DS1972-F3+ Maxim Integrated Products, DS1972-F3+ Datasheet - Page 12

DS1972-F3+
Manufacturer Part Number
DS1972-F3+
Description
IBUTTON EEPROM 1KBit F3
Manufacturer
Maxim Integrated Products
Series
iButton®r
Datasheet
1.DS1972-F3.pdf
(23 pages)
Specifications of DS1972-F3+
Rohs Information
IButton RoHS Compliance Plan
Memory Size
128B
Memory Type
EEPROM
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Lead free / RoHS Compliant
1024-Bit EEPROM iButton
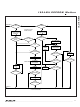
The Copy Scratchpad command is used to copy data
from the scratchpad to writable memory sections. After
issuing the Copy Scratchpad command, the master
must provide a 3-byte authorization pattern, which
should have been obtained by an immediately preced-
ing Read Scratchpad command. This 3-byte pattern
must exactly match the data contained in the three
address registers (TA1, TA2, E/S, in that order). If the
pattern matches, the target address is valid, the PF flag
is not set, and the target memory is not copy protected,
then the AA flag is set and the copy begins. All 8 bytes
of scratchpad contents are copied to the target memo-
ry location. The duration of the device’s internal data
transfer is t
bus must not fall below 2.8V. A pattern of alternating 0s
and 1s are transmitted after the data has been copied
until the master issues a reset pulse. If the PF flag is set
or the target memory is copy protected, the copy does
not begin and the AA flag is not set.
If the copy command was disturbed due to lack of
power or for other reasons, the master will read a con-
stant stream of FFh bytes until it sends a 1-Wire Reset
Pulse. In this case, the destination memory may be
incompletely programmed requiring a Write Scratchpad
command and Copy Scratchpad command be repeat-
ed to ensure proper programming of the EEPROM. This
requires careful consideration when designing applica-
tion software that writes to the DS1972 in an intermittent
contact environment.
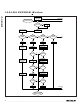
The Read Memory command is the general function to
read data from the DS1972. After issuing the com-
mand, the master must provide the 2-byte target
address. After these 2 bytes, the master reads data
beginning from the target address and can continue
until address 008Fh. If the master continues reading,
the result is logic 1s. The device’s internal TA1, TA2,
E/S, and scratchpad contents are not affected by a
Read Memory command.
The 1-Wire bus is a system that has a single bus mas-
ter and one or more slaves. In all instances the DS1972
is a slave device. The bus master is typically a micro-
controller. The discussion of this bus system is broken
12
______________________________________________________________________________________
PROG
during which the voltage on the 1-Wire
1-Wire Bus System
Copy Scratchpad [55h]
Read Memory [F0h]
down into three topics: hardware configuration, trans-
action sequence, and 1-Wire signaling (signal types
and timing). The 1-Wire protocol defines bus transac-
tions in terms of the bus state during specific time slots,
which are initiated on the falling edge of sync pulses
from the bus master.
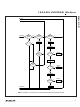
The 1-Wire bus has only a single line by definition; it is
important that each device on the bus be able to drive
it at the appropriate time. To facilitate this, each device
attached to the 1-Wire bus must have open-drain or
three-state outputs. The 1-Wire port of the DS1972 is
open drain with an internal circuit equivalent to that
shown in Figure 8.
A multidrop bus consists of a 1-Wire bus with multiple
slaves attached. The DS1972 supports both a standard
and overdrive communication speed of 15.4kbps (max)
and 125kbps (max), respectively. Note that legacy
1-Wire products support a standard communication
speed of 16.3kbps and overdrive of 142kbps. The
slightly reduced rates for the DS1972 are a result of
additional recovery times, which in turn were driven by
a 1-Wire physical interface enhancement to improve
noise immunity. The value of the pullup resistor primari-
ly depends on the network size and load conditions.
The DS1972 requires a pullup resistor of 2.2kΩ (max) at
any speed.
The idle state for the 1-Wire bus is high. If for any rea-
son a transaction needs to be suspended, the bus
must be left in the idle state if the transaction is to
resume. If this does not occur and the bus is left low for
more than 16µs (overdrive speed) or more than 120µs
(standard speed), one or more devices on the bus
could be reset.
The protocol for accessing the DS1972 through the
1-Wire port is as follows:
• Initialization
• ROM Function Command
• Memory Function Command
• Transaction/Data
Hardware Configuration
Transaction Sequence