ADSP-2189MBSTZ-266 Analog Devices Inc, ADSP-2189MBSTZ-266 Datasheet - Page 12

ADSP-2189MBSTZ-266
Manufacturer Part Number
ADSP-2189MBSTZ-266
Description
IC,DSP,16-BIT,CMOS,QFP,100PIN,PLASTIC
Manufacturer
Analog Devices Inc
Series
ADSP-21xxr
Type
Fixed Pointr
Datasheet
1.ADSP-2189MBSTZ-266.pdf
(32 pages)
Specifications of ADSP-2189MBSTZ-266
Interface
Host Interface, Serial Port
Clock Rate
66MHz
Non-volatile Memory
External
On-chip Ram
192kB
Voltage - I/o
3.30V
Voltage - Core
2.50V
Operating Temperature
-40°C ~ 85°C
Mounting Type
Surface Mount
Package / Case
100-LQFP
Device Core Size
16b
Format
Fixed Point
Clock Freq (max)
66MHz
Mips
66
Device Input Clock Speed
66MHz
Ram Size
192KB
Operating Supply Voltage (typ)
2.5/3.3V
Operating Supply Voltage (min)
2.25V
Operating Supply Voltage (max)
2.75/3.6V
Operating Temp Range
-40C to 85C
Operating Temperature Classification
Industrial
Mounting
Surface Mount
Pin Count
100
Package Type
LQFP
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Lead free / RoHS Compliant
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Lead free / RoHS Compliant
Other names
ADSP-2189MBSTZ266
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Company:
Part Number:
ADSP-2189MBSTZ-266
Manufacturer:
MICROCHIP
Quantity:
16 700
Company:
Part Number:
ADSP-2189MBSTZ-266
Manufacturer:
AD
Quantity:
5 510
Company:
Part Number:
ADSP-2189MBSTZ-266
Manufacturer:
Analog Devices Inc
Quantity:
10 000
ADSP-2189M
Bus Request and Bus Grant
The ADSP-2189M can relinquish control of the data and ad-
dress buses to an external device. When the external device
requires access to memory, it asserts the bus request (BR) sig-
nal. If the ADSP-2189M is not performing an external memory
access, it responds to the active BR input in the following pro-
cessor cycle by:
• Three-stating the data and address buses and the PMS,
• Asserting the bus grant (BG) signal, and
• Halting program execution.
If Go Mode is enabled, the ADSP-2189M will not halt program
execution until it encounters an instruction that requires an
external memory access.
If the ADSP-2189M is performing an external memory access
when the external device asserts the BR signal, it will not three-
state the memory interfaces or assert the BG signal until the
processor cycle after the access completes. The instruction does
not need to be completed when the bus is granted. If a single
instruction requires two external memory accesses, the bus will
be granted between the two accesses.
When the BR signal is released, the processor releases the BG
signal, reenables the output drivers and continues program
execution from the point at which it stopped.
The bus request feature operates at all times, including when
the processor is booting and when RESET is active.
The BGH pin is asserted when the ADSP-2189M requires the
external bus for a memory or BDMA access, but is stopped.
The other device can release the bus by deasserting bus request.
Once the bus is released, the ADSP-2189M deasserts BG and
BGH and executes the external memory access.
Flag I/O Pins
The ADSP-2189M has eight general purpose programmable
input/output flag pins. They are controlled by two memory
mapped registers. The PFTYPE register determines the direc-
tion, 1 = output and 0 = input. The PFDATA register is used to
read and write the values on the pins. Data being read from a
pin configured as an input is synchronized to the ADSP-2189M’s
clock. Bits that are programmed as outputs will read the value
being output. The PF pins default to input during reset.
In addition to the programmable flags, the ADSP-2189M has
five fixed-mode flags, FLAG_IN, FLAG_OUT, FL0, FL1 and
FL2. FL0-FL2 are dedicated output flags. FLAG_IN and
FLAG_OUT are available as an alternate configuration of
SPORT1.
Note: Pins PF0, PF1, PF2 and PF3 are also used for device
configuration during reset.
INSTRUCTION SET DESCRIPTION
The ADSP-2189M assembly language instruction set has an
algebraic syntax that was designed for ease of coding and read-
ability. The assembly language, which takes full advantage of the
processor’s unique architecture, offers the following benefits:
DMS, BMS, CMS, IOMS, RD, WR output drivers,
–12–
• The algebraic syntax eliminates the need to remember cryp-
• Every instruction assembles into a single, 24-bit word that
• The syntax is a superset ADSP-2100 Family assembly language
• Sixteen condition codes are available. For conditional jump,
• Multifunction instructions allow parallel execution of an
DESIGNING AN EZ-ICE-COMPATIBLE SYSTEM
The ADSP-2189M has on-chip emulation support and an ICE-
Port, a special set of pins that interface to the EZ-ICE. These
features allow in-circuit emulation without replacing the target
system processor by using only a 14-pin connection from the
target system to the EZ-ICE. Target systems must have a 14-pin
connector to accept the EZ-ICE’s in-circuit probe, a 14-pin
plug.
Issuing the chip reset command during emulation causes the
DSP to perform a full chip reset, including a reset of its memory
mode. Therefore, it is vital that the mode pins are set correctly
PRIOR to issuing a chip reset command from the emulator user
interface. If you are using a passive method of maintaining
mode information (as discussed in Setting Memory Modes),
then it does not matter that the mode information is latched by
an emulator reset. However, if using the RESET pin as a
method of setting the value of the mode pins, the effects of an
emulator reset must be taken into consideration.
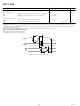
One method of ensuring that the values located on the mode
pins are those desired is to construct a circuit like the one shown
in Figure 12. This circuit forces the value located on the Mode
A pin to logic high; regardless if it latched via the RESET or
ERESET pin.
See the ADSP-2100 Family EZ-Tools data sheet for complete
information on ICE products.
tic assembler mnemonics. For example, a typical arithmetic
add instruction, such as AR = AX0 + AY0, resembles a
simple equation.
can execute in a single instruction cycle.
and is completely source-and-object-code-compatible with
other family members. Programs may need to be relocated to
utilize on-chip memory and conform to the ADSP-2189M’s
interrupt vector and reset vector map.
call, return, or arithmetic instructions, the condition can be
checked and the operation executed in the same instruction
cycle.
arithmetic instruction with up to two fetches or one write to
processor memory space during a single instruction cycle.
Figure 12. Mode A Pin/EZ-ICE Circuit
1k
PROGRAMMABLE I/O
ADSP-2189M
ERESET
RESET
MODE A/PFO
REV. A