ADM1041-EVAL Analog Devices Inc, ADM1041-EVAL Datasheet - Page 38

ADM1041-EVAL
Manufacturer Part Number
ADM1041-EVAL
Description
BOARD EVALUATION ADM1041
Manufacturer
Analog Devices Inc
Datasheet
1.ADM1041AARQZ-REEL7.pdf
(64 pages)
Specifications of ADM1041-EVAL
Main Purpose
AC/DC, Secondary Side
Outputs And Type
1, Non-Isolated
Power - Output
24W
Voltage - Output
12V
Current - Output
2A
Voltage - Input
85 ~ 132VAC
Board Type
Fully Populated
Utilized Ic / Part
ADM1041
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Contains lead / RoHS non-compliant
Frequency - Switching
-
Regulator Topology
-
Lead Free Status / Rohs Status
Not Compliant
ADM1041
6.
7.
8.
9.
10. The master asserts a stop condition on SDA to end the
When performing a block write to EEPROM, the page that
contains the location to be written should not be write-
protected (Register 03h) prior to sending the above SMBus
packet. Block writes are limited to within a 32-byte page
boundary and cannot cross into the next page.
SMBus READ OPERATIONS
The ADM1041 uses the following SMBus read protocols.
Receive Byte
In this operation, the master device receives a single byte from a
slave device, as follows:
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
In the ADM1041, the receive byte protocol is used to read a
single byte of data from a RAM or EEPROM location whose
address has been set previously by a send byte or write byte/
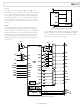
word operation. This is illustrated in Figure 35.
S
1
ADDRESS
SLAVE
The master sends a data byte that tells the slave device how
many data bytes will be sent. The SMBus specification
allows a maximum of 32 data bytes to be sent in a block
write.
The slave asserts ACK on SDA.
The master sends N data bytes.
The slave asserts ACK on SDA after each data byte.
transaction.
The master device asserts a start condition on SDA.
The master sends the 7-bit slave address followed by the
read bit (high).
The addressed slave device asserts ACK on SDA.
The master receives a data byte.
The master asserts NO ACK on SDA.
The master asserts a stop condition on SDA and the
transaction ends.
2
W A
Figure 35. Single-Byte Read from EEPROM or RAM
3
Figure 34. Block Write to EEPROM or RAM
(BLOCK WRITE)
COMMAND A0h
1
S
ADDRESS
4
SLAVE
2
1
S
A
5
R A
ADDRESS
COUNT
BYTE
SLAVE
3
6
2
DATA
4
A
7
W A
DATA 1
A
5
8
3
P
6
COMMAND A1h
(BLOCK READ)
A
9
DATA 2
4
Figure 36. Block Read from EEPROM or RAM
A
DATA N
A
5
Rev. A | Page 38 of 64
S
6
ADDRESS
A P
SLAVE
10
7
R A
Block Read
In this operation, the master device reads a block of data from a
slave device. The start address for a block read must previously
have been set. In the case of the ADM1041, this is done by a
send byte operation to set a RAM address or by a write byte/word
operation to set an EEPROM address. The block read operation
itself consists of a send byte operation that sends a block read
command to the slave, immediately followed by a repeat start,
and a read operation that reads out multiple data bytes, as follows:
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10. The master asserts ACK on SDA.
11. The master receives N data bytes.
12. The master asserts ACK on SDA after each data byte.
13. The slave does not acknowledge after the Nth data byte.
14. The master asserts a stop condition on SDA to end the
8
COUNT
BYTE
The master device asserts a start condition on SDA.
The master sends the 7-bit slave address followed by the
write bit (low).
The addressed slave device asserts ACK on SDA.
The master sends a command code that tells the slave
device to expect a block read. The ADM1041 command
code for a block read is A1h (10100001).
The slave asserts ACK on SDA.
The master asserts a repeat start condition on SDA.
The master sends the 7-bit slave address followed by the
read bit (high).
The slave asserts ACK on SDA.
The master receives a byte count data byte that tells it how
many data bytes will be received. The SMBus specification
allows a maximum of 32 data bytes to be received in a
block read.
transaction.
9
10
A
DATA 1
11
12
A DATA N
13
A
14
P