PIC18F8520-I/PT Microchip Technology Inc., PIC18F8520-I/PT Datasheet - Page 235

PIC18F8520-I/PT
Manufacturer Part Number
PIC18F8520-I/PT
Description
80 PIN, 32 KB FLASH, 2048 RAM, 68 I/O
Manufacturer
Microchip Technology Inc.
Datasheet
1.PIC18F8520-IPT.pdf
(380 pages)
Specifications of PIC18F8520-I/PT
A/d Inputs
16-Channel, 10-Bit
Comparators
2
Cpu Speed
10 MIPS
Eeprom Memory
1024 Bytes
Input Output
68
Interface
I2C/SPI/UART/USART
Memory Type
Flash
Number Of Bits
8
Package Type
80-pin TQFP
Programmable Memory
32K Bytes
Ram Size
2K Bytes
Speed
40 MHz
Timers
2-8-bit, 3-16-bit
Voltage, Range
2-5.5 V
Lead Free Status / Rohs Status
RoHS Compliant part
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Company:
Part Number:
PIC18F8520-I/PT
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology
Quantity:
10 000
Part Number:
PIC18F8520-I/PT
Manufacturer:
MICRCOHI
Quantity:
20 000
- Current page: 235 of 380
- Download datasheet (7Mb)
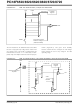
22.0
In many applications, the ability to determine if the
device voltage (V
is a desirable feature. A window of operation for the
application can be created, where the application soft-
ware can do “housekeeping tasks” before the device
voltage exits the valid operating range. This can be
done using the Low-Voltage Detect module.
This module is a software programmable circuitry,
where a device voltage trip point can be specified.
When the voltage of the device becomes lower then the
specified point, an interrupt flag is set. If the interrupt is
enabled, the program execution will branch to the inter-
rupt vector address and the software can then respond
to that interrupt source.
FIGURE 22-1:
The block diagram for the LVD module is shown in
Figure 22-2. A comparator uses an internally gener-
ated reference voltage as the set point. When the
selected tap output of the device voltage crosses the
set point (is lower than), the LVDIF bit is set.
Each node in the resistor divider represents a “trip
point” voltage. The “trip point” voltage is the minimum
supply voltage level at which the device can operate
before the LVD module asserts an interrupt. When the
2004 Microchip Technology Inc.
LOW-VOLTAGE DETECT
PIC18F6520/8520/6620/8620/6720/8720
DD
V
V
) is below a specified voltage level
A
B
TYPICAL LOW-VOLTAGE DETECT APPLICATION
Time
T
A
T
B
The Low-Voltage Detect circuitry is completely under
software control. This allows the circuitry to be “turned
off” by the software, which minimizes the current
consumption for the device.
Figure 22-1 shows a possible application voltage curve
(typically for batteries). Over time, the device voltage
decreases. When the device voltage equals voltage V
the LVD logic generates an interrupt. This occurs at
time T
until the device voltage is no longer in valid operating
range, to shut down the system. Voltage point V
minimum valid operating voltage specification. This
occurs at time T
time for shutdown.
supply voltage is equal to the trip point, the voltage
tapped off of the resistor array is equal to the 1.2V
internal reference voltage generated by the voltage ref-
erence module. The comparator then generates an
interrupt signal, setting the LVDIF bit. This voltage is
software programmable to any one of 16 values (see
Figure 22-2). The trip point is selected by programming
the LVDL3:LVDL0 bits (LVDCON<3:0>).
A
. The application software then has the time,
Legend:
V
V
A
B
= LVD trip point
= Minimum valid device
B
operating voltage
. The difference T
DS39609B-page 233
B
– T
A
is the total
B
is the
A
,
Related parts for PIC18F8520-I/PT
Image
Part Number
Description
Manufacturer
Datasheet
Request
R

Part Number:
Description:
20-Pin USB Flash Microcontrollers
Manufacturer:
MICROCHIP [Microchip Technology]
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
PIC18F With 128-segment LCD Driver And 12-bit ADC, 8KB Flash, 768B RAM, CCP, MSS
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
PIC18F With 128-segment LCD Driver And 12-bit ADC, 16KB Flash, 768B RAM, CCP, MS
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
PIC18F With 192-segment LCD Driver And 12-bit ADC, 8KB Flash, 768B RAM, CCP, MSS
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
PIC18F With 192-segment LCD Driver And 12-bit ADC, 16KB Flash, 768B RAM, CCP, MS
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Microcontrollers (MCU) 48KB 3328 RAM 52 I/O
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Microcontrollers (MCU) 64KB 3328 RAM 52 I/O
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
32kB Flash, 2kB RAM, 1kB EE, NanoWatt XLP, LCD 64 QFN 9x9x0.9mm T/R
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
32kB Flash, 2kB RAM, 1kB EE, NanoWatt XLP, LCD 64 TQFP 10x10x1mm T/R
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
128kB Flash, 4kB RAM, 1kB EE, 16MIPS, NanoWatt XLP, LCD, 5V 80 TQFP 12x12x1mm T/
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
32kB Flash, 2kB RAM, 1kB EE, NanoWatt XLP, LCD 64 QFN 9x9x0.9mm TUBE
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
32kB Flash, 2kB RAM, 1kB EE, NanoWatt XLP, LCD 64 TQFP 10x10x1mm TRAY
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology

Part Number:
Description:
128kB Flash, 4kB RAM, 1kB EE, 16MIPS, NanoWatt XLP, LCD, 5V 80 TQFP 12x12x1mm TR
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology