AT88SC3216CRF-MVB1G Atmel, AT88SC3216CRF-MVB1G Datasheet - Page 134

AT88SC3216CRF-MVB1G
Manufacturer Part Number
AT88SC3216CRF-MVB1G
Description
CRYPTOMEMORY 32KBIT 16ZONE MVB
Manufacturer
Atmel
Series
CryptoMemory®, CryptoRF®r
Datasheets
1.AT88RF04C-MVB1G.pdf
(158 pages)
2.AT88RF04C-MVB1G.pdf
(2 pages)
3.AT88SC3216CRF-MR1.pdf
(9 pages)
Specifications of AT88SC3216CRF-MVB1G
Rf Type
Read / Write
Frequency
13.56MHz
Features
ISO1444-2, 1444-3, 32-kbits
Package / Case
MVB Module
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Lead free / RoHS Compliant
- Current page: 134 of 158
- Download datasheet (892Kb)
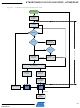
Appendix N. Understanding Anticollision
134
This section of the specification and the flow chart in Figure 45 describe the Anticollision procedure for the CryptoRF
family. The command and response definitions are detailed in the “Anticollision Command Definitions” section 5 of this
specification. For additional information on the anticollision command coding see section 7 of ISO/IEC 14443 Part 3 or
Atmel Application note Understanding the Requirements of ISO/IEC 14443 for Type B Proximity Contactless
Identification Cards.
When the PICC enters the 13.56 MHz RF field of the host reader (PCD) it performs a power on reset (POR) and waits
silently for a valid Type B polling command. The CryptoRF PICC processes the anti-tearing registers as part of the
POR process.
The PCD initiates the anticollision process by issuing an REQB or WUPB command. The WUPB command activates
any card (PICC) in the field with a matching AFI code. The REQB command performs the same function, but does not
affect a PICC in the Halt State. The REQB and WUPB commands contain an integer “N” indicating the number of Slots
assigned to the anticollision process.
If “N” = 1 then all PICCs (with a matching AFI) respond with the ATQB response. If “N” is greater than one, then the
PICC selects a random number “R” in the range of 1 to “N” ; if “R” = 1 then the PICC responds with ATQB. If “R” is
greater than 1, then the PICC waits for a Slot MARKER command where the slot number “S” is equal to “R”, then it
responds with ATQB. The PCD polls all of the slots to determine if any PICC is present in the field.
The ATQB response contains a PUPI card serial number which is used to direct commands to a specific PICC during
the anticollision process. When the PCD receives an ATQB response, it can respond with a matching HLTB command
to Halt the PICC, or it can respond with a matching ATTRIB command to assign a Card ID Number (CID) and place the
PICC in the Active State. Once placed in the Active State the PICC is ready for transactions using the CryptoRF Active
State commands. A PICC in the Active State ignores all commands that do not contain a CID number which matches
the CID assigned by the ATTRIB command. A PICC in the Active State ignores all REQB, WUPB, Slot MARKER,
ATTRIB, and HLTB commands.
When the PCD receives an ATQB response with a CRC error, then a collision is assumed to have occurred. Typically
the PCD will complete transactions with any other PICCs in the field, and then place them in the Halt State using a
DESELECT command. The PCD will then issue a new REQB command, causing each PICC in the field (with a
matching AFI) that has not been Halted to select a new random number “R”. This procedure resolves the conflict
between the previously colliding PICCs, allowing the PCD to communicate with them.
The anticollision process continues in this manner until all PICCs in the field have completed their transactions. Any
command received by the PICC with a CRC error is ignored.
Note:
AT88SC0808/1616/3216/6416CRF, AT88RF04C
ISO/IEC 14443 Part 3 describes two anticollision options for Type B PICCs; the Timeslot option has been
implemented in the CryptoRF family.
5276C–RFID–3/09
Related parts for AT88SC3216CRF-MVB1G
Image
Part Number
Description
Manufacturer
Datasheet
Request
R

Part Number:
Description:
CryptoMemory 32 Kbit
Manufacturer:
ATMEL [ATMEL Corporation]
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
IC EEPROM 32KBIT 1.5MHZ 8SOIC
Manufacturer:
Atmel
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
IC EEPROM 32KBIT 1.5MHZ 8DIP
Manufacturer:
Atmel
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
IC EEPROM 32KBIT 1.5MHZ 8DIP
Manufacturer:
Atmel
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
CRYPTOMEM 32KBIT 16ZONE MOD J TW
Manufacturer:
Atmel
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
IC EEPROM 32KBIT 1.5MHZ 8LAP
Manufacturer:
Atmel
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
IC EEPROM 32KBIT 1.5MHZ M2J
Manufacturer:
Atmel
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Atmel
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Atmel
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Atmel
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
DEV KIT FOR AVR/AVR32
Manufacturer:
Atmel
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
INTERVAL AND WIPE/WASH WIPER CONTROL IC WITH DELAY
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Low-Voltage Voice-Switched IC for Hands-Free Operation
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
MONOLITHIC INTEGRATED FEATUREPHONE CIRCUIT
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet: