LMP8100AEVAL National Semiconductor, LMP8100AEVAL Datasheet
LMP8100AEVAL
Specifications of LMP8100AEVAL
Related parts for LMP8100AEVAL
LMP8100AEVAL Summary of contents
Page 1
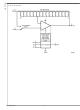
... The LMP8100 comes in a 14-Pin SOIC package. Simplified Block Diagram LMP ® registered trademark of National Semiconductor Corporation. © 2008 National Semiconductor Corporation Features Typical Values, T ■ Gain error (over temperature range) — ...
Page 2
Block Diagram www.national.com 2 20147602 ...
Page 3
... Absolute Maximum Ratings If Military/Aerospace specified devices are required, please contact the National Semiconductor Sales Office/ Distributors for availability and specifications. ESD Tolerance (Note 2) Human Body Model Machine Model V Differential IN Output Short Circuit Duration (Note 3) Supply Voltage ( – V − Voltage at Input and Output Pins ...
Page 4
Symbol Parameter I Supply Current, Power Down PD Feedback Resistance R Input Impedance IN 3.3V Electrical Characteristics Unless otherwise specified, all limits are guaranteed for kΩ /2; Gain = 1 V/V. Boldface limits ...
Page 5
Electrical Characteristics (Serial Interface) Unless otherwise specified, all limits guaranteed for T Symbol Parameter V Logic Low Threshold IL V Logic High Threshold IH I Output Source Current, SDO SDO Output Sink Current, SDO I Output Tri-state Leakage Current, OZ ...
Page 6
Connection Diagram Ordering Information Package Part Number LMP8100AMA LMP8100AMAX 14-Pin SOIC LMP8100MA LMP8100MAX www.national.com 14-Pin SOIC 20147601 Top View Package Marking Transport Media 55 Units/Rail LMP8100AMA 2.5k units Tape and Reel 55 Units/Rail LMP8100MA 2.5k units Tape and Reel 6 ...
Page 7
Timing Diagram Test Circuit Timing Diagram 20147653 7 20147603 www.national.com ...
Page 8
Test Circuit Diagram www.national.com Test Circuit 8 20147609 ...
Page 9
Typical Performance Characteristics Offset Voltage Distribution TCV Distribution Offset Voltage Distribution 20147685 TCV 20147683 20147666 9 20147686 Distribution OS 20147684 V vs 20147667 www.national.com ...
Page 10
www.national.com S 20147665 20147662 S 20147660 20147664 I vs 20147663 I vs 20147661 ...
Page 11
DC Gain Error Gain Error Small Signal Gain Error vs. +IN DC Level DC Gain Error 20147689 DC Gain Error 20147690 Small Signal Gain Error vs. +IN ...
Page 12
PSRR vs. Frequency I vs. V (Source) OUT OUT I vs. V (Source) OUT OUT www.national.com PSRR vs. Frequency 20147610 I OUT 20147669 I OUT 20147671 12 20147611 vs. V (Sink) OUT 20147668 vs. V (Sink) OUT 20147670 ...
Page 13
Small Signal Step Response 20147635 Small Signal Step Response 20147637 Small Signal Step Response 20147639 Small Signal Step Response Small Signal Step Response Small Signal Step Response 13 20147636 20147638 20147640 www.national.com ...
Page 14
Small Signal Step Response Large Signal Step Response Large Signal Step Response www.national.com Small Signal Step Response 20147641 Large Signal Step Response 20147643 Large Signal Step Response 20147645 14 20147642 20147644 20147646 ...
Page 15
Large Signal Step Response 20147647 Large Signal Step Response 20147649 THD+N vs. Frequency 20147675 Large Signal Step Response Large Signal Step Response THD+N vs. Frequency 15 20147648 20147650 20147674 www.national.com ...
Page 16
THD+N vs. V Bandwidth vs. Capacitive Load Peaking vs. Capacitive Load www.national.com OUT 20147673 20147617 20147621 16 THD+N vs. V OUT 20147672 Bandwidth vs. Capacitive Load 20147618 Peaking vs. Capacitive Load 20147622 ...
Page 17
Peaking vs. Capacitive Load 20147623 Gain vs. Frequency 20147629 Gain vs. Frequency 20147627 Gain vs. Frequency Gain vs. Frequency AC Gain Error vs. Frequency 17 20147630 20147628 20147656 www.national.com ...
Page 18
AC Gain Error vs. Frequency AC Gain Error vs. Frequency Noise vs. Frequency www.national.com AC Gain Error vs. Frequency 20147655 AC Gain Error vs. Frequency 20147658 0 Noise 20147654 18 20147657 20147659 201476a2 ...
Page 19
Closed Loop Output Impedance vs. Frequency SDO V vs. I Input Impedance 20147631 20147634 19 201476a1 SDO V vs. I 20147652 www.national.com ...
Page 20
Applications Information LIFETIME DRIFT Offset voltage (V ) and gain are electrical parameters which OS may drift over time. This drift, known as lifetime drift, is very common in operational amplifiers; however, its effect is more evident in precision amplifiers. ...
Page 21
FIGURE 5. THBT V Drift OS 20147696 FIGURE 6. THBT V Drift OS 20147697 FIGURE 7. THBT Gain Drift FIGURE 8. THBT Gain Drift POWER-ON RESET The LMP8100 has a power-up reset feature ...
Page 22
TABLE 2. Input Zero, Power-Down and Gain Setting Codes Zero ...
Page 23
GRT PINS The GRT pins must have a low impedance connection to ei- ther ground or a reference voltage. Any parasitical impedance on these pins will affect the gain accuracy of the LMP8100. Figure 10 shows a simplified schematic of ...
Page 24
SERIAL CONTROL INTERFACE OPERATION The LMP8100 gain, bandwidth compensation, power down, and input zeroing are controlled by data stored in a program- ming register. Data to be written into the control register is first loaded into the LMP8100 via the ...
Page 25
The serial control pins can be connected in one of two ways when two or more LMP8100s are used in an application. Star Configuration This configuration can be used if each LMP8100 will always have the same value in each ...
Page 26
POWER SUPPLY PURITY AND BYPASSING Particular attention to power supply purity is needed in order to preserve the LMP8100's gain accuracy and low noise. The LMP8100 worst-case PSRR 56.2 µV/V. Never- theless, the usable dynamic range, ...
Page 27
BRIDGE AMPLIFIER In Figure 17 two LMP8100s are used with a LMP7711 to build an amplifier for the signal from a GMR Magnetic Field Sensor. The advantage of using the LMP8100 is that as the signal strength from the Magnetic ...
Page 28
Physical Dimensions www.national.com inches (millimeters) unless otherwise noted 14-Pin SOIC NS Package Number M14A 28 ...
Page 29
Notes 29 www.national.com ...
Page 30
... For more National Semiconductor product information and proven design tools, visit the following Web sites at: Products Amplifiers www.national.com/amplifiers Audio www.national.com/audio Clock Conditioners www.national.com/timing Data Converters www.national.com/adc Displays www.national.com/displays Ethernet www.national.com/ethernet Interface www.national.com/interface LVDS www.national.com/lvds Power Management www.national.com/power Switching Regulators www.national.com/switchers LDOs www ...