ATMEGA64-16MJ Atmel, ATMEGA64-16MJ Datasheet - Page 248

ATMEGA64-16MJ
Manufacturer Part Number
ATMEGA64-16MJ
Description
IC MCU AVR 64K 5V 16MHZ 64-QFN
Manufacturer
Atmel
Series
AVR® ATmegar
Specifications of ATMEGA64-16MJ
Core Processor
AVR
Core Size
8-Bit
Speed
16MHz
Connectivity
I²C, SPI, UART/USART
Peripherals
Brown-out Detect/Reset, POR, PWM, WDT
Number Of I /o
53
Program Memory Size
64KB (32K x 16)
Program Memory Type
FLASH
Eeprom Size
2K x 8
Ram Size
4K x 8
Voltage - Supply (vcc/vdd)
4.5 V ~ 5.5 V
Data Converters
A/D 8x10b
Oscillator Type
Internal
Operating Temperature
-40°C ~ 85°C
Package / Case
64-MLF®, 64-QFN
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Lead free / RoHS Compliant
- Current page: 248 of 392
- Download datasheet (8Mb)
JTAG Interface
and On-chip
Debug System
Features
Overview
TAP – Test Access
Port
2490Q–AVR–06/10
•
•
•
•
•
•
The AVR IEEE std. 1149.1 compliant JTAG interface can be used for:
•
•
•
A brief description is given in the following sections. Detailed descriptions for Programming via
the JTAG interface, and using the Boundary-scan chain can be found in the sections
ming Via the JTAG Interface” on page 311
254, respectively. The On-chip Debug support is considered being private JTAG instructions,
and distributed within ATMEL and to selected third party vendors only.
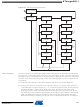
Figure 123
TAP Controller is a state machine controlled by the TCK and TMS signals. The TAP Controller
selects either the JTAG Instruction Register or one of several data registers as the scan chain
(Shift Register) between the TDI – input and TDO – output. The Instruction Register holds JTAG
instructions controlling the behavior of a data register.
The ID-Register, Bypass Register, and the Boundary-scan Chain are the data registers used for
board-level testing. The JTAG Programming Interface (actually consisting of several physical
and virtual data registers) is used for serial programming via the JTAG interface. The Internal
Scan Chain and Break Point Scan Chain are used for On-chip debugging only.
The JTAG interface is accessed through four of the AVR’s pins. In JTAG terminology, these pins
constitute the Test Access Port – TAP. These pins are:
•
•
•
•
JTAG (IEEE std. 1149.1 Compliant) Interface
Boundary-scan Capabilities According to the IEEE std. 1149.1 (JTAG) Standard
Debugger Access to:
Extensive On-chip Debug Support for Break Conditions, Including
Programming of Flash, EEPROM, Fuses, and Lock Bits through the JTAG Interface
On-chip Debugging Supported by AVR Studio
– All Internal Peripheral Units
– Internal and External RAM
– The Internal Register File
– Program Counter
– EEPROM and Flash Memories
– AVR Break Instruction
– Break on Change of Program Memory Flow
– Single Step Break
– Program Memory Break Points on Single Address or Address Range
– Data Memory Break Points on Single Address or Address Range
Testing PCBs by using the JTAG Boundary-scan capability.
Programming the non-volatile memories, Fuses and Lock bits.
On-chip debugging.
TMS: Test mode select. This pin is used for navigating through the TAP-controller state
machine.
TCK: Test clock. JTAG operation is synchronous to TCK.
TDI: Test Data In. Serial input data to be shifted in to the Instruction Register or Data
Register (Scan Chains).
TDO: Test Data Out. Serial output data from Instruction Register or Data Register.
shows a block diagram of the JTAG interface and the On-chip Debug system. The
and
®
“IEEE 1149.1 (JTAG) Boundary-scan” on page
ATmega64(L)
“Program-
248
Related parts for ATMEGA64-16MJ
Image
Part Number
Description
Manufacturer
Datasheet
Request
R

Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Atmel Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
ATMEL Corporation
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
IC AVR MCU 64K 16MHZ 5V 64TQFP
Manufacturer:
Atmel
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
IC AVR MCU 64K 16MHZ 5V 64-QFN
Manufacturer:
Atmel
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
IC AVR MCU 64K 16MHZ COM 64-TQFP
Manufacturer:
Atmel
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
IC AVR MCU 64K 16MHZ IND 64-TQFP
Manufacturer:
Atmel
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
IC AVR MCU 64K 16MHZ COM 64-QFN
Manufacturer:
Atmel
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
MCU AVR 64KB FLASH 16MHZ 64TQFP
Manufacturer:
Atmel
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
MCU AVR 64KB FLASH 16MHZ 64QFN
Manufacturer:
Atmel
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
IC AVR MCU 64K 16MHZ IND 64-QFN
Manufacturer:
Atmel
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
IC MCU AVR 64K 5V 16MHZ 64-TQFP
Manufacturer:
Atmel
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
MCU 8-Bit ATmega AVR RISC 64KB Flash 5V 64-Pin TQFP T/R
Manufacturer:
Atmel
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
DEV KIT FOR AVR/AVR32
Manufacturer:
Atmel
Datasheet: