ATmega16 Atmel Corporation, ATmega16 Datasheet - Page 8

ATmega16
Manufacturer Part Number
ATmega16
Description
Manufacturer
Atmel Corporation
Specifications of ATmega16
Flash (kbytes)
16 Kbytes
Pin Count
44
Max. Operating Frequency
16 MHz
Cpu
8-bit AVR
# Of Touch Channels
16
Hardware Qtouch Acquisition
No
Max I/o Pins
32
Ext Interrupts
3
Usb Speed
No
Usb Interface
No
Spi
1
Twi (i2c)
1
Uart
1
Graphic Lcd
No
Video Decoder
No
Camera Interface
No
Adc Channels
8
Adc Resolution (bits)
10
Adc Speed (ksps)
15
Analog Comparators
1
Resistive Touch Screen
No
Temp. Sensor
No
Crypto Engine
No
Sram (kbytes)
1
Eeprom (bytes)
512
Self Program Memory
YES
Dram Memory
No
Nand Interface
No
Picopower
No
Temp. Range (deg C)
-40 to 85
I/o Supply Class
2.7 to 5.5
Operating Voltage (vcc)
2.7 to 5.5
Fpu
No
Mpu / Mmu
no / no
Timers
3
Output Compare Channels
4
Input Capture Channels
1
Pwm Channels
4
32khz Rtc
Yes
Calibrated Rc Oscillator
Yes
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Part Number:
ATMEGA16
Manufacturer:
ATMEL/爱特梅尔
Quantity:
20 000
Part Number:
ATmega16-16AI
Manufacturer:
ATMEL/爱特梅尔
Quantity:
20 000
Company:
Part Number:
ATmega16-16AU
Manufacturer:
ATMEL
Quantity:
537
Part Number:
ATmega16-16AU
Manufacturer:
ATMEL/爱特梅尔
Quantity:
20 000
Company:
Part Number:
ATmega16-16AUR
Manufacturer:
Encoders
Quantity:
101
Company:
Part Number:
ATmega16-16PC
Manufacturer:
ATM
Quantity:
100
Company:
Part Number:
ATmega16-16PI
Manufacturer:
RFMD
Quantity:
101
Company:
Part Number:
ATmega16-16PU
Manufacturer:
Atmel
Quantity:
140
AVR CPU Core
Introduction
Architectural
Overview
2466T–AVR–07/10
This section discusses the AVR core architecture in general. The main function of the CPU core
is to ensure correct program execution. The CPU must therefore be able to access memories,
perform calculations, control peripherals, and handle interrupts.
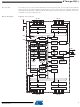
Figure 3. Block Diagram of the AVR MCU Architecture
In order to maximize performance and parallelism, the AVR uses a Harvard architecture – with
separate memories and buses for program and data. Instructions in the program memory are
executed with a single level pipelining. While one instruction is being executed, the next instruc-
tion is pre-fetched from the program memory. This concept enables instructions to be executed
in every clock cycle. The program memory is In-System Reprogrammable Flash memory.
The fast-access Register File contains 32 × 8-bit general purpose working registers with a single
clock cycle access time. This allows single-cycle Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU) operation. In a typ-
ical ALU operation, two operands are output from the Register File, the operation is executed,
and the result is stored back in the Register File – in one clock cycle.
Six of the 32 registers can be used as three 16-bit indirect address register pointers for Data
Space addressing – enabling efficient address calculations. One of the these address pointers
can also be used as an address pointer for look up tables in Flash Program memory. These
added function registers are the 16-bit X-register, Y-register, and Z-register, described later in
this section.
The ALU supports arithmetic and logic operations between registers or between a constant and
a register. Single register operations can also be executed in the ALU. After an arithmetic opera-
tion, the Status Register is updated to reflect information about the result of the operation.
Control Lines
Instruction
Instruction
Program
Memory
Register
Decoder
Flash
Program
Counter
and Control
EEPROM
Registrers
I/O Lines
General
Purpose
SRAM
Data Bus 8-bit
Status
32 x 8
Data
ALU
ATmega16(L)
Comparator
I/O Module1
I/O Module 2
I/O Module n
Watchdog
Interrupt
Timer
Analog
Unit
Unit
SPI
8