PIC16LF1827-I/P Microchip Technology, PIC16LF1827-I/P Datasheet - Page 254

PIC16LF1827-I/P
Manufacturer Part Number
PIC16LF1827-I/P
Description
IC, 8BIT MCU, PIC16LF, 32MHZ, DIP-18
Manufacturer
Microchip Technology
Series
PIC® XLP™ 16Fr
Specifications of PIC16LF1827-I/P
Controller Family/series
PIC16LF
Eeprom Memory Size
256Byte
Ram Memory Size
384Byte
Cpu Speed
32MHz
No. Of Timers
5
Interface
EUSART, I2C, SPI
Core Size
8 Bit
Program Memory Size
4kWords
Core Processor
PIC
Speed
32MHz
Connectivity
I²C, SPI, UART/USART
Peripherals
Brown-out Detect/Reset, POR, PWM, WDT
Number Of I /o
16
Program Memory Type
FLASH
Eeprom Size
256 x 8
Ram Size
384 x 8
Voltage - Supply (vcc/vdd)
1.8 V ~ 3.6 V
Data Converters
A/D 12x10b
Oscillator Type
Internal
Operating Temperature
-40°C ~ 85°C
Package / Case
18-DIP (0.300", 7.62mm)
Processor Series
PIC16LF
Core
PIC
Data Bus Width
8 bit
Data Ram Size
256 B
Interface Type
I2C, SPI, UART
Maximum Clock Frequency
32 KHz
Number Of Programmable I/os
16
Number Of Timers
5
Operating Supply Voltage
1.8 V to 3.6 V
Maximum Operating Temperature
+ 125 C
Mounting Style
Through Hole
3rd Party Development Tools
52715-96, 52716-328, 52717-734
Development Tools By Supplier
PG164130, DV164035, DV244005, DV164005
Minimum Operating Temperature
- 40 C
On-chip Adc
10 bit, 12 Channel
On-chip Dac
5 bit
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Lead free / RoHS Compliant
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Lead free / RoHS Compliant, Lead free / RoHS Compliant
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Part Number:
PIC16LF1827-I/P
Manufacturer:
MICROCHIP/微芯
Quantity:
20 000
- Current page: 254 of 406
- Download datasheet (4Mb)
PIC16F/LF1826/27
24.5.3
When the R/W bit of the incoming address byte is set
and an address match occurs, the R/W bit of the
SSPxSTAT register is set. The received address is
loaded into the SSPxBUF register, and an ACK pulse is
sent by the slave on the ninth bit.
Following the ACK, slave hardware clears the CKP bit
and the SCLx pin is held low (see Section 24.5.6
“Clock Stretching” for more detail). By stretching the
clock, the master will be unable to assert another clock
pulse until the slave is done preparing the transmit
data.
The transmit data must be loaded into the SSPxBUF
register which also loads the SSPxSR register. Then
the SCLx pin should be released by setting the CKP bit
of the SSPxCON1 register. The eight data bits are
shifted out on the falling edge of the SCLx input. This
ensures that the SDAx signal is valid during the SCLx
high time.
The ACK pulse from the master-receiver is latched on
the rising edge of the ninth SCLx input pulse. This ACK
value is copied to the ACKSTAT bit of the SSPxCON2
register. If ACKSTAT is set (not ACK), then the data
transfer is complete. In this case, when the not ACK is
latched by the slave, the slave goes idle and waits for
another occurrence of the Start bit. If the SDAx line was
low (ACK), the next transmit data must be loaded into
the SSPxBUF register. Again, the SCLx pin must be
released by setting bit CKP.
An MSSPx interrupt is generated for each data transfer
byte. The SSPxIF bit must be cleared by software and
the SSPxSTAT register is used to determine the status
of the byte. The SSPxIF bit is set on the falling edge of
the ninth clock pulse.
24.5.3.1
A slave receives a Read request and begins shifting
data out on the SDAx line. If a bus collision is detected
and the SBCDE bit of the SSPxCON3 register is set,
the BCLxIF bit of the PIRx register is set. Once a bus
collision is detected, the slave goes Idle and waits to be
addressed again. User software can use the BCLxIF bit
to handle a slave bus collision.
DS41391C-page 254
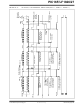
SLAVE TRANSMISSION
Slave Mode Bus Collision
Preliminary
24.5.3.2
A master device can transmit a read request to a
slave, and then clock data out of the slave. The list
below outlines what software for a slave will need to
do
Figure 24-17 can be used as a reference to this list.
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10. SSPxIF is set after the ACK response from the
11. SSPxIF bit is cleared.
12. The slave software checks the ACKSTAT bit to
13. Steps 9-13 are repeated for each transmitted
14. If the master sends a not ACK; the clock is not
15. The master sends a Restart condition or a Stop.
16. The slave is no longer addressed.
Note 1: If the master ACKs the clock will be
Master sends a Start condition on SDAx and
SCLx.
S bit of SSPxSTAT is set; SSPxIF is set if inter-
rupt on Start detect is enabled.
Matching address with R/W bit set is received by
the Slave setting SSPxIF bit.
Slave hardware generates an ACK and sets
SSPxIF.
SSPxIF bit is cleared by user.
Software reads the received address from
SSPxBUF, clearing BF.
R/W is set so CKP was automatically cleared
after the ACK.
The slave software loads the transmit data into
SSPxBUF.
CKP bit is set releasing SCLx, allowing the mas-
ter to clock the data out of the slave.
master is loaded into the ACKSTAT register.
see if the master wants to clock out more data.
byte.
held, but SSPxIF is still set.
to
2: ACKSTAT is the only bit updated on the
accomplish
stretched.
rising edge of SCLx (9th) rather than the
falling.
7-bit Transmission
2010 Microchip Technology Inc.
a
standard
transmission.
Related parts for PIC16LF1827-I/P
Image
Part Number
Description
Manufacturer
Datasheet
Request
R

Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology Inc.
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology Inc.
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology Inc.
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology Inc.
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology Inc.
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology Inc.
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology Inc.
Datasheet:

Part Number:
Description:
Manufacturer:
Microchip Technology Inc.
Datasheet: