SAF-C505CA-4EM Infineon Technologies AG, SAF-C505CA-4EM Datasheet

SAF-C505CA-4EM
Available stocks
Related parts for SAF-C505CA-4EM
SAF-C505CA-4EM Summary of contents
Page 1
Microcomputer Components 8-Bit CMOS Microcontroller C505 C505C/C505A C505CA Data Sheet 12.97 ...
Page 2
... A critical component is a component used in a life-support device or system whose failure can reasonably be expected to cause the failure of that life-support device or system affect its safety or effectiveness of that device or system. 2 Life support devices or systems are intended ( implanted in the human body, or (b) to support and/or maintain and sustain hu- man life ...
Page 3
CMOS Microcontroller Advance Information • Fully compatible to standard 8051 microcontroller • Superset of the 8051 architecture with 8 datapointers • MHz operating frequency – 375 ns instruction cycle time @16 MHz – 300 ns instruction ...
Page 4
... Idle mode (can be combined with slow-down mode) – Software power-down mode with wake up capability through P3.2/INT0 or P4.1/RXDC pin • P-MQFP-44 package • Pin configuration is compatible to C501, C504, C511/C513-family • Temperature ranges: SAB-C505 versions SAF-C505 versions SAH-C505 versions SAK-C505 versions Table 1 Differences in Functionality of the C505 MCUs Device ...
Page 5
... SAB-C505C-LM Q67127-C2029 SAF-C505C-2RM Q67127-DXXXX SAF-C505C-LM Q67127-C2030 SAB-C505A-4EM Q67127-C2060 SAF-C505A-4EM Q67127-C2061 SAB-C505CA-4EM Q67127-C1082 SAB-C505CA-4EM Q67127-C2058 Note: The ordering number of the ROM types (DXXXX extension) is defined after program release (verification) of the customer. Versions for the extended temperature range – 110 C (SAH-C505) and – 125 C (SAK-C505) are available on request ...
Page 6
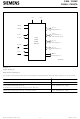
V AREF V AGND XTAL1 XTAL2 RESET EA ALE PSEN Figure 2 Logic Symbol Additional Literature For further information about the C505/C505C/C505A/C505CA the following literature is available: Title C505 8-Bit CMOS Microcontroller User’s Manual C500 Microcontroller Family Architecture and Instruction ...
Page 7
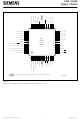
P0.3 / AD3 P0.2 / AD2 P0.1 / AD1 P0.0 / AD0 V AREF V AGND P1.0 / AN0 / INT3 / CC0 P1.1 / AN1 / INT4 / CC1 P1.2 / AN2 / INT5 / CC2 P1.3 / AN3 ...
Page 8
Table 3 Pin Definitions and Functions Symbol Pin Number P1.0-P1.7 40-44,1 Input O = Output Semiconductor Group I/O Function *) I/O Port 8-bit quasi-bidirectional port with ...
Page 9
Table 3 Pin Definitions and Functions (cont’d) Symbol Pin Number RESET 4 P3.0-P3 Input O = Output Semiconductor Group I/O Function *) I RESET A high level ...
Page 10
Table 3 Pin Definitions and Functions (cont’d) Symbol Pin Number P4.0 6 P4.1 28 XTAL2 14 XTAL1 Input O = Output Semiconductor Group I/O Function *) I/O Port 4 I 2-bit quasi-bidirectional port with ...
Page 11
Table 3 Pin Definitions and Functions (cont’d) Symbol Pin Number P2.0-P2.7 18-25 PSEN 26 ALE Input O = Output Semiconductor Group I/O Function *) I/O Port 8-bit quasi-bidirectional I/O port with internal ...
Page 12
Table 3 Pin Definitions and Functions (cont’d) Symbol Pin Number EA 29 P0.0-P0.7 37- AREF V 39 AGND Input O = Output Semiconductor Group I/O Function *) I External ...
Page 13
V CC Oscillator Watchdog V SS XTAL1 OSC & Timing XTAL2 RESET CPU 8 Datapointers ALE PSEN Programmable Watchdog Timer EA Timer 0 Timer 1 Timer 2 USART Baudrate Generator Full-CAN Controller Interrupt Unit Converter AREF ...
Page 14
CPU The C505 is efficient both as a controller and as an arithmetic processor. It has extensive facilities for binary and BCD arithmetic and excels in its bit-handling capabilities. Efficient use of program memory results from an instruction set consisting ...
Page 15
Memory Organization The C505 CPU manipulates operands in the following four address spaces: – On-chip program memory : – Totally Kbyte internal/external program memory – Kbyte of external data memory – 256 bytes of ...
Page 16
Reset and System Clock The reset input is an active high input at pin RESET. Since the reset is synchronized internally, the RESET pin must be held high for at least two machine cycles (12 oscillator periods) while the oscillator ...
Page 17
Figure 7 shows the recommended oscillator circuits for crystal and external clock operation. External Clock Signal Figure 7 Recommended Oscillator Circuitries Semiconductor Group C XTAL2 MHz C505CA C XTAL1 for crystal ...
Page 18
Multiple Datapointers As a functional enhancement to the standard 8051 architecture, the C505 contains eight 16-bit datapointers instead of only one datapointer. The instruction set uses just one of these datapointers at a time. The selection of the actual datapointer ...
Page 19
Enhanced Hooks Emulation Concept The Enhanced Hooks Emulation Concept of the C500 microcontroller family is a new, innovative way to control the execution of C500 MCUs and to gain extensive information on the internal operation of the controllers. Emulation of ...
Page 20
Special Function Registers The registers, except the program counter and the four general purpose register banks, reside in the special function register area. The special function register area consists of two portions : the standard special function register area and ...
Page 21
Table 4 Special Function Registers - Functional Blocks Block Symbol Name CPU ACC Accumulator B B-Register DPH Data Pointer, High Byte DPL Data Pointer, Low Byte DPSEL Data Pointer Select Register PSW Program Status Word Register SP Stack Pointer SYSCON ...
Page 22
Table 4 Special Function Registers - Functional Blocks (cont’d) Block Symbol Name Ports P0 Port 0 P1 Port 1 P1ANA 2) 4) Port 1 Analog Input Selection Register P2 Port 2 P3 Port 3 P4 Port 4 Serial ADCON0 2) ...
Page 23
Table 4 Special Function Registers - Functional Blocks (cont’d) Block Symbol Name CAN CR Control Register Controller SR Status Register IR Interrupt Register (C505C/ BTR0 Bit Timing Register Low C505CA BTR1 Bit Timing Register High only) GMS0 Global Mask Short ...
Page 24
Table 5 Contents of the SFRs, SFRs in numeric order of their addresses Addr Register Content after 1) Reset DPL DPH 00 H ...
Page 25
Table 5 Contents of the SFRs, SFRs in numeric order of their addresses (cont’d) Addr Register Content after 1) Reset SYSCON XX10- 4) 0X01 SYSCON XX10- 4) 0001 B ...
Page 26
Table 5 Contents of the SFRs, SFRs in numeric order of their addresses (cont’d) Addr Register Content after 1) Reset D9 H ADDATH ADST 6) XXXX- XXXX ADDATL 00XX- 7) XXXX B ...
Page 27
Table 6 Contents of the CAN Registers in numeric order of their addresses (C505C/C505CA only) Addr. Register Content n=1-F H after 2) 1) Reset F700 F701 F702 F704 ...
Page 28
Table 6 Contents of the CAN Registers in numeric order of their addresses (cont’d) (C505C/C505CA only) Addr. Register Content n=1-F H after 2) 1) Reset F7n7 H DB0n XX H F7n8 H DB1n XX H F7n9 H DB2n XX H ...
Page 29
I/O Ports The C505 has four 8-bit I/O ports and one 2-bit I/O port. Port open-drain bidirectional I/O port, while ports are quasi-bidirectional I/O ports with internal pullup resistors. That means, when configured as ...
Page 30
Timer / Counter 0 and 1 Timer/Counter 0 and 1 can be used in four operating modes as listed in table 7 : Table 7 Timer/Counter 0 and 1 Operating Modes Mode Description 0 8-bit timer/counter with a divide-by-32 prescaler ...
Page 31
Timer/Counter 2 with Compare/Capture/Reload The timer 2 of the C505 provides additional compare/capture/reload features. which allow the selection of the following operating modes: – Compare : PWM signals with 16-bit/300 ns resolution (@ 20 MHz clock) – ...
Page 32
Timer 2 Operating Modes The timer 2, which is a 16-bit-wide register, can operate as timer, event counter, or gated timer. A roll-over of the count value in TL2/TH2 from all 1’s to all 0’s sets the timer overflow flag ...
Page 33
Timer 2 Compare Modes The compare function of a timer/register combination operates as follows : the 16-bit value stored in a compare or compare/capture register is compared with the contents of the timer register; if the count value in the ...
Page 34
Compare Mode 1 If compare mode 1 is enabled and the software writes to the appropriate output latch at the port, the new value will not appear at the output pin until the next compare match occurs. Thus, it can ...
Page 35
Serial Interface (USART) The serial port is full duplex and can operate in four modes (one synchronous mode, three asynchronous modes) as illustrated in table 8. Table 8 USART Operating Modes SCON Mode SM0 SM1 ...
Page 36
Timer 1 Overflow Baud Rate Generator f OSC (SRELH SRELL) ÷ 6 Note: The switch configuration shows the reset state. Figure 14 Block Diagram of Baud Rate Generation for the Serial Interface Table 9 below lists the values/formulas for the ...
Page 37
CAN Controller (C505C and C505CA only) The on-chip CAN controller, compliant to version 2.0B, is the functional heart which provides all resources that are required to run the standard CAN protocol (11-bit identifiers) as well as the extended CAN protocol ...
Page 38
The TX/RX Shift Register holds the destuffed bit stream from the bus line to allow the parallel access to the whole data or remote frame for the acceptance match test and the parallel transfer of the frame to and from ...
Page 39
CAN Controller Software Initialization The very first step of the initialization is the CAN controller input clock selection. A divide-by-2 prescaler is enabled by default after reset (figure 16). Setting bit CMOD (SYSCON.3) disables the prescaler. The purpose of the ...
Page 40
A/D Converter (C505 and C505C only) The C505/C505C includes a high performance / high speed 8-bit A/D converter (ADC) with 8 analog input channels. It operates with a successive approximation technique and provides the following features: – 8 multiplexed ...
Page 41
IEN1 ( EXEN2 SWDT IRCON ( EXF2 TF2 P1ANA ( EAN7 EAN6 ADCON1 ( ADCL1 ADCL0 ADCON0 ( CLK Port 1 MUX Conversion f OSC Clock Prescaler V AREF ...
Page 42
A/D Converter (C505A and C505CA only) The C505 includes a high performance / high speed 10-bit A/D-Converter (ADC) with 8 analog input channels. It operates with a successive approximation technique and uses self calibration mechanisms for reduction and compensation ...
Page 43
IEN1 ( EXEN2 SWDT IRCON ( EXF2 TF2 P1ANA ( EAN7 EAN6 ADCON1 ( ADCL1 ADCL0 ADCON0 ( CLK Port 1 MUX Conversion f OSC Clock Prescaler V AREF ...
Page 44
Interrupt System The C505 provides 12 interrupt vectors with four priority levels. Five interrupt requests can be generated by the on-chip peripherals (timer 0, timer 1, timer 2, serial interface, A/D converter). One interrupt can be generated by the CAN ...
Page 45
P3.2 / INT0 IT0 TCON Converter Timer 0 Overflow SWI IRCON.1 Status SIE CR.2 >1 Error EIE CR.3 Message Transmit >1 TXIE MCR0 Message Receive RXIE MCR0 Bit addressable Request flag is cleared ...
Page 46
P3.3 / INT1 IT1 TCON.2 P1.0 / AN0 / INT3 / CC0 I3FR T2CON.6 Timer 1 Overflow P1.1 / AN1 / INT4 / CC1 Bit addressable Request flag is cleared by hardware Figure 22 Interrupt Structure, Overview Part 2 Semiconductor ...
Page 47
RI SCON.0 USART TI SCON.1 P1.2 / AN2 / INT5 / CC2 Timer 2 TF2 Overflow IRCON.6 P1.5 / AN5 / EXF2 T2EX IRCON.7 EXEN2 IEN1.7 P1.3 / INT6 / CC3 Bit addressable Request flag is cleared by hardware Figure ...
Page 48
... Fail Save Mechanisms The C505 offers enhanced fail safe mechanisms, which allow an automatic recovery from software upset or hardware failure : – a programmable watchdog timer (WDT), with variable time-out period from 192 approx. 412 MHz. – an oscillator watchdog (OWD) which monitors the on-chip oscillator and forces the microcontroller into reset state in case the on-chip oscillator fails ...
Page 49
Oscillator Watchdog The oscillator watchdog unit serves for three functions: – Monitoring of the on-chip oscillator's function The watchdog supervises the on-chip oscillator's frequency lower than the frequency of the auxiliary RC oscillator in the watchdog unit, ...
Page 50
EWPD WS (PCON1.7) (PCON1.4) P4.1 / RXDC Control P3.2 / INT0 Logic Start / Stop RC f Oscillator RC 3 MHz Start / XTAL1 Stop On-Chip XTAL2 Oscillator Figure 25 Functional Block Diagram of the Oscillator Watchdog Semiconductor Group Power ...
Page 51
Power Saving Modes The C505 provides two basic power saving modes, the idle mode and the power down mode. Additionally, a slow down mode is available. This power saving mode reduces the internal clock rate in normal operating mode and ...
Page 52
OTP Memory Operation (C505A and C505CA only) The C505A/C505CA contains a 32k byte one-time programmable (OTP) program memory. With the C505A/C505CA fast programming cycles are achieved (1 byte in 100 sec). Also several levels of OTP memory protection can be ...
Page 53
Pin Configuration in Programming Mode N.C. N.C. N.C. N.C. N.C. N.C. N.C. Figure 27 P-MQFP-44 Pin Configuration of the C505A/C505CA in Programming Mode (Top View) Semiconductor Group ...
Page 54
The following table 12 contains the functional description of all C505A/C505CA pins which are required for OTP memory programming. Table 12 Pin Definitions and Functions in Programming Mode Symbol Pin Number I/O RESET 4 PMSEL0 5 PMSEL1 7 PSEL 8 ...
Page 55
Table 12 Pin Definitions and Functions in Programming Mode (cont’d) Symbol Pin Number I/O P2.0-7 18-25 PSEN 26 PROG 27 EA D7-0 30-37 N.C. 1-3, 6, 11-13, 28, 38- Input O = Output Semiconductor Group ...
Page 56
Basic Programming Mode Selection The basic programming mode selection scheme is shown in figure 28 Clock (XTAL1 / XTAL2) RESET PSEN PMSEL1,0 PROG PRD PSEL PALE During this period signals are not actively driven ...
Page 57
Table 13 Access Modes Selection Access Mode Program OTP memory byte Read OTP memory byte Program OTP lock bits Read OTP lock bits Read OTP version byte Lock Bits Programming / Read The C505A/C505CA has two programmable lock bits which, ...
Page 58
Absolute Maximum Ratings Ambient temperature under bias ( Storage temperature ( T ) .......................................................................... – 150 C stg V Voltage on pins with respect to ground ( CC Voltage on any pin with respect to ground ( ...
Page 59
... Supply current at EA/ CC Notes see next but one page 61 Semiconductor Group for the SAB- versions – for the SAF- versions – 110 C for the SAH- versions – 125 C for the SAK- versions A Symbol Limit Values min ...
Page 60
Power Supply Currents Parameter C505 / Active Mode C505C Idle Mode Active Mode with slow-down enabled Idle Mode with slow-down enabled Power down current C505A Active Mode C505CA Idle Mode Active Mode with slow-down enabled Idle Mode with slow-down enabled ...
Page 61
Notes: 1) Capacitive loading on ports 0 and 2 may cause spurious noise pulses to be superimposed on the and port 3. The noise is due to external bus capacitance discharging into the port 0 and port 2 pins when ...
Page 62
CC max typ Figure 29 ICC Diagram of C505 and C505C C505/C505C: Power Supply Current Calculation Formulas Parameter Symbol Active mode I CC typ I CC max I Idle ...
Page 63
CC max typ Figure 30 ICC Diagram of C505A and C505CA C505A : Power Supply Current Calculation Formulas Parameter Symbol Active mode I CC typ I CC max I ...
Page 64
... Further timing conditions : t Semiconductor Group for the SAB- versions – for the SAF- versions – 110 C for the SAH- versions – 125 C for the SAK- versions A V – 0.2 V ...
Page 65
Notes may exeed V or AIN AGND these cases will During the sample time the input capacitance internal resistance of the analog source must allow the capacitance to reach their final voltage ...
Page 66
... Further timing conditions : t Semiconductor Group for the SAB- versions – for the SAF- versions – 110 C for the SAH- versions – 125 C for the SAK- versions A V – 0.2 V ...
Page 67
Notes may exeed V or AIN AGND these cases will be X000 or X3FF H 2) During the sample time the input capacitance internal resistance of the analog source must allow the capacitance to reach their final voltage ...
Page 68
... Interfacing the C505 to devices with float times permissible. This limited bus contention will not cause any damage to port 0 drivers. Semiconductor Group for the SAB- versions – for the SAF- versions – 110 C for the SAH- versions – 125 C for the SAK- versions A ...
Page 69
AC Characteristics (12 MHz, 0.5 Duty Cycle, cont’d) External Data Memory Characteristics Parameter RD pulse width WR pulse width Address hold after ALE RD to valid data in Data hold after RD Data float after RD ALE to valid data ...
Page 70
... Interfacing the C505 to devices with float times permissible. This limited bus contention will not cause any damage to port 0 drivers. Semiconductor Group for the SAB- versions for the SAF- versions A C for all other outputs = 80 pF) L Symbol 16-MHz clock Duty Cycle ...
Page 71
AC Characteristics (16 MHz, 0.4 to 0.6 Duty Cycle, cont’d) External Data Memory Characteristics Parameter RD pulse width WR pulse width Address hold after ALE RD to valid data in Data hold after RD Data float after RD ALE to ...
Page 72
AC Characteristics (16 MHz, 0.4 to 0.6 Duty Cycle, cont’d) External Clock Drive Characteristics Parameter Symbol Oscillator period CLP High time TCL Low time TCL t Rise time t Fall time Oscillator duty cycle DC Clock cycle TCL Note: The ...
Page 73
... Interfacing the C505 to devices with float times permissible. This limited bus contention will not cause any damage to port 0 drivers. Semiconductor Group for the SAB- versions – for the SAF- versions A C for all other outputs = 80 pF) L Symbol 20 MHz clock 0.5 Duty Cycle min ...
Page 74
AC Characteristics (20 MHz, 0.5 Duty Cycle, cont’d) External Data Memory Characteristics Parameter RD pulse width WR pulse width Address hold after ALE RD to valid data in Data hold after RD Data float after RD ALE to valid data ...
Page 75
ALE PSEN Port 0 Port 2 Figure 31 Program Memory Read Cycle Semiconductor Group t LHLL t t AVLL PLPH t LLPL t LLIV t PLIV t AZPL t LLAX Instr.IN t AVIV A8 - A15 75 ...
Page 76
ALE PSEN RD t AVLL from Port DPL t AVWL Port 2 Figure 32 Data Memory Read Cycle Semiconductor Group t LLDV t t LLWL RLRH t RLDV t LLAX2 t RLAZ Data IN ...
Page 77
ALE PSEN WR t AVLL from Port DPL t AVWL Port 2 Figure 33 Data Memory Write Cycle TCL XTAL1 Figure 34 External Clock Drive on XTAL1 Semiconductor Group t t LLWL WLWH t ...
Page 78
AC Characteristics of Programming Mode (C505A and C505CA only 11 Parameter ALE pulse width PMSEL setup to ALE rising edge Address setup to ALE, PROG, or PRD falling edge ...
Page 79
PAW PALE t PMS PMSEL1,0 t A8-A14 Port 2 Port 0 PROG Notes: PRD must be high during a programming write cycle. Figure 35 Programming Code Byte - Write Cycle Timing Semiconductor Group PAS PAH t ...
Page 80
PAW PALE t PMS PMSEL1,0 t Port 2 Port 0 PRD Notes: PROG must be high during a programming read cycle. Figure 36 Verify Code Byte - Read Cycle Timing Semiconductor Group PAS PAH A8-A14 t ...
Page 81
PMSEL1,0 Port 0 t PMS PROG PRD Note: PALE should be low during a lock bit read / write cycle. Figure 37 Lock Bit Access Timing PMSEL1,0 Port 2 Port 0 PRD Note: Figure 38 Version Byte Read Timing Semiconductor ...
Page 82
ROM/OTP Verification Characteristics for C505 ROM Verification Mode 1 (C505-2R and C505C-2R only) Parameter Address to valid data P1.0 - P1.7 P2.0 - P2.6 Port 0 Address: P1 Data: Figure 39 ROM Verification Mode ...
Page 83
ROM/OTP Verification Characteristics for C505 (cont’d) ROM/OTP Verification Mode 2 Parameter ALE pulse width ALE period Data valid after ALE Data stable after ALE P3.5 setup to ALE low Oscillator frequency ALE Port 0 P3.5 Figure 40 ROM/OTP Verification Mode ...
Page 84
Inputs during testing are driven at Timing measurements are made at Figure 41 AC Testing: Input, Output Waveforms V +0.1 V Load V Load -0 Load For timing purposes a port ...
Page 85
P-MQFP-44-1 (SMD) (Plastic Metric Quad Flat Package) Figure 44 P-MQFP-44 Package Outline Sorts of Packing Package outlines for tubes, trays etc. are contained in our Data Book “Package Information” SMD = Surface Mounted Device Semiconductor Group 85 C505 / C505C ...