MCP6V01DM-VOS Microchip Technology, MCP6V01DM-VOS Datasheet - Page 25
MCP6V01DM-VOS
Manufacturer Part Number
MCP6V01DM-VOS
Description
DEMO BOARD FOR MCP6V01
Manufacturer
Microchip Technology
Specifications of MCP6V01DM-VOS
Channels Per Ic
1 - Single
Amplifier Type
Chopper (Zero-Drift)
Output Type
Rail-to-Rail
Slew Rate
0.5 V/µs
Current - Output / Channel
22mA
Operating Temperature
-40°C ~ 125°C
Voltage - Supply, Single/dual (±)
1.8 V ~ 5.5 V
Board Type
Fully Populated
Utilized Ic / Part
MCP6V01
Silicon Manufacturer
Microchip
Application Sub Type
Operational Amplifier
Kit Application Type
Amplifier
Silicon Core Number
MCP6V01, MCP6V03, MCP6V06, MCP6V08
Kit Contents
Board
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Lead free / RoHS Compliant
-3db Bandwidth
-
Current - Supply (main Ic)
-
Lead Free Status / Rohs Status
Lead free / RoHS Compliant
After selecting R
resulting frequency response peaking and step
response overshoot. Modify R
response is reasonable. Bench evaluation and
simulations with the MCP6V01 SPICE macro model
(good for all of the MCP6V01/2/3 op amps) are helpful.
4.3.6
This family of auto-zeroed op amps has an output
impedance
double zero when the gain is low. This can cause a
large phase shift in feedback networks that have low
resistance near the part’s bandwidth. This large phase
shift can cause stability problems.
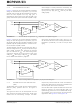
Figure 4-8
resistance near the part’s bandwidth. R
pole at 0.16 kHz, so the noise gain (G
circuit’s bandwidth (roughly 1.3 MHz). The load seen
by the op amp’s output at 1.3 MHz is R
This is low enough to be a real concern.
FIGURE 4-8:
To solve this problem, increase the resistive load to at
least 3 kΩ. Methods to accomplish this task include:
• Increase R
• Remove C
• Add a 3 kΩ resistor at the op amp’s output that is
FIGURE 4-9:
Load Issue.
© 2008 Microchip Technology Inc.
V
not in the signal path; see
V
IN
IN
100Ω
100Ω
100Ω
100Ω
R
R
R
R
shows one circuit example that has low
N
G
STABILIZING OUTPUT LOADS
(Figure 2-31
G
N
F
G
(relocate the filter)
ISO
MCP6V0X
MCP6V0X
for your circuit, double check the
10.0 kΩ
10.0 kΩ
0.1 µF
0.1 µF
Output Load Issue.
One Solution To Output
R
C
R
C
F
F
and
F
F
Figure 4-9
Figure
ISO
's value until the
R
3.01 kΩ
2-32) that has a
X
N
) is 1 V/V at the
F
R
10.0 kΩ
R
10.0 kΩ
L
and C
G
L
||R
L
V
V
F
(99Ω).
OUT
OUT
set a
4.3.7
Reduce undesired noise and signals with:
• Low bandwidth signal filters:
• Good PCB layout techniques:
• Good power supply design:
4.3.8
With this family of operational amplifiers, the power
supply pin (V
bypass capacitor (i.e., 0.01 µF to 0.1 µF) within 2 mm
of the pin for good high-frequency performance.
These parts also need a bulk capacitor (i.e., 1 µF or
larger) within 100 mm to provide large, slow currents.
This bulk capacitor can be shared with other low noise,
analog parts.
Additional filtering of high frequency power supply
noise (e.g., switched mode power supplies) can be
achieved using resistors. The resistors need to be
small enough to prevent a large drop in V
amp, which would cause a reduced output range and
possible load-induced power supply noise. The resis-
tors also need to be large enough to dissipate little
power when V
cuit in
switched mode power supplies. Smaller resistors and
capacitors are a better choice for designs where the
power supply is reasonably quiet.
FIGURE 4-10:
V
to other analog parts
- Minimizes random analog noise
- Reduces interfering signals
- Minimizes crosstalk
- Minimizes parasitic capacitances and
- Isolation from other parts
- Filtering of interference on supply line(s)
S_ANA
inductances that interact with fast switching
edges
Figure 4-10
100 µF
143Ω
1/4W
REDUCING UNDESIRED NOISE
AND SIGNALS
SUPPLY BYPASSING AND
FILTERING
DD
DD
for single supply) should have a local
1/10W
100 µF
143Ω
is turned on and off quickly. The cir-
gives good rejection out to 1 MHz for
MCP6V01/2/3
Additional Supply Filtering.
MCP6V0X
DS22058C-page 25
0.1 µF
DD
for the op