ST92150CV1Q-Auto STMicroelectronics, ST92150CV1Q-Auto Datasheet - Page 339

ST92150CV1Q-Auto
Manufacturer Part Number
ST92150CV1Q-Auto
Description
8-bit MCU for automotive
Manufacturer
STMicroelectronics
Datasheet
1.ST92150JDV1QAUTO.pdf
(430 pages)
Specifications of ST92150CV1Q-Auto
Internal Memory
Single Voltage FLASH up to 256 Kbytes, RAM up to 8Kbytes, 1K byte E3 TM (Emulated EEPROM)
Minimum Instruction Time
83 ns (24 MHz int. clock)
- Current page: 339 of 430
- Download datasheet (7Mb)
CONTROLLER AREA NETWORK (Cont’d)
10.10.5.7 Bit Timing
The bit timing logic monitors the serial bus-line and
performs sampling and adjustment of the sample
point by synchronizing on the start-bit edge and re-
synchronizing on the following edges.
Its operation may be explained simply by splitting
nominal bit time into three segments as follows:
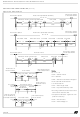
– Synchronization segment (SYNC_SEG): a bit
– Bit segment 1 (BS1): defines the location of the
– Bit segment 2 (BS2): defines the location of the
Figure 152. Bit Timing
change is expected to occur within this time seg-
ment. It has a fixed length of one time quantum
(1 x t
sample point. It includes the PROP_SEG and
PHASE_SEG1 of the CAN standard. Its duration
is programmable between 1 and 16 time quanta
but may be automatically lengthened to compen-
sate for positive phase drifts due to differences in
the frequency of the various nodes of the net-
work.
transmit point. It represents the PHASE_SEG2
of the CAN standard. Its duration is programma-
ble between 1 and 8 time quanta but may also be
automatically shortened to compensate for neg-
ative phase drifts.
B
NominalBitTime
with:
t
t
t
t
BRP = BRP[5:0] + 1 = Baud Rate Prescaler
BRP[5:0] is defined in the CBTR0 Register,
TS1[3:0] and TS2[2:0] are defined in the CBTR1 Register.
CAN
BS1
BS2
CAN
CPU
audRate
SYNC_SEG
= t
= t
).
= t
= time period of the CPU clock,
1 x t
CAN
CAN
CPU
CAN
x (TS1[3:0] + 1) ,
x (TS2[2:0] + 1),
x BRP,
=
------------------------------------------------ -
NominalBitTime
=
1
1
×
BIT SEGMENT 1 (BS1)
t
CAN
+
t
BS1
t
BS1
NOMINAL BIT TIME
+
ST92124xxx-Auto/150xxxxx-Auto/250xxxx-Auto
t
BS2
The resynchronization jump width (RJW) defines
an upper bound to the amount of lengthening or
shortening of the bit segments. It is programmable
between 1 and 4 time quanta.
A valid edge is defined as the first transition in a bit
time from dominant to recessive bus level provid-
ed the controller itself does not send a recessive
bit.
If a valid edge is detected in BS1 instead of
SYNC_SEG, BS1 is extended by up to RJW so
that the sample point is delayed.
Conversely, if a valid edge is detected in BS2 in-
stead of SYNC_SEG, BS2 is shortened by up to
RJW so that the transmit point is moved earlier.
As a safeguard against programming errors, the
configuration of the Bit Timing Register (BTR) is
only possible while the device is in STANDBY
mode.
Note: for a detailed description of the CAN bit tim-
ing and resynchronization mechanism, please re-
fer to the ISO 11898 standard.
SAMPLE POINT
BIT SEGMENT 2 (BS2)
t
BS2
TRANSMIT POINT
339/430
9
Related parts for ST92150CV1Q-Auto
Image
Part Number
Description
Manufacturer
Datasheet
Request
R

Part Number:
Description:
8/16-BIT SINGLE VOLTAGE FLASH MCU FAMILY WITH RAM / E3 TMEMULATED EEPROM / CAN 2.0B AND J1850 BLPD
Manufacturer:
ST Microelectronics
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
STMicroelectronics [RIPPLE-CARRY BINARY COUNTER/DIVIDERS]
Manufacturer:
STMicroelectronics
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
STMicroelectronics [LIQUID-CRYSTAL DISPLAY DRIVERS]
Manufacturer:
STMicroelectronics
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
BOARD EVAL FOR MEMS SENSORS
Manufacturer:
STMicroelectronics
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
NPN TRANSISTOR POWER MODULE
Manufacturer:
STMicroelectronics
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
TURBOSWITCH ULTRA-FAST HIGH VOLTAGE DIODE
Manufacturer:
STMicroelectronics
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
STMicroelectronics
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
DIODE / SCR MODULE
Manufacturer:
STMicroelectronics
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
DIODE / SCR MODULE
Manufacturer:
STMicroelectronics
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Search -----> STE16N100
Manufacturer:
STMicroelectronics
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Search ---> STE53NA50
Manufacturer:
STMicroelectronics
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
NPN Transistor Power Module
Manufacturer:
STMicroelectronics
Datasheet: