ST72F63BK4M1 STMicroelectronics, ST72F63BK4M1 Datasheet - Page 37

ST72F63BK4M1
Manufacturer Part Number
ST72F63BK4M1
Description
IC MCU 8BIT LS 16K 34-SOIC
Manufacturer
STMicroelectronics
Series
ST7r
Datasheet
1.ST72F63BD6U1TR.pdf
(186 pages)
Specifications of ST72F63BK4M1
Core Processor
ST7
Core Size
8-Bit
Speed
8MHz
Connectivity
I²C, SCI, USB
Peripherals
DMA, LVD, POR, PWM, WDT
Number Of I /o
19
Program Memory Size
16KB (16K x 8)
Program Memory Type
FLASH
Ram Size
512 x 8
Voltage - Supply (vcc/vdd)
4 V ~ 5.5 V
Data Converters
A/D 8x8b
Oscillator Type
Internal
Operating Temperature
0°C ~ 70°C
Package / Case
34-SOIC (7.5mm Width)
Processor Series
ST72F6x
Core
ST7
Data Bus Width
8 bit
Data Ram Size
512 B
Interface Type
I2C, SCI, USB
Maximum Clock Frequency
8 MHz
Number Of Programmable I/os
27
Number Of Timers
2 x 16 bit
Operating Supply Voltage
4 V to 5.5 V
Maximum Operating Temperature
+ 70 C
Mounting Style
SMD/SMT
Development Tools By Supplier
ST7MDTU3-EPB/US, ST72F63B-SK/RAIS, ST7MDTU3-EMU3, STX-RLINK
Minimum Operating Temperature
0 C
On-chip Adc
8 bit
For Use With
497-5521 - EVAL BOARD LOW SPEED USB
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Lead free / RoHS Compliant
Eeprom Size
-
Lead Free Status / Rohs Status
Details
Other names
497-2115-5
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Part Number:
ST72F63BK4M1
Manufacturer:
ST
Quantity:
20 000
ST7263Bxx
7
Note:
Interrupts
The ST7 core may be interrupted by one of two different methods: maskable hardware
interrupts as listed in
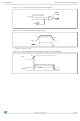
processing flowchart is shown in
The maskable interrupts must be enabled clearing the I bit in order to be serviced. However,
disabled interrupts may be latched and processed when they are enabled (see external
interrupts subsection).
When an interrupt has to be serviced:
●
●
●
●
The interrupt service routine should finish with the IRET instruction which causes the
contents of the saved registers to be recovered from the stack.
As a consequence of the IRET instruction, the I bit will be cleared and the main program will
resume.
Priority management
By default, a servicing interrupt cannot be interrupted because the I bit is set by hardware
entering in interrupt routine.
In the case several interrupts are simultaneously pending, a hardware priority defines which
one will be serviced first (see
Non-maskable software interrupts
This interrupt is entered when the TRAP instruction is executed regardless of the state of
the I bit. It will be serviced according to the flowchart on
Interrupts and low power mode
All interrupts allow the processor to leave the Wait low power mode. Only external and
specific mentioned interrupts allow the processor to leave the Halt low power mode (refer to
the “Exit from HALT“ column in
External interrupts
The pins ITi/PAk and ITj/PBk (i=1,2; j= 5,6; k=4,5) can generate an interrupt when a rising
edge occurs on this pin. Conversely, the ITl/PAn and ITm/PBn pins (l=3,4; m= 7,8; n=6,7)
can generate an interrupt when a falling edge occurs on this pin.
Interrupt generation will occur if it is enabled with the ITiE bit (i=1 to 8) in the ITRFRE
register and if the I bit of the CC is reset.
Normal processing is suspended at the end of the current instruction execution.
The PC, X, A and CC registers are saved onto the stack.
The I bit of the CC register is set to prevent additional interrupts.
The PC is then loaded with the interrupt vector of the interrupt to service and the first
instruction of the interrupt service routine is fetched (refer to
addresses).
Table 9
and a non-maskable software interrupt (TRAP). The Interrupt
Table
Doc ID 7516 Rev 8
Table
Figure
9).
9).
19.
Figure
19.
Table 9
for vector
Interrupts
37/186