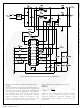
FAN9612 Fairchild Semiconductor, FAN9612 Datasheet - Page 26
FAN9612
Manufacturer Part Number
FAN9612
Description
Manufacturer
Fairchild Semiconductor
Datasheet
1.FAN9612.pdf
(36 pages)
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
© 2008 Fairchild Semiconductor Corporation
FAN9611 / FAN9612 • Rev. 1.1.4
R
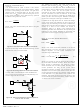
Step 16: Gate Resistors
It is recommended to place at least a 15 resistor
between each of the gate drive outputs (DRV1, DRV2)
and their corresponding power devices. The gate drive
resistors have a beneficial effect to limit the current
drawn from the V
of the power MOSFETs and to attenuate any potential
oscillation in the gate drive circuits.
where 1.0A is the recommended peak value of the gate
drive current.
A speed-up discharge diode that feeds switching current
back into the IC is not recommended.
In cases where it is desirable to control the MOSFET
turn-on and turn-off transition times independently, the
circuit of Figure 36 can be used.
G1
Figure 36. Gate Drive Schematic with Independent
Figure 35. Discharge Diode is Not Recommended
Figure 34. Recommended Gate Drive Schematic
R
G2
VDD
1.0
Turn-On and Turn-Off
DD
MAX
A
bypass capacitor during the turn-on
(29)
26
R
P
The FAN9611/12 sources high peak current to the
MOSFET gate through R
control the turn-on transition time. When the MOSFET is
commanded to turn off, Q
to the source, where the turn-off speed can be
controlled by the value of R
off time is desired, the value of R
serves the dual purpose of protecting the Q
emitter junction and blocking the MOSFET discharge
current from sinking back through the FAN9611/12.
In addition to the high-speed turn-off, another advantage
of this circuit is that the FAN9611/12 does not have to
sink the high peak discharge current from the MOSFET,
reducing the internal power dissipation in the gate drive
circuitry by a factor of two. Instead, the current is
discharged locally in a tighter, more controlled loop,
minimizing parasitic trace inductance while protecting the
FAN9611/12 from injected disturbances associated with
ground bounce and ringing due to high-speed turn-off.
Step 17: Current-Sense Resistors
where 0.18V is the worst-case threshold of the current
limit comparator. The size and type of current sense
resistors depends on their power dissipation and
manufacturing considerations.
where the 1.5 factor is used for the worst-case effect of
the current-limit threshold variation. When the current-
sense resistor is determined, the minimum current-
sense threshold must be used to avoid activating over-
current protection too early as the power supply
approaches full-load condition. The worst-case power
dissipation of the current sense resistor occurs when the
current-sense threshold is at its maximum value defined
in the datasheet. The ratio between the minimum and
maximum thresholds squared (since the square of the
current determines power dissipation) yields exactly the
1.5 factor used in the calculation.
RCS1
CS1
R
1.5
CS2
I
L,PK
2
0.18V
I
L,
R
PK
CS1
6
1
G
OFF
and D
4
OFF
conducts, shorting the gate
9
. Where maximum turn-
2
ON
π
V
, where R
OFF
LINE,
V
OUT
can be 0Ω. D
OFF
www.fairchildsemi.com
G
OFF
is used to
base-
(30)
(31)
ON