MCU 16K 16MHZ COM 44-QFN
Manufacturer:
Atmel
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
IC AVR MCU 16K 16MHZ IND 40-DIP
Manufacturer:
Atmel
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
IC AVR MCU 16K 16MHZ IND 44-QFN
Manufacturer:
Atmel
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
IC AVR MCU 16K 16MHZ IND 44-TQFP
Manufacturer:
Atmel
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
IC MCU 8BIT 16KB FLASH 44TQFP
Manufacturer:
Atmel
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
MCU AVR 16K FLASH 16MHZ 44-TQFP
Manufacturer:
Atmel
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
IC AVR MCU 16K 16MHZ COM 44-TQFP
Manufacturer:
Atmel
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
IC MCU AVR 16K 5V 16MHZ 44-TQFP
Manufacturer:
Atmel
Datasheet: