DP8344BV National Semiconductor, DP8344BV Datasheet - Page 71

DP8344BV
Manufacturer Part Number
DP8344BV
Description
IC BIPHASE COMM PROCESSR 84-PLCC
Manufacturer
National Semiconductor
Datasheet
1.DP8344BV.pdf
(184 pages)
Specifications of DP8344BV
Processor Type
8-Bit RISC
Speed
20MHz
Voltage
4.5 ~ 5.5V
Mounting Type
Surface Mount
Package / Case
84-PLCC
Operating Supply Voltage (typ)
5V
Operating Supply Voltage (max)
5.5V
Operating Supply Voltage (min)
4.5V
Mounting
Surface Mount
Operating Temperature (max)
70C
Operating Temperature (min)
0C
Operating Temperature Classification
Commercial
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Contains lead / RoHS non-compliant
Features
-
Lead Free Status / Rohs Status
Not Compliant
Other names
*DP8344BV
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Company:
Part Number:
DP8344BV
Manufacturer:
NSC
Quantity:
5 510
Part Number:
DP8344BV
Manufacturer:
NS/国半
Quantity:
20 000
4 0 Remote Interface and Arbitration System (RIAS)
Programmed wait states delay when WAIT must be assert-
ed since programmed wait states are inserted before WAIT
is tested to see if any more wait states should be added
LOCK prevents local accesses of Data Memory If LOCK is
asserted a half T-state before T1 of a BCP instruction cycle
further local accesses will be prevented by waiting the Tim-
ing Control Unit The Timing Control Unit (TCU) is the BCP
CPU sub system responsible for timing each instruction For
a more detailed description of the operation of LOCK refer
to the CPU Timing section LOR allows the BCP to prevent
remote accesses Once LOR
high further remote accesses are waited by XACK remain-
ing low
Though the BCP CPU runs independently of RIAS there is
some interaction between the two systems
such interaction In addition two bits allow the BCP CPU to
keep track of remote accesses These bits are the Remote
Write bit RW and the Remote Read bit RR and are lo-
cated in CCR 6 –5
tive remote access to DMEM reaches its Termination
Phase Once one of these bits has been set it will remain
high until a ‘‘1’’ is written to that bit to reset it low
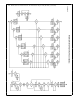
4 2 RIAS FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
In this section the operation of the Remote Arbitration State
Machine (RASM) is described in detail Discussed among
other things are the sequence of events in a remote ac-
cess arbitration of the data buses timing of external sig-
nals when inputs are sampled and when wait states are
added Each of the five Interface Modes is described in
functional state machine form Although each interface
mode is broken out in a separate flow chart they are all part
of a single state machine (RASM) Thus the first state in
each flow chart is actually the same state
The functional state machine form is similar to a flow chart
except that transitions to a new state (states are denoted as
rectangular boxes) can only occur on the rising edge of the
internal CPU clock (CPU-CLK) CPU-CLK is high during the
first half of its cycle A state box can specify several actions
and each action is separated by a horizontal line A signal
name listed in a state box indicates that that pin will be
asserted high when RASM has entered that state Signals
not listed are assumed low
Note This sometimes necessitates using the inversion of the external pin
This same rule applies to the A and AD buses By default
these buses are active The A bus will have the upper byte
of the last used data address The AD bus will display
condition specified will be in effect only during that state
Decision blocks are shown as diamonds and their meaning
is the same as in a flow chart The hexagon box is used to
denote a conditional state not synchronous with the clock
When the path following a decision block encounters a con-
ditional state the action specified inside the hexagon box is
executed immediately
RIC When one of these buses appears in a state box the
name
Each bit goes high when its respec-
located in ACR
LOR is one
is set
71
Also provided is a memory arbitration example in the form of
a timing diagram for each of the five modes These exam-
ples show back to back local accesses punctuated by a
remote access Both the state of RASM and the Timing
Control Unit are listed for every clock at the top of each
timing diagram The RASM states listed correspond to the
flow charts The Timing Control Unit states are described in
Section 2 2 2 Timing portion of the data sheet
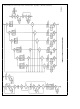
4 2 1 Buffered Read
The unique feature of this mode is the extension of the read
until REM-RD is deasserted high The complete flow chart
for the Buffered Read mode is shown in Figure 4-14 Until a
Remote Read is initiated (RAE REM-RD true) the state ma-
chine (RASM) loops in state RS
initiated and LOR is set high RASM will move to state
RS
es have been granted locally (i e Local Bus Request
RASM will move to state RS
in state RS
granted locally If the BCP CPU needs to access Data Mem-
ory while in either RS
do so A local access is requested by the Timing Control
Unit asserting the Local Bus Request (LCL-BREQ) signal A
local bus grant will be given by RASM if the buses are not
being used (as is the case in the RS
XACK is taken low as soon as RAE REM-RD is true re-
gardless of an ongoing local access If LOR is low RASM
will move into RS
true and there is no local bus request No further local bus
requests will be granted until the remote access is complete
and RASM returns to RS
the A bus (and AD bus if the access is to Data Memory)
goes into TRI-STATE
On the next CPU-CLK RASM enters RS
high while XACK remains low The wait state counters i
and i
0 respectively in DCR
is to Data Memory) remains in TRI-STATE and the Access
Phase begins
The state machine can move into one of several states
depending on the state of CMD and MS1–0 on the next
clock XACK remains low and LCL remains high in all the
possible next states If CMD is high the access is to RIC
and the next state will be RS
AD is RIC
The five other next states all have CMD low and depend on
the Memory Select bits If MS1–0 is 10 or 11 the state
machine will enter either RS
bytes of the Program Counter respectively will be read
moves RASM into RS
and A and AD continue to be in TRI-STATE This allows the
Remote Processor to drive the Data Memory address for
the read Since DMEM is subject to wait states RS
looped upon until all the wait states have been inserted
MS1 –0
A2
DW
Likewise if a Remote Read is initiated while the bus-
are loaded in this state from IW1 –0 and DW2–
e
A2
it will not transition in this state
00 designates a Data Memory access and
as long as LOR is set high or the buses are
B
on the next clock after RAE REM-RD is
(Continued)
A
D4
state (and LOCK is high) it can still
A
READ will be asserted in this state
Half a T-state after entering RS
The A bus (and AD if the access
D2
A2
D1
or RS
The state machine will loop
Since the default state of
A1
A
D3
If a Remote Read is
states)
and the low or high
C
and LCL is taken
e
D4
1)
IW
is
B