HC5513 Intersil Corporation, HC5513 Datasheet - Page 10

HC5513
Manufacturer Part Number
HC5513
Description
TR909 DLC/FLC SLIC with Low Power Standby
Manufacturer
Intersil Corporation
Datasheet
1.HC5513.pdf
(18 pages)
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Company:
Part Number:
HC5513BIM
Manufacturer:
HARRIS
Quantity:
7
Company:
Part Number:
HC5513BIM
Manufacturer:
INTERSIL
Quantity:
1 570
Company:
Part Number:
HC5513BIM
Manufacturer:
NSC
Quantity:
1 572
Company:
Part Number:
HC5513BIP
Manufacturer:
SJEMENS
Quantity:
243
Part Number:
HC5513BIP
Manufacturer:
INTERSIL
Quantity:
20 000
Part Number:
HC5513IM
Manufacturer:
HAR
Quantity:
20 000
where:
V
including the voltage drop across the fuse resistors R
V
referenced 4-wire side or the SLIC tip and ring terminals.
I
R
Z
V
Z
E
Z
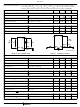
(AC) 2-Wire Impedance
The AC 2-wire impedance (Z
into the SLIC, including the fuse resistors, and is calculated
as follows:
Let V
Z
Substituting in Equation 9 for V
Substituting in Equation 12 for V
Therefore
Equation 16 can now be used to match the SLIC’s
impedance to any known line impedance (Z
V
Z
Z
Z
Z
M
T
RX
L
TR
TR
TX
F
RX
G
TR
TR
TR
T
TX
= Is the AC metallic current.
= Is used to set the SLIC’s 2-wire impedance.
= Is the line impedance.
= Is a fuse resistor.
= Is the AC open circuit voltage.
=
= Is the AC metallic voltage. Either at the ground
is defined as:
= Is the AC metallic voltage between tip and ring,
= Is used to set the 4-wire to 2-wire gain.
= Is the analog ground referenced receive signal.
=
=
=
=
RX
1000
V
Z
V
---------- -
V
---------- -
------------ -
1000
TR
I
I
Z
T
TR
TX
= 0. Then from Equation 10
M
M
T
+
-
------------ -
1000
+
+
I
Z
2R
---------------------- -
M
2R
TR
Z
L
F
I
F
M
–
+
-
E
2R
I
G
M
Z
TR
F
RING
TIP
63
TR
R
R
I
I
M
M
TR
F
F
) is the impedance looking
TX
V
TX
+
-
FIGURE 16. SIMPLIFIED AC TRANSMISSION CIRCUIT
HC5513
TR
).
(EQ. 12)
(EQ. 13)
(EQ. 14)
(EQ. 15)
(EQ. 16)
F
+
-
.
1
HC5513
A = 250
A = 250
Example:
Calculate Z
R
Z
(AC) 2-Wire to 4-Wire Gain
The 2-wire to 4-wire gain is equal to V
From Equations 9 and 10 with V
(AC) 4-Wire to 2-Wire Gain
The 4-wire to 2-wire gain is equal to V
From Equations 9, 10 and 11 with E
For applications where the 2-wire impedance (Z
Equation 15) is chosen to equal the line impedance (Z
expression for A
(AC) 4-Wire to 4-Wire Gain
The 4-wire to 4-wire gain is equal to V
From Equations 9, 10 and 11 with E
A
A
A
Z
A
T
F
2 4
4 2
4 4
T
4 2
–
–
–
= 560k in series with 2.16nF.
–
= 20 :
=
1000
=
=
=
=
–
V
---------- -
V
-----------
V
V
-----------
V
V
---------- -
Z
TR
RX
TX
TR
RX
TX
Z
RX
T
T
to make Z
600
=
=
=
----------------------------------------- -
Z
1
-- -
2
–
–
4-2
---------- -
Z
T
---------- -
Z
+
Z
Z
A = 4
RX
RX
Z
----------------------------------------- 2 20
j
T
T
1000
simplifies to:
T
1000
2.16 10
------------------------------------------- -
------------ -
1000
------------------------------------------- -
------------ -
1000
TR
Z
Z
+
T
1
T
2R
Z
= 600 in series with 2.16 F.
L
+
+
F
+
Z
2R
2R
V
RSN
L
2R
TX
–
1000
6
I
RX
F
F
M
–
F
+
+
Z
= 0:
Z
G
G
L
L
Z
TX
TR
TX
= 0:
= 0:
T
/ V
/V
/V
RX
RX
TR
Z
RX
V
.
.
.
TX
+
TR
-
V
,
RX
(EQ. 17)
(EQ. 18)
(EQ. 19)
(EQ. 20)
+
-
L
), the