TXC-06885BIOG Transwitch Corporation, TXC-06885BIOG Datasheet - Page 19

TXC-06885BIOG
Manufacturer Part Number
TXC-06885BIOG
Description
Manufacturer
Transwitch Corporation
Datasheet
1.TXC-06885BIOG.pdf
(128 pages)
Specifications of TXC-06885BIOG
Operating Supply Voltage (typ)
1.8/3.3V
Operating Temperature Classification
Industrial
Package Type
BGA
Mounting
Surface Mount
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Not Compliant
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Company:
Part Number:
TXC-06885BIOG
Manufacturer:
TRANSWITCH
Quantity:
10
PRELIMINARY TXC-06885-MB, Ed. 6A
February 2005
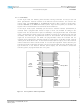
Microprocessor Clock (UPCLK)
Microprocessor Data Bus (UPD)
Microprocessor Address Bus (UPA) Host Address Bus
Chip Select (CS)
Write/Transfer Start (WRDS)
Transfer Acknowledge (DTACK)
Read/Write (RDWR)
Interrupt (IRQ)
2.1.8 Microprocessor Interface
2.1.9 JTAG Boundary Scan
Envoy-CE4 Pin Name
The Envoy-CE4 configuration, status, and device management is performed via its
microprocessor interface. The interface has a 15 bit wide address bus UPA(14-0) and a pin
configurable 8 or 16 bit wide data bus UPD(15-0). It is compatible with standard Intel/
Motorola micro-controllers. The interface operates from a minimum clock (UPCLK) frequency
of 33 MHz to a maximum clock frequency of 66 MHz.
The following table shows the Pin description for the Host interface in Intel and Motorola
modes:
All internal registers (control and status) are 32 bits wide. In order to complete a write
operation, all 32 bits must be written. All accesses require writing or reading the complete 32
bits. Hence, when performing a write when the Microprocessor Interface is configured as an 8
bit wide bus, it is required to do 4 writes to write to the internal register. Similarly, when doing
a read when the bus is configured as an 8 bit wide bus, 4 reads need to be performed to
access the register. The diagrams in
the bus accesses in Motorola and Intel modes for both read and write operations. The
minimum CS to DTACK time is 6 UPCLK cycles and the maximum CS to DTACK time is 22
UPCLK cycles.
The IEEE 1149.1 standard defines the requirements of a boundary scan architecture that has
been specified by the IEEE Joint Test Action Group (JTAG). Boundary scan is a specialized
scan architecture that provides observability and controllability for the interface leads of the
device. As shown in
or output lead to be observed or tested (bidirectional leads may have two cells). The
boundary scan capability is based on a Test Access Port (TAP) controller, instruction and
bypass registers, and a boundary scan register path bordering the input and output leads.
The boundary scan test bus interface consists of four input signals and an output signal. The
four input signals are Test Clock (TCK), Test Mode Select (TMS), Test Data Input (TDI) and
Test Mode Reset (TRST). The output signal is Test Data Output (TDO). In addition to the TAP,
a pin is provided (DEVHIZ) to place the output buffers in a high impedance state for systems
that do not support the IEEE 1149.1 standard. Boundary scan signal timing is shown in
20.
Figure
- Functional Description -
Host Interface Clock
Host Data Bus
Device Chip Select
Write Strobe (Active Low)
Ready
Read Strobe (Active Low)
Interrupt Pin
9, one cell of a boundary scan register is assigned to each input
Intel Mode Description
Figure
21,
Figure
22,
Host Interface Clock
Host Data Bus
Host Address Bus
Device Chip Select
Active Low Transfer Start
Active Low Transfer Acknowledge
Read/Write Strobe
Interrupt Pin
Figure
Motorola Mode Description
23, and
Envoy-CE4 Device
Figure 24
DATA SHEET
TXC-06885
19 o f 12 8
illustrate
Figure