C8051F320 Silicon Laboratories Inc, C8051F320 Datasheet - Page 207
C8051F320
Manufacturer Part Number
C8051F320
Description
IC 8051 MCU 16K FLASH 32LQFP
Manufacturer
Silicon Laboratories Inc
Series
C8051F32xr
Datasheet
1.C8051F320R.pdf
(256 pages)
Specifications of C8051F320
Core Processor
8051
Core Size
8-Bit
Speed
25MHz
Connectivity
SMBus (2-Wire/I²C), SPI, UART/USART, USB
Peripherals
Brown-out Detect/Reset, POR, PWM, Temp Sensor, WDT
Number Of I /o
25
Program Memory Size
16KB (16K x 8)
Program Memory Type
FLASH
Ram Size
2.25K x 8
Voltage - Supply (vcc/vdd)
2.7 V ~ 3.6 V
Data Converters
A/D 17x10b
Oscillator Type
Internal
Operating Temperature
-40°C ~ 85°C
Package / Case
32-LQFP
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Contains lead / RoHS non-compliant
Eeprom Size
-
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Company:
Part Number:
C8051F320
Manufacturer:
Silicon Laboratories Inc
Quantity:
10 000
Part Number:
C8051F320
Manufacturer:
SILICON LABS/芯科
Quantity:
20 000
Company:
Part Number:
C8051F320-GQ
Manufacturer:
SiliconL
Quantity:
18 793
Company:
Part Number:
C8051F320-GQ
Manufacturer:
SILICON
Quantity:
1
Company:
Part Number:
C8051F320-GQ
Manufacturer:
Silicon Laboratories Inc
Quantity:
10 000
Company:
Part Number:
C8051F320-GQR
Manufacturer:
SiliconL
Quantity:
1 000
Company:
Part Number:
C8051F320-GQR
Manufacturer:
Silicon Laboratories Inc
Quantity:
10 000
Part Number:
C8051F320-GQR
Manufacturer:
SILICON LABS/芯科
Quantity:
20 000
Company:
Part Number:
C8051F320DK
Manufacturer:
SiliconL
Quantity:
4
Company:
Part Number:
C8051F320R
Manufacturer:
Silicon Laboratories Inc
Quantity:
10 000
18.3. SPI0 Slave Mode Operation
When SPI0 is enabled and not configured as a master, it will operate as a SPI slave. As a slave, bytes are shifted in
through the MOSI pin and out through the MISO pin by a master device controlling the SCK signal. A bit counter in
the SPI0 logic counts SCK edges. When 8 bits have been shifted through the shift register, the SPIF flag is set to logic
1, and the byte is copied into the receive buffer. Data is read from the receive buffer by reading SPI0DAT. A slave
device cannot initiate transfers. Data to be transferred to the master device is pre-loaded into the shift register by writ-
ing to SPI0DAT. Writes to SPI0DAT are double-buffered, and are placed in the transmit buffer first. If the shift regis-
ter is empty, the contents of the transmit buffer will immediately be transferred into the shift register. When the shift
register already contains data, the SPI will load the shift register with the transmit buffer’s contents after the last SCK
edge of the next (or current) SPI transfer.
When configured as a slave, SPI0 can be configured for 4-wire or 3-wire operation. The default, 4-wire slave mode,
is active when NSSMD1 (SPI0CN.3) = 0 and NSSMD0 (SPI0CN.2) = 1. In 4-wire mode, the NSS signal is routed to
a port pin and configured as a digital input. SPI0 is enabled when NSS is logic 0, and disabled when NSS is logic 1.
The bit counter is reset on a falling edge of NSS. Note that the NSS signal must be driven low at least 2 system clocks
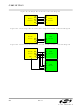
before the first active edge of SCK for each byte transfer. Figure 18.4 shows a connection diagram between two slave
devices in 4-wire slave mode and a master device.
3-wire slave mode is active when NSSMD1 (SPI0CN.3) = 0 and NSSMD0 (SPI0CN.2) = 0. NSS is not used in this
mode, and is not mapped to an external port pin through the crossbar. Since there is no way of uniquely addressing
the device in 3-wire slave mode, SPI0 must be the only slave device present on the bus. It is important to note that in
3-wire slave mode there is no external means of resetting the bit counter that determines when a full byte has been
received. The bit counter can only be reset by disabling and re-enabling SPI0 with the SPIEN bit. Figure 18.3 shows
a connection diagram between a slave device in 3-wire slave mode and a master device.
18.4. SPI0 Interrupt Sources
When SPI0 interrupts are enabled, the following four flags will generate an interrupt when they are set to logic 1:
Note that all of the following bits must be cleared by software.
1.
occur in all SPI0 modes.
2.
the transmit buffer has not been emptied to the SPI shift register. When this occurs, the write to SPI0DAT
will be ignored, and the transmit buffer will not be written.This flag can occur in all SPI0 modes.
3.
multi-master mode and the NSS pin is pulled low. When a Mode Fault occurs, the MSTEN and SPIEN bits
in SPI0CN are set to logic 0 to disable SPI0 and allow another master device to access the bus.
4.
transfer is completed and the receive buffer still holds an unread byte from a previous transfer. The new byte
is not transferred to the receive buffer, allowing the previously received data byte to be read. The data byte
which caused the overrun is lost.
The SPI Interrupt Flag, SPIF (SPI0CN.7) is set to logic 1 at the end of each byte transfer. This flag can
The Write Collision Flag, WCOL (SPI0CN.6) is set to logic 1 if a write to SPI0DAT is attempted when
The Mode Fault Flag MODF (SPI0CN.5) is set to logic 1 when SPI0 is configured as a master, and for
The Receive Overrun Flag RXOVRN (SPI0CN.4) is set to logic 1 when configured as a slave, and a
Rev. 1.1
C8051F320/1
207