ATmega64 Atmel Corporation, ATmega64 Datasheet - Page 222

ATmega64
Manufacturer Part Number
ATmega64
Description
Manufacturer
Atmel Corporation
Specifications of ATmega64
Flash (kbytes)
64 Kbytes
Pin Count
64
Max. Operating Frequency
16 MHz
Cpu
8-bit AVR
# Of Touch Channels
16
Hardware Qtouch Acquisition
No
Max I/o Pins
53
Ext Interrupts
8
Usb Speed
No
Usb Interface
No
Spi
1
Twi (i2c)
1
Uart
2
Graphic Lcd
No
Video Decoder
No
Camera Interface
No
Adc Channels
8
Adc Resolution (bits)
10
Adc Speed (ksps)
15
Analog Comparators
1
Resistive Touch Screen
No
Temp. Sensor
No
Crypto Engine
No
Sram (kbytes)
4
Eeprom (bytes)
2048
Self Program Memory
YES
Dram Memory
No
Nand Interface
No
Picopower
No
Temp. Range (deg C)
-40 to 85
I/o Supply Class
2.7 to 5.5
Operating Voltage (vcc)
2.7 to 5.5
Fpu
No
Mpu / Mmu
no / no
Timers
4
Output Compare Channels
8
Input Capture Channels
2
Pwm Channels
7
32khz Rtc
Yes
Calibrated Rc Oscillator
Yes
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Company:
Part Number:
ATMEGA64
Manufacturer:
ATMEL
Quantity:
9 500
Company:
Part Number:
ATmega64-16AU
Manufacturer:
ATM
Quantity:
5 400
Company:
Part Number:
ATmega64-16AU
Manufacturer:
ATMEL
Quantity:
9 500
Company:
Part Number:
ATmega64-16AU
Manufacturer:
Atmel
Quantity:
3 589
Part Number:
ATmega64-16AU
Manufacturer:
MICROCHIP/微芯
Quantity:
20 000
Company:
Part Number:
ATmega64-16MI
Manufacturer:
ATMEL
Quantity:
260
Part Number:
ATmega640-16AU
Manufacturer:
ATMEL/爱特梅尔
Quantity:
20 000
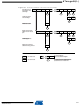
Slave Transmitter
Mode
2490Q–AVR–06/10
In the Slave Transmitter mode, a number of data bytes are transmitted to a master receiver (see
Figure
zero or are masked to zero.
Figure 102. Data Transfer in Slave Transmitter Mode
To initiate the Slave Transmitter mode, TWAR and TWCR must be initialized as follows:
The upper seven bits are the address to which the Two-wire Serial Interface will respond when
addressed by a master. If the LSB is set, the TWI will respond to the general call address (0x00),
otherwise it will ignore the general call address.
TWEN must be written to one to enable the TWI. The TWEA bit must be written to one to enable
the acknowledgment of the device’s own slave address or the general call address. TWSTA and
TWSTO must be written to zero.
When TWAR and TWCR have been initialized, the TWI waits until it is addressed by its own
slave address (or the general call address if enabled) followed by the data direction bit. If the
direction bit is “1” (read), the TWI will operate in ST mode, otherwise SR mode is entered. After
its own slave address and the write bit have been received, the TWINT flag is set and a valid
status code can be read from TWSR. The status code is used to determine the appropriate soft-
ware action. The appropriate action to be taken for each status code is detailed in
Slave Transmitter mode may also be entered if arbitration is lost while the TWI is in the Master
mode (see state 0xB0).
If the TWEA bit is written to zero during a transfer, the TWI will transmit the last byte of the trans-
fer. State 0xC0 or state 0xC8 will be entered, depending on whether the master receiver
transmits a NACK or ACK after the final byte. The TWI is switched to the not addressed Slave
mode, and will ignore the master if it continues the transfer. Thus the master receiver receives
all “1” as serial data. State 0xC8 is entered if the master demands additional data bytes (by
transmitting ACK), even though the slave has transmitted the last byte (TWEA zero and expect-
ing NACK from the master).
While TWEA is zero, the TWI does not respond to its own slave address. However, the Two-wire
Serial Bus is still monitored and address recognition may resume at any time by setting TWEA.
This implies that the TWEA bit may be used to temporarily isolate the TWI from the Two-wire
Serial Bus.
TWAR
TWCR
Value
Value
SDA
SCL
102). All the status codes mentioned in this section assume that the prescaler bits are
TRANSMITTER
Device 1
SLAVE
TWINT
TWA6
0
TWA5
TWEA
Device 2
RECEIVER
MASTER
1
TWSTA
TWA4
Device’s Own Slave Address
0
Device 3
TWSTO
TWA3
0
........
TWWC
TWA2
0
Device n
TWA1
TWEN
V
1
CC
ATmega64(L)
TWA0
R1
–
0
TWGCE
R2
TWIE
Table
X
91. The
222