ST92T141K4M6 STMicroelectronics, ST92T141K4M6 Datasheet

ST92T141K4M6
Specifications of ST92T141K4M6
Available stocks
Related parts for ST92T141K4M6
ST92T141K4M6 Summary of contents
Page 1
MCU FOR 3-PHASE AC MOTOR CONTROL Register File based 8/16 bit Core Architecture with RUN, WFI, SLOW, HALT and STOP modes 0-25 MHz Operation (internal clock) @ 5V±10% voltage range -40°C to +85°C Operating Temperature Range Fully Programmable PLL ...
Page 2
GENERAL DESCRIPTION . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ...
Page 3
INTERRUPT VECTORING . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ...
Page 4
PORT CONTROL REGISTERS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ...
Page 5
GENERAL INFORMATION . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ...
Page 6
... ST92141 - GENERAL DESCRIPTION 1 GENERAL DESCRIPTION 1.1 INTRODUCTION The ST92141 microcontroller is developed and manufactured by STMicroelectronics using a pro- prietary n-well HCMOS process. Its performance derives from the use of a flexible 256-register pro- gramming model for ultra-fast context switching and real-time event response. The intelligent on- ...
Page 7
Low Voltage Reset The on-chip Low Voltage Detector (LVD) gener- ates a static reset when the supply voltage is be- low a reference value. The LVD works both during power-on as well as when the power supply drops (brown-out). ...
Page 8
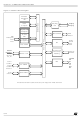
ST92141 - GENERAL DESCRIPTION Figure 1. ST92141 Block Diagram EPROM/ FASTROM 16K RAM 512 bytes Register File 256 bytes 8/16-bit CPU NMI WKUP[3:0] Interrupt INT0 Management INT6 ST9+ CORE OSCIN OSCOUT RCCU + LVD RESET INTCLK CK_AF ICAP1 OCMP1 EF ...
Page 9
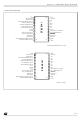
PIN DESCRIPTION SCK/STIN/WKUP3/P3.2 STOUT/SSN/P3.3 EXTRG/OCMP2/P3.4 INT6/OCMP1/P3.5 ICAP1/WKUP2/P3.6 INTCLK/AIN7/P5.7 CK_AF/AIN6/P5.6 AIN3/EXTCLK/WDOUT/P5.3 AIN2/INT0/WDIN/P5.2 SCK/STIN/WKUP3/P3.2 STOUT/SSN/P3.3 EXTRG/OCMP2/P3.4 INT6/OCMP1/P3.5 ICAP1/WKUP2/P3.6 INTCLK/AIN7/P5.7 CK_AF/AIN6/P5.6 AIN3/EXTCLK/WDOUT/P5.3 AIN2/INT0/WDIN/P5.2 ST92141 - GENERAL DESCRIPTION MOSI/P3.0 MISO/P3 AIN5/P5.5 AIN4/P5 PSDIP32/CSDIP32W ...
Page 10
ST92141 - GENERAL DESCRIPTION Table 1. Power Supply Pins Name Function Programming voltage for V EPROM/OTP devices. Must be PP connected user mode. SS Main power supply voltage ( 10% (2 pins internally connected) Digital ...
Page 11
I/O Port Configuration All ports can be individually configured as input, bi- directional, output, or alternate function. Refer to the Port Bit Configuration Table in the I/O Port Chapter. All I/Os are implemented with a High Hysteresis or Standard ...
Page 12
ST92141 - GENERAL DESCRIPTION Table 4. ST92141 Alternate functions Port General Purpose I/O Name SDIP32 PSO34 P3.0 P3.1 P3.2 P3.3 P3.4 P3.5 P3.6 All ports useable for general pur- P5.0 23 pose I/O (input, output or bidi- rectional) P5.1 22 ...
Page 13
An alternate function can be selected as follows. AF Inputs: – selected implicitly by enabling the corre- sponding peripheral. Exceptions to this are ADC analog inputs which must be explicitly selected software. AF Outputs or ...
Page 14
... Apart from this case no other part of the Program memory has a predeter- mined function except segment 21h which is re- served for use by STMicroelectronics. 1.3.2 EPROM Programming The 16K bytes of EPROM memory of the ST92E141 may be programmed by using the EPROM Programming Boards (EPB) or gang pro- grammers available from STMicroelectronics ...
Page 15
REGISTER MAP The following pages contain a list of ST92141 reg- isters, grouped by peripheral or function. Table 6. Common Registers Function or Peripheral ADC WDT I/O PORTS EXTERNAL INTERRUPT RCCU ST92141 - GENERAL DESCRIPTION Be very careful to ...
Page 16
ST92141 - GENERAL DESCRIPTION Table 7. Group F Pages Resources available on the ST92141 devices: Register 0 2 R255 Res. R254 Res. PORT R253 3 R252 WCR R251 Res. R250 WDT R249 R248 R247 R246 Res. PORT R245 EXT INT ...
Page 17
Table 8. Detailed Register Map Page Reg. Block No. (Decimal) R230 R231 R232 R233 R234 Core R235 R236 N/A R237 R238 R239 R224 I/O R225 Port R226 5:4,2:0 R228 R229 R242 R243 R244 INT R245 R246 0 R247 R248 R249 ...
Page 18
ST92141 - GENERAL DESCRIPTION Page Reg. Block No. (Decimal) R240 R241 R242 MMU R243 21 R244 R248 R249 R245 EM R246 R240 R241 R242 R243 R244 R245 R246 R247 28 EFT R248 R249 R250 R251 R252 R253 R254 R255 R248 ...
Page 19
Page Reg. Block No. (Decimal) R240 R241 R242 R243 R244 R245 R246 R247 51 IMC R248 R249 R250 R251 R252 R253 R254 R255 R240 55 RCCU R242 R246 R249 R250 R251 57 WUIMU R252 R253 R254 R255 R240 R241 R242 ...
Page 20
ST92141 - DEVICE ARCHITECTURE 2 DEVICE ARCHITECTURE 2.1 CORE ARCHITECTURE The ST9 Core or Central Processing Unit (CPU) features a highly optimised instruction set, capable of handling bit, byte (8-bit) and word (16-bit) data, as well as BCD and Boolean ...
Page 21
MEMORY SPACES (Cont’d) Figure 4. Register Groups 255 F PAGED REGISTERS 240 239 E SYSTEM REGISTERS 224 223 Figure 6. Addressing the Register ...
Page 22
ST92141 - DEVICE ARCHITECTURE MEMORY SPACES (Cont’d) 2.2.2 Register Addressing Register File registers, including Group F paged registers (but excluding Group D), may be ad- dressed explicitly by means of a decimal, hexa- decimal or binary address; thus R231, RE7h ...
Page 23
SYSTEM REGISTERS The System registers are listed in tem Registers (Group E). They are used to per- form all the important system settings. Their pur- pose is described in the following pages. Refer to the chapter dealing with I/O ...
Page 24
ST92141 - DEVICE ARCHITECTURE SYSTEM REGISTERS (Cont’d) 2.3.2 Flag Register The Flag Register contains 8 flags which indicate the CPU status. During an interrupt, the flag regis- ter is automatically stored in the system stack area and recalled at the ...
Page 25
SYSTEM REGISTERS (Cont’d) If the bit is set, data is accessed using the Data Pointers (DPRs registers), otherwise it is pointed to by the Code Pointer (CSR register); therefore, the user initialization routine must include a Sdm instruction. Note that ...
Page 26
ST92141 - DEVICE ARCHITECTURE SYSTEM REGISTERS (Cont’d) POINTER 0 REGISTER (RP0) R232 - Read/Write Register Group: E (System) Reset Value: xxxx xx00 (xxh) 7 RG4 RG3 RG2 RG1 RG0 Bits 7:3 = RG[4:0]: Register Group number. These bits contain the ...
Page 27
SYSTEM REGISTERS (Cont’d) Figure 7. Pointing to a single group of 16 registers REGISTER BLOCK GROUP NUMBER REGISTER FILE r15 3 ...
Page 28
ST92141 - DEVICE ARCHITECTURE SYSTEM REGISTERS (Cont’d) 2.3.4 Paged Registers pages, each containing 16 registers, may be mapped to Group F. These paged registers hold data and control information relating to the on-chip peripherals, each peripheral always ...
Page 29
SYSTEM REGISTERS (Cont’d) state by setting the HIMP bit. When this bit is reset, it has no effect. Setting the HIMP bit is recommended for noise re- duction when only internal Memory is used. If Port 1 and/or 2 are ...
Page 30
ST92141 - DEVICE ARCHITECTURE SYSTEM REGISTERS (Cont’d) USER STACK POINTER HIGH REGISTER (USPHR) R236 - Read/Write Register Group: E (System) Reset value: undefined 7 USP15 USP14 USP13 USP12 USP11 USP10 USP9 USER STACK POINTER LOW REGISTER (USPLR) R237 - Read/Write ...
Page 31
MEMORY ORGANIZATION Code and data are accessed within the same line- ar address space. All of the physically separate memory areas, including the internal ROM, inter- nal RAM and external memory are mapped in a common address space. The ...
Page 32
ST92141 - DEVICE ARCHITECTURE 2.5 MEMORY MANAGEMENT UNIT The CPU Core includes a Memory Management Unit (MMU) which must be programmed to per- form memory accesses (even if external memory is not used). The MMU is controlled by 7 registers ...
Page 33
ADDRESS SPACE EXTENSION To manage 4 Mbytes of addressing space necessary to have 22 address bits. The MMU adds 6 bits to the usual 16-bit address, thus trans- lating a 16-bit virtual address into a 22-bit physical ...
Page 34
ST92141 - DEVICE ARCHITECTURE ADDRESS SPACE EXTENSION (Cont’d) 2.6.2 Addressing 64-Kbyte Segments This extension mode is used to address Data memory space during a DMA and Program mem- ory space during any code execution (normal code and interrupt routines). Three ...
Page 35
MMU REGISTERS (Cont’d) DATA PAGE REGISTER 0 (DPR0) R240 - Read/Write Register Page: 21 Reset value: undefined This register is relocated to R224 if EMR2.5 is set. 7 DPR0_7 DPR0_6 DPR0_5 DPR0_4 DPR0_3 DPR0_2 DPR0_1 DPR0_0 Bits 7:0 = DPR0_[7:0]: ...
Page 36
ST92141 - DEVICE ARCHITECTURE MMU REGISTERS (Cont’d) 2.7.2 CSR: Code Segment Register This register selects the 64-Kbyte code segment being used at run-time to access instructions. It can also be used to access data if the spm instruc- tion has ...
Page 37
MMU REGISTERS (Cont’d) Figure 14. Memory Addressing Scheme (example) DPR3 DPR2 DPR1 DPR0 DMASR ISR CSR ST92141 - DEVICE ARCHITECTURE 4M bytes 16K 16K 16K 64K 64K 16K 64K 3FFFFFh 294000h 240000h 23FFFFh 20C000h 200000h 1FFFFFh 040000h 03FFFFh 030000h 020000h ...
Page 38
ST92141 - DEVICE ARCHITECTURE 2.8 MMU USAGE 2.8.1 Normal Program Execution Program memory is organized as a set of 64- Kbyte segments. The program can span as many segments as needed, but a procedure cannot stretch across segment boundaries. jps, ...
Page 39
INTERRUPTS 3.1 INTRODUCTION The ST9 responds to peripheral and external events through its interrupt channels. Current pro- gram execution can be suspended to allow the ST9 to execute a specific response routine when such an event occurs, providing that ...
Page 40
ST92141 - INTERRUPTS 3.2.2 Segment Paging Routines The ENCSR bit in the EMR2 register can be used to select between original ST9 backward compati- bility mode and ST9+ interrupt management mode. ST9 backward compatibility mode (ENCSR = 0) If ENCSR ...
Page 41
PRIORITY LEVEL ARBITRATION (Cont’d) with the highest position in the chain, as shown in Table 11. Table 11. Daisy Chain Priority Highest Position INTA0 / Watchdog Timer INTA1 / Standard Timer INTB0 / Extended Function Timer INTC1 / SPI INTD0 ...
Page 42
ST92141 - INTERRUPTS ARBITRATION MODES (Cont’d) Examples In the following two examples, three interrupt re- quests with different priority levels (2, 3 & 4) occur simultaneously during the interrupt 5 service rou- tine. Figure 17. Simple Example of a Sequence ...
Page 43
ARBITRATION MODES (Cont’d) Example 2 In the second example, (more complex, 18), each interrupt service routine sets Interrupt Enable with the ei instruction at the beginning of the routine. Placed here, it minimizes response time for requests with a higher ...
Page 44
ST92141 - INTERRUPTS ARBITRATION MODES (Cont’d) 3.5.2 Nested Mode The difference between Nested mode and Con- current mode, lies in the modification of the Cur- rent Priority Level (CPL) during interrupt process- ing. The arbitration phase is basically identical to ...
Page 45
ARBITRATION MODES (Cont’d) End of Interrupt Routine The iret Interrupt Return instruction executes the following steps: – The Flag register is popped from system stack. – If ENCSR is set, CSR is popped from system stack. – The PC high ...
Page 46
ST92141 - INTERRUPTS 3.6 EXTERNAL INTERRUPTS The standard ST9 core contains 8 external inter- rupts sources grouped into four pairs. Table 12. External Interrupt Channel Grouping External Interrupt none INT6 none none none none none INT0 Each source has a ...
Page 47
EXTERNAL INTERRUPTS (Cont’d) Figure 22. External Interrupts Control Bits and Vectors n Watchdog/Timer End of count TEA0 INT 0 pin STIM Interrupt not connected EFT Interrupt not connected not connected not connected SPI Interrupt not connected RCCU interrupt TED0 INT ...
Page 48
ST92141 - INTERRUPTS 3.7 TOP LEVEL INTERRUPT The Top Level Interrupt channel can be assigned either to the external pin NMI or to the Timer/ Watchdog according to the status of the control bit EIVR.TLIS (R246.2, Page 0). If this ...
Page 49
NMI/WKP0 LINE MANAGEMENT In the ST92141, the Non Maskable Interrupt (NMI) and the Wake Up 0 line (WKUP0) functionalities are both physically mapped on the same I/O Port pin P5.1 (refer to Section 1.2). The NMI/WKUP0 is a single ...
Page 50
ST92141 - INTERRUPTS NMI/WKP0 LINE MANAGEMENT (Cont’d) 3.9.1 NMI/Wake-Up Event Handling in Run mode The four external lines WKUP0/NMI, WKUP1-3 can also be used when the device is in Run Mode. In addition, if the WKUP0/NMI line is used and ...
Page 51
INTERRUPT RESPONSE TIME The interrupt arbitration protocol functions com- pletely asynchronously from instruction flow and requires 5 clock cycles. One more CPUCLK cycle is required when an interrupt is acknowledged. Requests are sampled every 5 CPUCLK cycles. If the ...
Page 52
ST92141 - INTERRUPTS 3.11 INTERRUPT REGISTERS CENTRAL INTERRUPT CONTROL REGISTER (CICR) R230 - Read/Write Register Group: System Reset value: 1000 0111 (87h) 7 GCEN TLIP TLI IEN IAM CPL2 CPL1 CPL0 Bit 7 = GCEN: Global Counter Enable. This bit ...
Page 53
INTERRUPT REGISTERS (Cont’d) EXTERNAL INTERRUPT PENDING REGISTER (EIPR) R243 - Read/Write Register Page: 0 Reset value: 0000 0000 (00h) 7 IPD1 IPD0 IPC1 IPC0 IPB1 IPB0 IPA1 IPA0 Bit 7 = IPD1: INTD1 Interrupt Pending bit Bit 6 = IPD0: ...
Page 54
ST92141 - INTERRUPTS INTERRUPT REGISTERS (Cont’d) EXTERNAL INTERRUPT VECTOR REGISTER (EIVR) R246 - Read/Write Register Page: 0 Reset value: xxxx 0110b (x6h TLTEV TLIS IAOS EWEN Bit 7:4 = V[7:4]: Most significant nibble of External ...
Page 55
WAKE-UP / INTERRUPT LINES MANAGEMENT UNIT (WUIMU) 3.12.1 Introduction The Wake-up/Interrupt Management Unit extends the number of external interrupt lines from (depending on the number of external interrupt lines mapped on external pins of the device). ...
Page 56
ST92141 - INTERRUPTS WAKE-UP / INTERRUPT LINES MANAGEMENT UNIT (Cont’d) 3.12.3 Functional Description 3.12.3.1 Interrupt Mode To configure the 16 wake-up lines as interrupt sources, use the following procedure: 1. Configure the mask bits of the 16 wake-up lines (WUMRL, ...
Page 57
WAKE-UP / INTERRUPT LINES MANAGEMENT UNIT (Cont’d) 2. Interrupt requests to CPU are enabled: in this case the ST9 will not enter STOP mode and the interrupt service routine will be executed. The status of STOP and EX_STP bits will ...
Page 58
ST92141 - INTERRUPTS WAKE-UP / INTERRUPT LINES MANAGEMENT UNIT (Cont’d) 3.12.4.2 Simultaneous Setting of Pending Bits It is possible that several simultaneous events set different pending bits. In order to accept subse- quent events on external wake-up/interrupt lines ...
Page 59
WAKE-UP / INTERRUPT LINES MANAGEMENT UNIT (Cont’d) 3.12.5 Register Description WAKE-UP CONTROL REGISTER (WUCTRL) R249 - Read/Write Register Page: 57 Reset Value: 0000 0000 (00h STOP Bit 2 = STOP: Stop bit. To enter ...
Page 60
ST92141 - INTERRUPTS WAKE-UP / INTERRUPT LINES MANAGEMENT UNIT (Cont’d) WAKE-UP MASK REGISTER HIGH (WUMRH) R250 - Read/Write Register Page: 57 Reset Value: 0000 0000 (00h) 7 WUM15 WUM14 WUM13 WUM12 WUM11 WUM10 WUM9 Bit 7:0 = WUM[15:8]: Wake-Up Mask ...
Page 61
WAKE-UP / INTERRUPT LINES MANAGEMENT UNIT (Cont’d) WAKE-UP TRIGGER REGISTER (WUTRH) R252 - Read/Write Register Page: 57 Reset Value: 0000 0000 (00h) 7 WUT15 WUT14 WUT13 WUT12 WUT11 WUT10 WUT9 Bit 7:0 = WUT[15:8]: Wake-Up Trigger Polarity Bits These bits ...
Page 62
ST92141 - EM CONFIGURATION REGISTERS (EM CONFIGURATION REGISTERS (EM) In ST9 devices with external memory, the EM reg- isters (External Memory Registers) are used to configure the external memory interface. In the ST92141, only the BSZ, ENCSR and ...
Page 63
RESET AND CLOCK CONTROL UNIT (RCCU) 5.1 INTRODUCTION The Reset and Clock Control Unit (RCCU) com- prises two distinct sections: – the Clock Control Unit, which generates and manages the internal clock signals. – the Reset/Stop Manager, which detects ...
Page 64
ST92141 - RESET AND CLOCK CONTROL UNIT (RCCU) Figure 27. ST92141 Clock Distribution Diagram (settings given for 5MHz crystal & 25MHz lnternal clock) N=1,4,6,8,10,12,14,16 Conversion time N X 138 X INTCLK A/D EFT P5.7 Baud Rate SCK Generator Master 1/N ...
Page 65
CLOCK MANAGEMENT The various programmable features and operating modes of the CCU are handled by four registers: – MODER (Mode Register) This is a System Register (R235, Group E). The input clock divide-by-two and the CPU clock prescaler factors ...
Page 66
ST92141 - RESET AND CLOCK CONTROL UNIT (RCCU) CLOCK MANAGEMENT (Cont’d) 5.3.1 PLL Clock Multiplier Programming The CLOCK1 signal generated by the oscillator drives a programmable divide-by-two circuit. If the DIV2 control bit in MODER is set (Reset Condi- tion), ...
Page 67
CLOCK MANAGEMENT (Cont’d) 5.3.4 Low Power Modes The user can select an automatic slowdown of clock frequency during Wait for Interrupt opera- tion, thus idling in low power mode while waiting for an interrupt. In WFI operation the clock to ...
Page 68
ST92141 - RESET AND CLOCK CONTROL UNIT (RCCU) Figure 30. Example of Low Power Mode programming PROGRAM FLOW Begin DIV2 XTSTOP = 0 CSU_CKSEL = 0 MX(1:0) DX2-0 WAIT CSU_CKSEL Wait for the WFI_CKSEL PLL locking (LOCK->1) XTSTOP LPOWFI User’s ...
Page 69
CLOCK CONTROL REGISTERS MODE REGISTER (MODER) R235 - Read/Write System Register Reset Value: 1110 0000 (E0h DIV2 PRS2 PRS1 *Note: This register contains bits which relate to other functions; these are described in the chapter dealing ...
Page 70
ST92141 - RESET AND CLOCK CONTROL UNIT (RCCU) CLOCK CONTROL REGISTERS (Cont’d) CLOCK FLAG REGISTER (CLK_FLAG) R242 -Read/Write Register Page: 55 Reset Value: 0100 1000 after a Watchdog Reset Reset Value: 0010 1000 after a Software Reset Reset Value: 0000 ...
Page 71
CLOCK CONTROL REGISTERS (Cont’d) PLL CONFIGURATION REGISTER (PLLCONF) R246 - Read/Write Register Page: 55 Reset Value: xx00 x111 MX1 MX0 - Bit 5:4 = MX[1:0]: PLL Multiplication Factor . Refer to Table 15 PLL Multiplication Factors multiplier ...
Page 72
ST92141 - RESET AND CLOCK CONTROL UNIT (RCCU) Figure 32. RCCU Timing during STOP (CK_AF System Clock) STOP request (*) Xtal clock CK_AF clock INTCLK 20478 x T (**) Xtal Exit from RESET (*) from WUIMU (**) +/- 1 T ...
Page 73
OSCILLATOR CHARACTERISTICS The on-chip oscillator circuit uses an inverting gate circuit with tri-state output. Notes: Owing to the Q factor required, Ceramic Resonators may not provide a reliable oscillator source . OSCOUT must not be directly used to drive ...
Page 74
ST92141 - RESET AND CLOCK CONTROL UNIT (RCCU) 5.6 RESET/STOP MANAGER The Reset/Stop Manager resets the MCU when one of the three following events occurs: – A Hardware reset, initiated by a low level on the Reset pin. – A ...
Page 75
RESET/STOP MANAGER (Cont’d) The on-chip Timer/Watchdog generates a reset condition if the Watchdog mode is enabled (WCR.WDEN cleared, R252 page 0), and if the programmed period elapses without the specific code (AAh, 55h) written to the appropriate register. The input ...
Page 76
ST92141 - RESET AND CLOCK CONTROL UNIT (RCCU) 5.7 STOP MODE Under control of the Wake-up Interrupt Manage- ment Unit (WUIMU), the Reset/Stop Manager can also stop all oscillators without resetting the de- vice. In Stop Mode all context information ...
Page 77
Figure 39. Oscillator Start-up sequence on Exit from Stop Mode V MAX DD V MIN DD OSCIN OSCOUT STOP disactivation 5.1 ms (*) < T INTCLK (*) with 4MHz quartz and RCCU programmed with XT_STOP bit = 1 when read ...
Page 78
ST92141 - RESET AND CLOCK CONTROL UNIT (RCCU) 5.8 LOW VOLTAGE DETECTOR (LVD) To allow the integration of power management features in the application, the Low Voltage Detec- tor function (LVD) generates a static reset when the V supply voltage ...
Page 79
I/O PORTS 6.1 INTRODUCTION ST9 devices feature flexible individually program- mable multifunctional input/output lines. Refer to the Pin Description Chapter for specific pin alloca- tions. These lines, which are logically grouped as 8-bit ports, can be individually programmed to ...
Page 80
ST92141 - I/O PORTS PORT CONTROL REGISTERS (Cont’d) During Reset, ports with weak pull-ups are set in bidirectional/weak pull-up mode and the output Data Register is set to FFh. This condition is also held after Reset, except for Ports 0 ...
Page 81
INPUT/OUTPUT BIT CONFIGURATION (Cont’d) Figure 42. Control Bits Bit 7 PxC2 PxC27 PxC1 PxC17 PxC0 PxC07 n Table 19. Port Bit Configuration Table ( 1... port number) PXC2n 0 PXC1n 0 PXC0n 0 PXn Configuration ...
Page 82
ST92141 - I/O PORTS INPUT/OUTPUT BIT CONFIGURATION (Cont’d) Figure 43. Basic Structure of an I/O Port Pin PUSH-PULL TRISTATE OPEN DRAIN WEAK PULL-UP OUTPUT SLAVE LATCH ALTERNATE FROM FUNCTION PERIPHERAL OUTPUT INPUT OUTPUT BIDIRECTIONAL OUTPUT MASTER LATCH Figure 44. Input ...
Page 83
INPUT/OUTPUT BIT CONFIGURATION (Cont’d) When Px.n is programmed as an Output: (Figure 45) – The Output Buffer is turned Open-drain or Push-pull configuration. – The data stored in the Output Master Latch is copied both into the ...
Page 84
ST92141 - I/O PORTS 6.5 ALTERNATE FUNCTION ARCHITECTURE Each I/O pin may be connected to three different types of internal signal: – Data bus Input/Output – Alternate Function Input – Alternate Function Output 6.5.1 Pin Declared as I/O A pin ...
Page 85
ON-CHIP PERIPHERALS 7.1 TIMER/WATCHDOG (WDT) Important Note: This chapter is a generic descrip- tion of the WDT peripheral. However depending on the ST9 device, some or all of WDT interface signals described may not be connected to exter- nal ...
Page 86
ST92141 - TIMER/WATCHDOG (WDT) TIMER/WATCHDOG (Cont’d) 7.1.2 Functional Description 7.1.2.1 External Signals The HW0SW1 pin can be used to permanently en- able Watchdog mode. Refer to section 7.1.3.1 on page 87. The WDIN Input pin can be used in one ...
Page 87
TIMER/WATCHDOG (Cont’d) 7.1.2.7 Gated Input Mode This mode can be used for pulse width measure- ment. The Timer is clocked by INTCLK/4, and is started and stopped by means of the input pin and the ST_SP bit. When the input ...
Page 88
ST92141 - TIMER/WATCHDOG (WDT) TIMER/WATCHDOG (Cont’d) 7.1.3.3 Preventing Watchdog System Reset In order to prevent a system reset, the sequence AAh, 55h must be written to WDTLR (Watchdog Timer Low Register). Once 55h has been written, the Timer reloads the ...
Page 89
TIMER/WATCHDOG (Cont’d) 7.1.4 WDT Interrupts The Timer/Watchdog issues an interrupt request at every End of Count, when this feature is ena- bled. A pair of control bits, IA0S (EIVR.1, Interrupt A0 se- lection bit) and TLIS (EIVR.2, Top Level Input ...
Page 90
ST92141 - TIMER/WATCHDOG (WDT) TIMER/WATCHDOG (Cont’d) 7.1.5 Register Description The Timer/Watchdog is associated with 4 registers mapped into Group F, Page 0 of the Register File. WDTHR: Timer/Watchdog High Register WDTLR: Timer/Watchdog Low Register WDTPR: Timer/Watchdog Prescaler Register WDTCR: Timer/Watchdog ...
Page 91
TIMER/WATCHDOG (Cont’d) Bit 3 = INEN: Input Enable . This bit is set and cleared by software. 0: Disable input section 1: Enable input section Bit 2 = OUTMD: Output Mode. This bit is set and cleared by software. 0: ...
Page 92
ST92141 - STANDARD TIMER (STIM) 7.2 STANDARD TIMER (STIM) Important Note: This chapter is a generic descrip- tion of the STIM peripheral. Depending on the ST9 device, some or all of the interface signals de- scribed may not be connected ...
Page 93
STANDARD TIMER (Cont’d) 7.2.2 Functional Description 7.2.2.1 Timer/Counter control Start-stop Count. The ST-SP bit (STC.7) is used in order to start and stop counting. An instruction which sets this bit will cause the Standard Timer to start counting at the ...
Page 94
ST92141 - STANDARD TIMER (STIM) STANDARD TIMER (Cont’d) 7.2.2.4 Standard Timer Output Modes OUTPUT modes are selected using 2 bits of the STC register: OUTMD1 and OUTMD2. No Output Mode (OUTMD1 = “0”, OUTMD2 = “0”) The output is disabled ...
Page 95
STANDARD TIMER (Cont’d) 7.2.5 Register Description COUNTER HIGH BYTE REGISTER (STH) R240 - Read/Write Register Page: 11 Reset value: 1111 1111 (FFh) 7 ST.15 ST.14 ST.13 ST.12 ST.11 ST.10 ST.9 ST.8 Bits 7:0 = ST.[15:8]: Counter High-Byte. COUNTER LOW BYTE ...
Page 96
ST92141 - EXTENDED FUNCTION TIMER (EFT) 7.3 EXTENDED FUNCTION TIMER (EFT) 7.3.1 Introduction The timer consists of a 16-bit free-running counter driven by a programmable prescaler. It may be used for a variety of purposes, including pulse length measurement of ...
Page 97
EXTENDED FUNCTION TIMER (Cont’d) Figure 53. Timer Block Diagram INTCLK 8 low 8 high 8-bit buffer EXEDG 16 BIT 1/2 FREE RUNNING 1/4 COUNTER 1/8 COUNTER ALTERNATE REGISTER CC1 CC0 OVERFLOW EXTCLK DETECT CIRCUIT ICF1 OCF1 TOF ICF2 ICIE OCIE ...
Page 98
ST92141 - EXTENDED FUNCTION TIMER (EFT) EXTENDED FUNCTION TIMER (Cont’d) 16-bit read sequence: (from either the Counter Register or the Alternate Counter Register). Beginning of the sequence Read MSB At t0 Other instructions Returns the buffered Read LSB At t0 ...
Page 99
EXTENDED FUNCTION TIMER (Cont’d) Figure 54. Counter Timing Diagram, INTCLK divided by 2 INTERNAL RESET TIMER CLOCK COUNTER REGISTER OVERFLOW FLAG TOF Figure 55. Counter Timing Diagram, INTCLK divided by 4 INTCLK INTERNAL RESET TIMER CLOCK COUNTER REGISTER OVERFLOW FLAG ...
Page 100
ST92141 - EXTENDED FUNCTION TIMER (EFT) EXTENDED FUNCTION TIMER (Cont’d) 7.3.3.3 Input Capture In this section, the index may The two input capture 16-bit registers (IC1R and IC2R) are used to latch the value ...
Page 101
EXTENDED FUNCTION TIMER (Cont’d) Figure 57. Input Capture Block Diagram ICAP1 EDGE DETECT CIRCUIT2 ICAP2 IC2R 16-BIT 16-BIT FREE RUNNING COUNTER Figure 58. Input Capture Timing Diagram TIMER CLOCK COUNTER REGISTER ICAPi PIN ICAPi FLAG ICAPi REGISTER ctive edge is ...
Page 102
ST92141 - EXTENDED FUNCTION TIMER (EFT) EXTENDED FUNCTION TIMER (Cont’d) 7.3.3.4 Output Compare In this section, the index may This function can be used to control an output waveform or indicating when a period ...
Page 103
EXTENDED FUNCTION TIMER (Cont’d) Figure 59. Output Compare Block Diagram 16 BIT FREE RUNNING COUNTER 16-bit OUTPUT COMPARE CIRCUIT 16-bit 16-bit OC2R OC1R Figure 60. Output Compare Timing Diagram, Internal Clock Divided by 2 OUTPUT COMPARE REGISTER COMPARE REGISTER LATCH ...
Page 104
ST92141 - EXTENDED FUNCTION TIMER (EFT) EXTENDED FUNCTION TIMER (Cont’d) 7.3.3.5 Forced Compare Mode In this section i may represent The following bits of the CR1 register are used: FOLV2 FOLV1 OLVL2 When the FOLV i bit ...
Page 105
EXTENDED FUNCTION TIMER (Cont’d) 7.3.3.7 Pulse Width Modulation Mode Pulse Width Modulation mode enables the gener- ation of a signal with a frequency and pulse length determined by the value of the OC1R and OC2R registers. The pulse width modulation ...
Page 106
ST92141 - EXTENDED FUNCTION TIMER (EFT) EXTENDED FUNCTION TIMER (Cont’d) 7.3.4 Interrupt Management The interrupts of the Extended Function Timer are mapped on the eight external interrupt channels of the microcontroller (refer to the “Interrupts” chap- ter). Depending on device ...
Page 107
EXTENDED FUNCTION TIMER (Cont’d) Note: A single access (read/write) to the SR regis- ter at the beginning of the interrupt routine is the first step needed to clear all the EFT interrupt flags second step, the lower bytes ...
Page 108
ST92141 - EXTENDED FUNCTION TIMER (EFT) EXTENDED FUNCTION TIMER (Cont’d) 7.3.5 Register Description Each Timer is associated with three control and one status registers, and with six pairs of data reg- isters (16-bit values) relating to the two input cap- ...
Page 109
EXTENDED FUNCTION TIMER (Cont’d) COUNTER HIGH REGISTER (CHR) R244 - Read Only Register Page: 28 Reset Value: 1111 1111 (FFh) This is an 8-bit register that contains the high part of the counter value. 7 MSB COUNTER LOW REGISTER (CLR) ...
Page 110
ST92141 - EXTENDED FUNCTION TIMER (EFT) EXTENDED FUNCTION TIMER (Cont’d) OUTPUT COMPARE 1 (OC1HR) R248 - Read/Write Register Page: 28 Reset Value: 1000 0000 (80h) This is an 8-bit register that contains the high part of the value to be ...
Page 111
EXTENDED FUNCTION TIMER (Cont’d) CONTROL REGISTER 1 (CR1) R252 - Read/Write Register Page: 28 Reset Value: 0000 0000 (00h) 7 ICIE OCIE TOIE FOLV2 FOLV1 OLVL2 IEDG1 OLVL1 Bit 7 = ICIE Input Capture Interrupt Enable. 0: Interrupt is inhibited. ...
Page 112
ST92141 - EXTENDED FUNCTION TIMER (EFT) EXTENDED FUNCTION TIMER (Cont’d) CONTROL REGISTER 2 (CR2) R253 - Read/Write Register Page: 28 Reset Value: 0000 0000 (00h) 7 OC1E OC2E OPM PWM CC1 CC0 IEDG2 EXEDG Bit 7 = OC1E Output Compare ...
Page 113
EXTENDED FUNCTION TIMER (Cont’d) STATUS REGISTER (SR) R254 - Read Only Register Page: 28 Reset Value: 0000 0000 (00h) The three least significant bits are not used. 7 ICF1 OCF1 TOF ICF2 OCF2 Bit 7 = ICF1 Input Capture Flag ...
Page 114
ST92141 - EXTENDED FUNCTION TIMER (EFT) EXTENDED FUNCTION TIMER (Cont’d) Table 23. Extended Function Timer Register Map Address Register 7 Name (Dec.) IC1HR MSB R240 Reset Value x IC1LR MSB R241 Reset Value x IC2HR MSB R242 Reset Value x ...
Page 115
EXTENDED FUNCTION TIMER (Cont’d) Table 24. Extended Function Timer Page Map Timer number EFT0 ST92141 - EXTENDED FUNCTION TIMER (EFT) Page (hex) 1C 115/179 9 ...
Page 116
ST92141 - 3-PHASE INDUCTION MOTOR CONTROLLER (IMC) 7.4 3-PHASE INDUCTION MOTOR CONTROLLER (IMC) 7.4.1 Introduction The IMC controller is designed for variable speed motor control applications. Three PWM outputs are available for controlling a three-phase motor drive. Rotor speed feedback ...
Page 117
INDUCTION MOTOR CONTROLLER (Cont’d) 7.4.3.1 Input and Output pins – Input Pin TACHO: Signal input from a tachogenerator for measuring the rotor speed. NMI: Input signal for disabling the IMC output and sending an interrupt request to the ST9 core. ...
Page 118
ST92141 - 3-PHASE INDUCTION MOTOR CONTROLLER (IMC) INDUCTION MOTOR CONTROLLER (Cont’d) If the 11-bit Compare register value is greater than the extended Compare 0 Register (the 11 set to ‘0’), the corresponding PWM output signal is held at ‘1’. Figure ...
Page 119
INDUCTION MOTOR CONTROLLER (Cont’d) PWM signals generation in Classical mode In this mode, each of the three PWM signals set to ‘0’ when the PWM Counter reaches, in up-count- ing, the corresponding 11-bit Compare register value and they are set ...
Page 120
ST92141 - 3-PHASE INDUCTION MOTOR CONTROLLER (IMC) INDUCTION MOTOR CONTROLLER (Cont’d) Repetition Down-Counter Both in Zerocentered and Classical working mode, the four Compare registers (one Compare 0 and three for the U, V and W phases) are updated when the ...
Page 121
INDUCTION MOTOR CONTROLLER (Cont’d) Figure 68. Dead Time waveforms with delay greater than the negative PWM pulse Figure 69. Dead Time waveforms with delay greater than the positive PWM pulse ST92141 - 3-PHASE INDUCTION ...
Page 122
ST92141 - 3-PHASE INDUCTION MOTOR CONTROLLER (IMC) INDUCTION MOTOR CONTROLLER (Cont’d) 7.4.3.5 Polarity Selection The Polarity Selection performs a logical comple- ment of the input signals (Uh, Ul, Vh, Vl, Wh, Wl) as programmed in the Polarity Selection register. 7.4.3.6 ...
Page 123
INDUCTION MOTOR CONTROLLER (Cont’d) 7.4.5.2 IMC Software Operating mode In this operating mode, the Repetition register and any Compare register can be independently up- dated by software by setting the SDT bit in the PCR2 register (this bit will be ...
Page 124
ST92141 - 3-PHASE INDUCTION MOTOR CONTROLLER (IMC) INDUCTION MOTOR CONTROLLER (Cont’d) 7.4.7 NMI management Figure 71 shows how the external input NMI signal is managed by the IMC peripheral. After an ST9 reset, the NMIE bit in the PCR1 reg- ...
Page 125
INDUCTION MOTOR CONTROLLER (Cont’d) 7.4.8 Register Description TACHO CAPTURE REGISTER HIGH (TCPTH) R240 - Read Only Register Page: 51 Reset Value: undefined 7 TCH7 TCH6 TCH5 TCH4 TCH3 TCH2 TCH1 TCH0 Bit 7:0 = TCH[7:0] Most Significant Byte of Tacho ...
Page 126
ST92141 - 3-PHASE INDUCTION MOTOR CONTROLLER (IMC) INDUCTION MOTOR CONTROLLER (Cont’d) INTERRUPT PENDING REGISTER (IPR) R243 - Read/Write Register Page: 51 Reset Value: 0000 0000 (00h) 7 CM0 CPT OTC ADT ZPC Bit 7 = CM0: Compare 0 of PWM ...
Page 127
INDUCTION MOTOR CONTROLLER (Cont’d) TACHO PRESCALER REGISTER (TPRSH) R244 - Read/Write Register Page: 51 Reset Value: 0000 0000 (00h) 7 TPRH - - - - 3 Bit 7:4 = Reserved. Bit 3:0 = TPRH[3:0] Most Significant Bits of tacho prescaler ...
Page 128
ST92141 - 3-PHASE INDUCTION MOTOR CONTROLLER (IMC) INDUCTION MOTOR CONTROLLER (Cont’d) COMPARE PHASE W PRELOAD REGISTER HIGH (CPWH) R248 - Read/Write Register Page: 51 Reset Value: 0000 0000 (00h) 7 CPWH CPWH CPWH CPWH CPWH ...
Page 129
INDUCTION MOTOR CONTROLLER (Cont’d) COMPARE PHASE U PRELOAD REGISTER HIGH (CPUH) R252 - Read/Write Register Page: 51 Reset Value: 0000 0000 (00h) 7 CPUH CPUH CPUH CPUH CPUH Bit 7:0 = CPUH[7:0] Most Significant Byte ...
Page 130
ST92141 - 3-PHASE INDUCTION MOTOR CONTROLLER (IMC) INDUCTION MOTOR CONTROLLER (Cont’d) PERIPHERAL CONTROL REGISTER 0 (PCR0) R248 - Read/Write Register Page: 48 Reset Value: 1000 0011 (83h) 7 DTE TCE PCE CTC CPC Bit 7 = DTE: Dead Time Counter ...
Page 131
INDUCTION MOTOR CONTROLLER (Cont’d)) PERIPHERAL CONTROL REGISTER 2 (PCR2) R250 - Read/Write Register Page: 48 Reset Value: 0000 0000 (00h) 7 GPIE RSE CWSE CVSE CUSE C0SE Bit 7 = GPIE: Global Peripheral Interrupt Enable. 0: Disable all IMC controller ...
Page 132
ST92141 - 3-PHASE INDUCTION MOTOR CONTROLLER (IMC) INDUCTION MOTOR CONTROLLER (Cont’d) OUTPUT PERIPHERAL REGISTER (OPR) R252 - Read/Write Register Page: 48 Reset Value: 0000 0000 (00h) 7 OPE ODS Bit 7 = OPE: Output Port Enable. This ...
Page 133
INDUCTION MOTOR CONTROLLER (Cont’d) DEAD TIME GENERATOR REGISTER (DTG) R254 - Read/Write Register Page: 48 Reset Value: 0011 1111 (3Fh DTG5 DTG4 DTG3 DTG2 DTG1 DTG0 Bit 7:6 = Reserved. Bit 5:0 = DTG[5:0] Dead time generator ...
Page 134
ST92141 - 3-PHASE INDUCTION MOTOR CONTROLLER (IMC) INDUCTION MOTOR CONTROLLER (Cont’d) Table 27. IMC Controller Register Map Page 51 Register 7 Register Name No. R240 TCPTH TCH7 R241 TCPTL TCL7 R242 TCMP TCP7 R243 IPR CM0 R244 TPRSH - R245 ...
Page 135
SERIAL PERIPHERAL INTERFACE (SPI) 7.5.1 Introduction The Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) allows full- duplex, synchronous, serial communication with external devices. An SPI system may consist of a master and one or more slaves or a system in which devices ...
Page 136
ST92141 - SERIAL PERIPHERAL INTERFACE (SPI) SERIAL PERIPHERAL INTERFACE (Cont’d) Figure 73. Serial Peripheral Interface Block Diagram Read Read Buffer MOSI MISO 8-Bit Shift Register Write SCK SS 1/2 ST9 PERIPHERAL CLOCK (INTCLK) 136/179 9 Internal Bus DR SPIE SPOE ...
Page 137
SERIAL PERIPHERAL INTERFACE (Cont’d) 7.5.4 Functional Description Figure 73 shows the serial peripheral interface (SPI) block diagram. This interface contains 4 dedicated registers: – A Control Register (CR) – A Prescaler Register (PR) – A Status Register (SR) – A ...
Page 138
ST92141 - SERIAL PERIPHERAL INTERFACE (SPI) SERIAL PERIPHERAL INTERFACE (Cont’d) 7.5.4.2 Slave Configuration In slave configuration, the serial clock is received on the SCK pin from the master device. The value of the PR register and SPR0 & SPR1 bits ...
Page 139
SERIAL PERIPHERAL INTERFACE (Cont’d) 7.5.4.3 Data Transfer Format During an SPI transfer, data is simultaneously transmitted (shifted out serially) and received (shifted in serially). The serial clock is used to syn- chronize the data transfer during a sequence of eight ...
Page 140
ST92141 - SERIAL PERIPHERAL INTERFACE (SPI) SERIAL PERIPHERAL INTERFACE (Cont’d) Figure 75. Data Clock Timing Diagram CPOL = 1 CPOL = 0 MSBit MISO (from master) MSBit MOSI (from slave) SS (to slave) CAPTURE STROBE CPOL = 1 CPOL = ...
Page 141
SERIAL PERIPHERAL INTERFACE (Cont’d) 7.5.4.4 Write Collision Error A write collision occurs when the software tries to write to the DR register while a data transfer is tak- ing place with an external device. When this hap- pens, the transfer ...
Page 142
ST92141 - SERIAL PERIPHERAL INTERFACE (SPI) SERIAL PERIPHERAL INTERFACE (Cont’d) 7.5.4.5 Master Mode Fault Master mode fault occurs when the master device has its SS pin pulled low, then the MODF bit is set. Master mode fault affects the SPI ...
Page 143
SERIAL PERIPHERAL INTERFACE (Cont’d) 7.5.4.7 Single Master and Multimaster Configurations There are two types of SPI systems: – Single Master System – Multimaster System Single Master System A typical single master system may be configured, using an MCU as the ...
Page 144
ST92141 - SERIAL PERIPHERAL INTERFACE (SPI) SERIAL PERIPHERAL INTERFACE (Cont’d) 7.5.5 Interrupt Management The interrupt of the Serial Peripheral Interface is mapped on one of the eight External Interrupt Channels of the microcontroller (refer to the “Inter- rupts” chapter). Each ...
Page 145
SERIAL PERIPHERAL INTERFACE (Cont’d) 7.5.6 Register Description DATA REGISTER (SPDR) R240 - Read/Write Register Page: 7 Reset Value: 0000 0000 (00h The DR register is used to transmit and receive data on the serial ...
Page 146
ST92141 - SERIAL PERIPHERAL INTERFACE (SPI) SERIAL PERIPHERAL INTERFACE (Cont’d) STATUS REGISTER (SPSR) R242 - Read Only Register Page: 7 Reset Value: 0000 0000 (00h) 7 SPIF WCOL - MODF Bit 7 = SPIF Serial Peripheral data transfer flag. This ...
Page 147
ANALOG TO DIGITAL CONVERTER (ADC) Important Note: This chapter is a generic descrip- tion of the ADC peripheral. However depending on the ST9 device, some or all of the interface signals described may not be connected to external pins. ...
Page 148
ST92141 - ANALOG TO DIGITAL CONVERTER (ADC) ANALOG TO DIGITAL CONVERTER (Cont’d) Single and continuous conversion modes are available. Conversion may be triggered by an ex- ternal signal or, internally, by the Multifunction Timer. Conversion Time The maximum conversion time ...
Page 149
ANALOG TO DIGITAL CONVERTER (Cont’d) On devices where two A/D Converters are present they can be triggered from the same source. Converter External Trigger A/D 0 EXTRG pin A/D 1 7.6.2.3 Analog Watchdogs Two internal Analog Watchdogs are available for ...
Page 150
ST92141 - ANALOG TO DIGITAL CONVERTER (ADC) ANALOG TO DIGITAL CONVERTER (Cont’d) Figure 80. Application Example: Analog Watchdog used in Motorspeed Control 7.6.3 Interrupts The ADC provides two interrupt sources: – End of Conversion – Analog Watchdog Request The A/D ...
Page 151
Register Description DATA REGISTERS (DiR) The conversion results for the 8 available chan- nels are loaded into the 8 Data registers following conversion of the corresponding analog input. CHANNEL 0 DATA REGISTER (D0R) R240 - Read/Write Register Page: 63 ...
Page 152
ST92141 - ANALOG TO DIGITAL CONVERTER (ADC) REGISTER DESCRIPTION (Cont’d) LOWER THRESHOLD REGISTERS (LTiR) The two Lower Threshold registers are used to store the user programmable lower threshold 8-bit values compared with the current conver- sion results, thus ...
Page 153
REGISTER DESCRIPTION (Cont’d) COMPARE RESULT REGISTER (CRR) R252 - Read/Write Register Page: 63 Reset Value: 0000 1111 (0Fh) 7 C7U C6U C7L C6L X The result of the comparison between the current value of data registers 6 and 7 and ...
Page 154
ST92141 - ANALOG TO DIGITAL CONVERTER (ADC) REGISTER DESCRIPTION (Cont’d) CONTROL LOGIC REGISTER (CLR) The Control Logic Register (CLR) manages the ADC’s logic. Writing to this register will cause the current conversion to be aborted and the autoscan logic to ...
Page 155
REGISTER DESCRIPTION (Cont’d) INTERRUPT CONTROL REGISTER (AD_ICR) The Interrupt Control Register contains the three priority level bits, the two source flags, and their bit mask: INTERRUPT CONTROL REGISTER (AD_ICR) R254 - Read/Write Register Page: 63 Reset Value: 0000 1111 (0Fh) ...
Page 156
ST92141 - ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS 8 ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS This product contains devices to protect the inputs against damage due to high static voltages, how- ever it is advisable to take normal precautions to avoid application of any voltage higher than the ...
Page 157
DC ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS ( 10 40°C to +85°C, unless otherwise specified) – Symbol Parameter Input High Level Standard Schmitt Trigger P5[7: Input High Level High Hyst. Schmitt Trigger P5[1:0]-P3[6:0]-TACHO Input Low Level ...
Page 158
ST92141 - ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS LOW VOLTAGE DETECTOR DC CHARACTERISTICS ( 10 40°C to +85°C, unless otherwise specified) – Symbol Parameter Reset release V LVDR Threshold Reset generation V LVDF Threshold (2) V Hysteresis LVDHyst ...
Page 159
AC ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS ( 10 40°C to +85°C, unless otherwise specified) – Symbol I Run Mode Current DDRUN I WFI Mode Current DDWFI I Low Power WFI Mode Current DDLPWFI I HALT Mode Current ...
Page 160
ST92141 - ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS EXTERNAL INTERRUPT TIMING TABLE ( 10 40°C to +85°C, C – N° Symbol 1 TwINTLR Low Level Pulse Width in Rising Edge Mode 2 TwINTHR High Level Pulse Width in ...
Page 161
WAKE-UP MANAGEMENT TIMING TABLE ( 10 40°C to +85°C, C – N° Symbol 1 TwWKPLR Low Level Pulse Width in Rising Edge Mode 2 TwWKPHR High Level Pulse Width in Rising Edge Mode 3 ...
Page 162
ST92141 - ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS RCCU CHARACTERISTICS ( 10 40°C to +85°C, C – Symbol Parameter V RESET Input High Level IHRS V RESET Input Low Level ILRS V RESET Input Hysteresis HYRS I RESET ...
Page 163
OSCILLATOR CHARACTERISTICS ( 10 40°C to +85°C, C – Symbol Parameter F Crystal Frequency OSC g Oscillator m V Clock Input High Level IHCK V Clock Input Low Level ILCK OSCIN/OSCOUT Pins Input I ...
Page 164
ST92141 - ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS WATCHDOG TIMING TABLE ( 10 40°C to +85°C, C – unless otherwise specified) N° Symbol Parameter 1 TwWDOL WDOUT Low Pulse Width 2 TwWDOH WDOUT High Pulse Width 3 TwWDIL ...
Page 165
STANDARD TIMER TIMING TABLE ( 10 40°C to +85°C, C – unless otherwise specified) N° Symbol Parameter 1 TwSTOL STOUT Low Pulse Width 2 TwSTOH STOUT High Pulse Width 3 TwSTIL STIN High Pulse ...
Page 166
ST92141 - ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS EXTENDED FUNCTION TIMER EXTERNAL TIMING TABLE ( 10 40°C to +105°C, C – N° Symbol 1 Tw External Clock low pulse width (EXTCLK) PEWL 2 Tw External Clock high pulse ...
Page 167
SPI TIMING TABLE ( 10 40°C to +85°C, C – Symbol Parameter f SPI frequency SPI 1 t SPI clock period SPI 2 t Enable lead time Lead 3 t Enable lag time ...
Page 168
ST92141 - ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS SPI Master Timing Diagram CPHA=0, CPOL=0 SS (INPUT) SCK (OUTPUT) MISO (INPUT) 6 MOSI (OUTPUT) 10 SPI Master Timing Diagram CPHA=0, CPOL=1 SS (INPUT) SCK (OUTPUT) MISO (INPUT) 6 MOSI (OUTPUT) 10 SPI Master Timing Diagram ...
Page 169
SPI Slave Timing Diagram CPHA=0, CPOL=0 SS (INPUT) 2 SCK (INPUT) MISO HIGH-Z D7-OUT (OUTPUT) 8 MOSI D7-IN (INPUT) 6 SPI Slave Timing Diagram CPHA=0, CPOL=1 SS (INPUT) 2 SCK (INPUT) 5 MISO HIGH-Z D7-OUT (OUTPUT) 8 MOSI D7-IN (INPUT) ...
Page 170
ST92141 - ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS A/D EXTERNAL TRIGGER TIMING TABLE ( 10 40°C to +85°C, C – N° Symbol Parameter 1 Tw External trigger pulse width LOW 2 Tw External trigger pulse distance HIGH 3 ...
Page 171
A/D ANALOG SPECIFICATIONS ( 5° INTCLK Parameter Conversion time Sample time Power-up time Resolution Monotonicity No missing codes Zero input reading Full scale reading Offset error Gain error Diff. Non Linearity error ...
Page 172
ST92141 - ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS Figure 81. A/D Conversion Characteristics 255 254 253 252 251 250 code out LSB (ideal Offset Error OSE 172/179 1 Offset Error ...
Page 173
IMC TIMING TABLE 10 40°C to +85°C, C – N° Symbol Tacho Low Level Minimum Pulse Width in Rising 1 TwTACLR Edge Mode Tacho High Level Minimum Pulse Width in Ris- 2 TwTACHR ...
Page 174
ST92141 - GENERAL INFORMATION 9 GENERAL INFORMATION 9.1 PACKAGE MECHANICAL DATA 32-PIN SHRINK PLASTIC DUAL IN LINE PACKAGE See Lead Detail 34-PIN PLASTIC SMALL OUTLINE PACKAGE 0.10mm .004 seating plane 174/179 1 E ...
Page 175
SHRINK CERAMIC DUAL IN-LINE PACKAGE ST92141 - GENERAL INFORMATION Dim. Min A A1 0.38 B 0.36 0.46 0.58 0.014 0.018 0.023 B1 0.64 0.89 1.14 0.025 0.035 0.045 C 0.20 0.25 0.36 0.008 0.010 0.014 D 29.41 29.97 30.53 ...
Page 176
... FASTROM ST92P141K4M6/xxx 16K ST92E141K4D0 EPROM ST92T141K4B6 16K OTP ST92T141K4M6 Note 1: xxx stands for the FASTROM code name assigned by STMicroelectronics. 176/179 1 imal file generated by the development tool. All un- used bytes must be set to FFh. The customer code should be communicated to STMicroelectronics with the correctly completed OPTION LIST appended ...
Page 177
... SO34. Authorized characters are letters, digits, ’.’, ’-’, ’/’ and spaces only. We have checked the FASTROM code verification file returned STMicroelectronics. It con- forms exactly with the FASTROM code file orginally supplied. We therefore authorize STMicroelec- tronics to proceed with device manufacture. ...
Page 178
ST92141 - SUMMARY OF CHANGES 10 SUMMARY OF CHANGES Description of the changes between the current release of the specification and the previous one. Rev. Added paragraph in section “PLL Clock Multiplier Programming” on page 66 about mandatory use of ...
Page 179
... No license is granted by implication or otherwise under any patent or patent rights of STMicroelectronics. Specifications mentioned in this publication are subject to change without notice. This publication supersedes and replaces all information previously supplied. STMicroelectronics products are not authorized for use as critical components in life support devices or systems without the express written approval of STMicroelectronics ...