AD779KD Analog Devices Inc, AD779KD Datasheet - Page 11
AD779KD
Manufacturer Part Number
AD779KD
Description
IC, ADC, 14BIT, 128KSPS, DIP-28
Manufacturer
Analog Devices Inc
Datasheet
1.AD779JNZ.pdf
(12 pages)
Specifications of AD779KD
Resolution (bits)
14bit
Sampling Rate
128kSPS
Input Channel Type
Single Ended
Data Interface
Parallel
Supply Current
25mA
Digital Ic Case Style
DIP
No. Of Pins
28
Rohs Status
RoHS non-compliant
Number Of Bits
14
Sampling Rate (per Second)
128k
Number Of Converters
1
Power Dissipation (max)
745mw
Voltage Supply Source
Dual ±
Operating Temperature
0°C ~ 70°C
Mounting Type
Through Hole
Package / Case
28-CDIP (0.600", 15.24mm)
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Contains lead / RoHS non-compliant
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
AD779 TO 80186
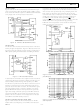
Figure 10 shows the AD779 interfaced to the 80186 micropro-
cessor. This interface allows the 80186’s built-in DMA control-
ler to transfer the AD779 output into a RAM based FIFO buffer
of any length, with no microprocessor intervention.
AD779 TO Z80
The AD779 can be interfaced to the Z80 processor in an I/O or
memory mapped configuration. Figure 11 illustrates an I/O con-
figuration, where the AD779 occupies several port addresses to
allow separate polling of the EOC status and reading of the data.
A useful feature of the Z80 is that a single wait state is automati-
cally inserted during I/O operations, allowing the AD779 to be
used with Z80 processors having clock speeds up to 8 MHz.
The AD779 is asynchronous which allows conversions to be ini-
tiated by an external trigger source independent of the micro-
processor clock. After each conversion, the AD779 EOC signal
generates a DMA request to Channel 1 (DRQ1). The subse-
quent DMA READ resets the interrupt latch. The system de-
signer must assign a sufficient priority to the DMA channel to
ensure that the DMA request will be serviced before the com-
pletion of the next conversion. This configuration can be used
with 6 MHz and 8 MHz 80186 processors.
AD779 TO ANALOG DEVICES ADSP-2100A
Figure 12 demonstrates the AD779 interfaced to an ADSP-
2100A. With a clock frequency of 12.5 MHz, and instruction
REV. B
Figure 10. AD779 to 80186 DMA Interface
Figure 11. AD779 to Z80 Interface
–11–
execution in one 80 ns cycle, the digital signal processor will
support the AD779 data memory interface with two wait states.
The converter runs asychronously using a sampling clock. The
EOC output to the AD779 gets asserted at the end of each
conversion and causes an interrupt. Upon interrupt, the ADSP-
2100A starts a data memory read by providing an address on
the DMA bus. The decoded address generates OE for the
converter. OE, together with logic and latch, is used to force the
ADSP-2100A into a one cycle wait state by generating
DMACK. The read operation is thus started and completed
within two processor cycles (160 ns).
Figure 13. Harmonic Distortion vs. Input Frequency
(0.5 dB Input)
Figure 14. Total Harmonic Distortion vs. Input Frequency
and Amplitude
Figure 12. AD779 to ADSP-2100A Interface
AD779