AT24RF08-EK Atmel, AT24RF08-EK Datasheet - Page 2

AT24RF08-EK
Manufacturer Part Number
AT24RF08-EK
Description
KIT EVAL FOR AT24RF08CN-10SC
Manufacturer
Atmel
Type
Dual Access EEPROMr
Specifications of AT24RF08-EK
Contents
Atmel Asset ID Kit CDROM, 4 RFID Tags, Reader with Serial Port Cable and 9V Power Supply
For Use With/related Products
AT24RF08C
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Contains lead / RoHS non-compliant
General Overview
The AT24RF08C is intended to be pin compatible with
standard serial EEPROM devices except for pins 1, 2 and
3, which are address pins in the standard part. Other
exceptions to the AT24C08 Serial EEPROM data sheet are
noted in the “Serial EEPROM Exceptions” section later in
this document. Connection of an external coil antenna and
optional tuning capacitor, normally via a two conductor
wire, is all that is required to complete the RFID hardware
requirements.
Throughout this document, the term “reader” is defined as
the base station that communicates with the chip. Under all
expected conditions, it actually serves as both a reader and
writer. The term ‘tag’ is used to indicate the chip when
operating as an RFID transponder with the coil attached.
All bits are sent to or read from the device, most significant
bit first, in a manner consistent with the AT24C08 Serial
E E P R O M . T h e b i t f i e l d s i n t h i s d o c u m e n t a r e
correspondingly listed with the MSB on the left and the LSB
on the right.
EEPROM Organization
The EEPROM memory is broken up into 8 blocks of 1K
bits (128 bytes) each. Within each block, the memory is
physically organized into 8 pages of 128 bits (16 bytes)
each. In some instances, accesses take place on a 32-bit
(4 byte) word basis. In addition to these 8K bits, there are
two more 128-bit pages that are used to store the access
protection and ID information. There are a total of 8448 bits
of EEPROM memory available on the AT24RF08C.
Access protection (both read and write) is organized on a
block basis for blocks 1 through 7 and on a page and block
basis for block 0. Protection information for these blocks
and pages is stored in one of the additional pages of
EEPROM memory that is addressed separately from the
main data storage array. See “Access Protection” on page
3 for more details.
The ID value (see “ID Configuration” on page 7) is located
in the ID page of the EEPROM, the second of the additional
16 byte pages.
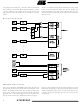
Device Access Examples
For Write Operations:
For Read Operations:
2
1 0 1 0 1 B
1 0 1 0 1 X X 1
2
B
1
0
AT24RF08C
D
7
B
D
0
6
P
D
2
P
5
1
D
P
4
0
D
A
3
3
D
A
2
2
D
A
1
1
D
A
0
0
…
D
7
D
6
D
5
Writes from the serial port may include from one to 16
bytes at a time, depending on the protocol followed by the
bus master. Accesses to the EEPROM from the RFID port
are on either a word (32 bits) or page (128 bits) basis only.
All page accesses must be properly aligned to the internal
EEPROM page.
The EEPROM memory offers an endurance of 100,000
write cycles per byte, with 10 year data retention. Writes to
the EEPROM and tamper bit take less than 10 ms to
complete.
Completion time for writes initiated from the RFID port are
different depending on the situation. When external power
is supplied to the chip through the VCC pin, writes to the
EEPROM and tamper bit take less than 11.8 ms when
measured from the last modulation edge before the write to
the first after the write. When powered from the coil pins at
125 KHz, the EEPROM write time will be 5.8 ms and the
tamper write time will be 7.9 ms.
After manufacturing, all EEPROM bits except in the device
revision byte (see “Access Protection” page 5) will be set to
a value of 1 and the tamper bit will be set to 0.
Device Access
The third device address bit in the two wire protocol that is
usually matched to A
E E P RO M is i n te r na l l y c o n ne c te d h i gh , s o de v i c e
addresses A8 through AF (hex) are used to access the
memory on the chip. The general command encoding used
by the serial port for EEPROM accesses is shown below in
Device Access Examples, where B
P
address within the page. Bits denoted as “x” are ignored by
the device.
The PROT pin is used as a power good signal. When this
pin is low, the serial port is held in reset and all sticky bits
are set to one. When high, activity on the serial bus is
permitted.
D
2-0
4
D
is the page number within the block and A
3
D
2
D
1
D
0
…
2
(pin 3) on a standard AT24C08 serial
2-0
is the block number,
3-0
is the byte