DS1972-F3 MAXIM [Maxim Integrated Products], DS1972-F3 Datasheet

DS1972-F3
Related parts for DS1972-F3
DS1972-F3 Summary of contents
Page 1
... ORDERING INFORMATION DS1972-F5# DS1972-F3# # indicates RoHS complience Contact factory lead-free compliance 1024 Bits of EEPROM Memory Partitioned into Four Pages of 256 Bits Individual Memory Pages can be Permanently Write Protected or Put in EPROM-Emulation Mode ("Write to 0") Switchpoint Hysteresis and Filtering to Optimize ...
Page 2
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS I/O Voltage to GND I/O Sink Current Operating Temperature Range Junction Temperature Storage Temperature Range Stresses beyond those listed under “Absolute Maximum Ratings” may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only, and functional ...
Page 3
... The earliest recognition of a negative edge is possible at t Note 14: Defines maximum possible bit rate. Equal to t Note 15: Interval after t during which a bus master is guaranteed to sample a logic there is a DS1972 present. Minimum limit RSTL maximum limit is t PDH(max) Note 16: Highlighted numbers are NOT in compliance with legacy 1-Wire product standards ...
Page 4
... The DS1972 has an additional memory area called the scratchpad that acts as a buffer when writing to the main memory or the register page. Data is first written to the scratchpad from which it can be read back. After the data has been verified, a Copy Scratchpad command transfers the data to its final memory location ...
Page 5
... Commands (see Figure 7) 64-BIT LASERED ROM Each DS1972 contains a unique ROM code that is 64 bits long. The first 8 bits are a 1-Wire family code. The next 48 bits are a unique serial number. The last 8 bits are a CRC (Cyclic Redundancy Check) of the first 56 bits. See Figure 3 for details ...
Page 6
... Data memory and registers are located in a linear address space, as shown in Figure 5. The data memory and the registers have unrestricted read access. The DS1972 EEPROM array consists of 18 rows of 8 bytes each. The first 16 rows are divided equally into 4 memory pages (32 bytes each). These 4 pages are the primary data memory. ...
Page 7
... The DS1972 employs three address registers: TA1, TA2, and E/S (Figure 6). These registers are common to many other 1-Wire devices but operate slightly differently with the DS1972. Registers TA1 and TA2 must be loaded with the target address to which the data is written or from which data is read. Register E read-only transfer- status register, used to verify data integrity with write commands ...
Page 8
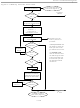
... The Memory Function Flow Chart (Figure 7) describes the protocols necessary for accessing the memory of the DS1972. An example on how to use these functions to write to and read from the device is included at the end of this document. The communication between master and DS1972 takes place either at regular speed (default Overdrive Speed ( ...
Page 9
... If write-protected, then the DS1972 copies the data byte from the tar- get address into the SP EPROM mode, then the DS1972 loads the bitwise logical AND of the transmitted byte and the data byte from the targeted address into the SP. ...
Page 10
... TA1 (T7:T0), TA2 (T15:T8) and E/S Byte DS1972 sets Scratchpad Byte Counter = T2:T0 Bus Master RX Data Byte from Scratchpad Y Master TX Reset ? N N Byte Counter = E2: Bus Master RX CRC16 of Command, Address, E/S Byte, Data Bytes as sent by the DS1972 N Master TX Reset ? Figure Part From Figure Part ...
Page 11
... N N Duration Master Y * 1-Wire idle high for power Figure Part Copy- Protected ? DS1972 copies Scratch- PROG pad Data to Address DS1972 TX “0” Y Master TX Reset ? N DS1972 TX “1” Master TX Reset ? Y From Figure Part * N ...
Page 12
... F0h 3 Part Read Memory ? Bus Master TX TA1 (T7:T0), TA2 (T15:T8) Address < 90h ? To Figure Part DS1972 sets Memory Address = (T15:T0) DS1972 Bus Master RX Increments Data Byte from Address Memory Address Counter Master TX Reset ? N Y Address < 8Fh ? N N Bus Master Master RX “ ...
Page 13
... The device's internal TA1, TA2, E/S, and scratchpad contents are not affected by a Read Memory command. 1-Wire BUS SYSTEM The 1-Wire bus is a system that has a single bus master and one or more slaves. In all instances the DS1972 is a slave device. The bus master is typically a microcontroller. The discussion of this bus system is broken down into three topics: hardware configuration, transaction sequence, and 1-Wire signaling (signal types and timing) ...
Page 14
... All transactions on the 1-Wire bus begin with an initialization sequence. The initialization sequence consists of a Reset Pulse transmitted by the bus master followed by Presence Pulse(s) transmitted by the slave(s). The Presence Pulse lets the bus master know that the DS1972 is on the bus and is ready to operate. For more details, see the 1-Wire Signaling section. ...
Page 15
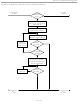
... The Overdrive-Match ROM command followed by a 64-bit ROM sequence transmitted at Overdrive Speed allows the bus master to address a specific DS1972 on a multidrop bus and to simultaneously set it in Overdrive mode. Only the DS1972 that exactly matches the 64-bit ROM sequence responds to the subsequent memory function command ...
Page 16
... Search ROM Command ? Command ? DS1972 TX Bit 0 Master TX Bit 0 DS1972 TX Bit 0 Master TX Bit Bit 0 Bit 0 Match ? Match ? Y DS1972 TX Bit 1 Master TX Bit 1 DS1972 TX Bit 1 Master TX Bit Bit 1 Bit 1 Match ? Match ? Y DS1972 TX Bit 63 Master TX Bit 63 DS1972 TX Bit 63 Master TX Bit ...
Page 17
Figure 9-2. ROM Functions Flow Chart (continued Figure 9, 1 Part From Figure 9 st A5h 1 Part Resume Command ? From Figure Part To Figure Part 3Ch ...
Page 18
... Figure 10 shows the initialization sequence required to begin any communication with the DS1972. A Reset Pulse followed by a Presence Pulse indicates the DS1972 is ready to receive data, given the correct ROM and memory function command. If the bus master uses slew-rate control on the falling edge, it must pull down the line for ...
Page 19
... For a write-zero time slot, the voltage on the data line must stay below the V W1LMAX threshold until the write-zero low time t data line should not exceed V ILMAX the DS1972 needs a recovery time t Figure 11. Read/Write Timing Diagram Write-One Time Slot t V PUP ...
Page 20
... RL line low; its internal timing generator determines when this pulldown ends and the voltage starts rising again. When responding with a 1, the DS1972 does not hold the data line low at all, and the voltage starts rising as soon as t over (rise time) on one side and the internal timing generator of the DS1972 on the other side define ...
Page 21
... CRC GENERATION With the DS1972 there are two different types of CRCs. One CRC is an 8-bit type and is stored in the most significant byte of the 64-bit ROM. The bus master can compute a CRC value from the first 56 bits of the 64-bit ROM and compare it to the value stored within the DS1972 to determine if the ROM data has been received error- free ...
Page 22
COMMAND-SPECIFIC 1-Wire COMMUNICATION PROTOCOL—LEGEND SYMBOL RST 1-Wire Reset Pulse generated by master. PD 1-Wire Presence Pulse generated by slave. Select Command and data to satisfy the ROM function protocol. WS Command "Write Scratchpad". RS Command "Read Scratchpad". CPS Command "Copy ...
Page 23
... MEMORY FUNCTION EXAMPLE Write to the first 8 bytes of memory page 1. Read the entire memory. With only a single DS1972 connected to the bus master, the communication looks like this: MASTER MODE ¾ ...