TS68230 SGS-Thomson-Microelectronics, TS68230 Datasheet

TS68230
Available stocks
Related parts for TS68230
TS68230 Summary of contents
Page 1
... LY ADDRESSABLE REGISTERS ARE ADDRESSED FOR MOVEP (Move Peripheral) AND DMAC COMPATIBILITY DESCRIPTION The TS68230 parallel interface/timer (PI/T) provides versatile double buffered parallel interfaces and a system oriented timer for TS68000 systems. The pa- rallel interfaces operate in unidirectional or bidirectio- nal modes, either bits wide. In the ...
Page 2
... SECTION 1 INTRODUCTION The TS68230 parallel interface/timer (PI/T) provides versatile double buffered parallel interfaces and a system oriented timer for TS68000 systems. The parallel interfaces operate in unidirectional or bidi- rectional modes, either bits wide. In the uni- directional modes, an associated data direction register determines whether each port pin is an input or output ...
Page 3
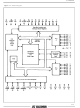
Figure 1.1 : Block Diagram. 3/61 ...
Page 4
Table 1.1 : Port Mode Control Summary. Mode 0 (unidirectional 8-bit mode) Port A Submode 00 - Pin-definable Double-buffered Input or Single-buffered Output H1 - Latches Input Data H2 - Status/interrupt Generating Input, General-purpose Output, or Operation with H1 in ...
Page 5
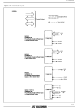
Figure 1.2 : Port Mode Layout. 5/61 ...
Page 6
Figure 1.2 : Port Mode Layout (continued). 1.2. SIGNAL DESCRIPTION Throughout this data sheet, signals are presented u- sing the terms active and inactive or asserted and negated independent of whether the signal is active in the high-voltage state or ...
Page 7
Table 1.2 : Signal Summary. Signal Name Input/Output CLK Input CS Input D0-D7 Input/output DMAREQ Output DTACK Output H1(H3)*** Input H2(H4)** Input or Output PA0-PA7**, PB0-PB7**, Input/output, PC0-PC7 Input or Output PIACK Input PIRQ Output RS1-RS5 Input R/W Input RESET ...
Page 8
READ/WRITE (R/W). R high impe- dance read/write input signal from the TS68000 bus master, indicating whether the current bus cycle is a read (high) or write (low) cycle. 1.2.4. CHIP SELECT (CS high-impedance input ...
Page 9
REGISTER MODEL A register model that includes the corresponding register selects is shown in table 1.3. Table 1.3 : Register Model. Register Select Bits Port Mode Control ...
Page 10
Table 1.3 : Register Model (continued). Register Select Bits TOUT/TIACK Control Bit Bit ...
Page 11
... The TS68230 CLK pin has the same specifica- tions as the TS68000 CLK pin, and must not be ga- ted off at any time. ...
Page 12
The system designer must take care that DTACK is negated and three-stated quickly enough after each bus cycle to avoid interference with the next one. With ...
Page 13
SECTION 2 PORT GENERAL INFORMATION AND CONVENTIONS This section introduces concepts that are generally applicable to the PI/T ports independent of the cho- sen mode and submode. For this reason, no parti- cular port or handshake pins are mentioned ; ...
Page 14
H2(H4) may be an output pin in the pulsed in- put handshake protocol asserted exactly as in the interlocked input protocol, but never remains asserted longer than four clock cy- cles. Typically, a four clock cycle pulse ...
Page 15
H2(H4) may be an output pin in the pulsed out- put handshake protocol asserted exactly as in the interlocked output protocol above, but never remains asserted longer than four clock cycles. Typically, a four clock pulse is ...
Page 16
... H1(H3) and falling edge for CS). Refer to 1.4 BUS INTERFACE OPERATION for the exception concer- 16/61 DMAREQ is generated on the bus side of the TS68230 by the synchronized* chip select. If the conditions of figures 2.3 or 2.4 are met, an assertion of CS will cause DMAREQ to be asserted three PI/T clocks (plus the delay time from the clock edge) after CS is synchronized ...
Page 17
Figure 2.4 : DMAREQ Associated with Input Transfers. 2.3. DIRECT METHOD OF RESETTING STATUS In certain modes one or more handshake pins can be used as edge-sensitive inputs for the sole pur- pose of setting bits in the port status ...
Page 18
SECTION 3 PORT MODES This section contains information that distinguishes the various port modes and submodes. General characteristics common to all modes are defined in Section 2 Port General Information and Conven- tions. A description of the port A control ...
Page 19
Table 3.1 : Mode 0 Port Data Paths Port A/B Data Register Mode DDR = 0 0 Submode 00 FIL Submode 01 0 Submode 1X Abbreviations : IOL - Initial Output Latch FOL - Final ...
Page 20
Programmable Options Mode 0 - Port A Submode 00 and Port B Submode 00 PACR 7 6 Port A Submode 0 0 Submode 00 PACR Control Input pin - edge-sensitive status input, H2S ...
Page 21
Programmable Options Mode 0 - Port A Submode 00 and Port B Submode 00 (continued) PBCR 2 H4 Interrupt Enable 0 The H4 interrupt is disabled. 1 The H4 interrupt is enabled. PBCR 1 H3 SVCRQ Enable 0 The H3 ...
Page 22
Programmable Options Mode 0 - Port A Submode 01 and Port B Submode 01 PACR 7 6 Port A Submode 0 1 Submode 01 PACR Control Input pin - edge-sensitive status inputs, H2S ...
Page 23
Programmable Options Mode 0 - Port A Submode 01 and Port B Submode 01 (continued) PBCR 2 H4 Interrupt Enable 0 The H4 interrupt is disabled. 1 The H4 interrupt is enabled. PBCR 1 H3 SVCRQ Enable 0 The H3 ...
Page 24
Programmable Option Mode 0 - Port A Submode 1X and Port B Submode 1X PACR 7 6 Port A Submode 1 X Submode 1X PACR Control Input pin - edge-sensitive status input, H2S ...
Page 25
Programmable Options Mode 0 - Port A Submode 1X and Port B Submode 1X (continued) PBCR 0 H3 Status Control edge-sensitive status input, H3S is set by an asserted edge of H3. 3.4. MODE 1 - ...
Page 26
PORT A CONTROL REGISTER (PACR Port A Interrupt Submode H2 Control Enable The port A control register, in conjunction with the programmed mode and the port B submode, controls the operation of ...
Page 27
H4 may be an output pin in the pulsed input handshake protocol asserted exactly as in the interlocked input protocol above, but never remains asserted longer than four clock cycles. Typically, a four clock cycle pulse is ...
Page 28
Programmable Options Mode 1 - Port A Submode XX and Port B Submode X0 (continued) PBCR Control Input pin - edge-sensitive status input, H4S is set on an asserted edge ...
Page 29
The H3S status bit may be programmed for two in- terpretations : 1. The H3S status bit is set when either the port initial or final output latch can accept new data clear when both latches are full ...
Page 30
Programmable Options Mode 1 - Port A Submode XX and Port B Submode X1 (continued) PBCR Control Input pin - edge-sensitive status input, H4S is set on an asserted edge ...
Page 31
Table 3.3 : Mode 2 Port A Data Paths Port A Data Register Mode DDR = 0 2 Abbreviations : Single Buffered FOL - Final Output Latch DDR - Data Direction Register 3.5.2. PORT B ...
Page 32
Typically, a four clock cycle pulse is ge- nerated. But in the case that a subsequent H1 asserted edge occurs before termination of the pulse negated asynchronously. Thus, anytime after the leading edge of the H2 pulse, ...
Page 33
Programmable Options Mode 2 - Port A Submode XX and Port B Submode XX (continued) PBCR Control Output pin - interlocked input handshake protocol, H4S is always cleared Output pin ...
Page 34
DOUBLE-BUFFERED OUTPUT TRANS- FERS. Data, written by the bus master to the PI/T, is stored in the port’s output latch. The peripheral ac- cepts the data by asserting H1, which causes the next data to be moved to the ...
Page 35
Programmable Options Mode 3 - Port A Submode XX and Port B Submode XX PACR 7 6 Port A Submode X X Submode XX. PACR Control Output pin - interlocked output handshake protocol, ...
Page 36
SECTION 4 PROGRAMMER’S MODEL This section describes the internal accessible regis- ter organization as represented in table 1.3 located Table 4.1 : PI/T Register Addressing Assignments. Register Port General Control Register Port Service Request Register Port A Data Direction Register ...
Page 37
PORT GENERAL CONTROL REGISTER (PGCR Port Mode H34 H12 H4 Control Enable Enable Sense Sense The port general control register controls many of the functions that are common to the overall opera- tion of ...
Page 38
DMA is not used. PSRR SVCRQ Select 1 0 The PC4/DMAREQ pin carries the DMAREQ function and is associatedwith double-buffered transfers controlled by H1 removed from PI/T’s interrupt structure, and thus, does not cause interrupt requests ...
Page 39
Bits 2, 1, and 0 determine port interrupt priority. The priority as shown in table 4 descending order left to right. 4.3. PORT DATA DIRECTION REGISTERS The following paragraphs describe the port data di- rection registers. 4.3.1. PORT ...
Page 40
Table 4.3 : PCDR Hardware Accesses. Operation PCDDR = 0 Read Port C Data Register Write Port C Data Output Register, Register Buffer Disabled ta direction register indicates the input or output di- rection. The port C data register is ...
Page 41
CLK and TIN pins to the counter controller ; ...
Page 42
TIN pin after being synchronized with the internal clock. The 24-bit counter is decremented, rolls over loaded from the counter preload registers when the prescaler rolls over from $00 to $1F. The ...
Page 43
... Programming of the timer control register is outlined with several examples given. 5.1. TIMER OPERATION The TS68230 timer can provide several facilities needed by TS68000 operating systems. It can ge- nerate periodic interrupts, a square wave single interrupt after a programmed time period. Also, it can be used for elapsed time measurement device watchdog ...
Page 44
For configurations in which the prescaler is not u- sed, the contents of the counter preload registers are transferred to the counter on the first asserted edge of the TIN input after entering the run state. On subsequent asserted ...
Page 45
Figure 5.1 :Periodic Interrupt Generator Example. Figure 5.2 : Square Wave Generator Example. 5.2.3. INTERRUPT AFTER TIMEOUT Z.D TOUT/TIACK * Control Control Changed In this configuration ...
Page 46
Figure 5.3 : Single Interrupt after Timeout Example. 5.2.4. ELAPSED TIME MEASUREMENT EXAM- PLES. Elapsed time measurement takes several forms ; two forms are described in the following paragraphs. 5.2.4.1. System Clock Example Z.D ...
Page 47
External Clock Z.D TOUT/TIACK * Control Control This configuration allows measurement (counting) of the number of input pulses occurring in an interval in which the counter is enabled. ...
Page 48
... SECTION 6 ELECTRICAL SPECIFICATIONS This section contains electrical specifications and associated timing information for the TS68230. 6.1 ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS Symbol V Supply Voltage CC V Input Voltage IN T Operating Temperature Range A TS68230C TS68230V T Storage Temperature st g This device contains circuitry to protect the inputs against damage due to high static voltages or electric fields ; however advised that normal precautions be taken to avoid application of any voltage higher than maximum-rated voltages to this high- 6 ...
Page 49
DC ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS (V Symbol V Input High Voltage IH V Input Low Voltage IL I Input Leakage Current ( Hi-Z Input Current ( Output High Voltage – 400 A, ...
Page 50
AC ELECTRICAL SPECIFICATIONS (V = 5.0Vdc 5 0Vdc Read and Write Cycle Timings (figures 6.2 and 6.3) Number 1 R/W, RS1-RS5 Valid to CS Low (setup time ...
Page 51
Figure 6.2 : Read Cycle Timing Diagram. Figure 6.3 : Write Cycle Timing Diagram. 51/61 ...
Page 52
AC ELECTRICAL SPECIFICATIONS (V = 5.0Vdc 5 0Vdc Peripheral Input Timings (figures 6.4) Number 14 Port Input Data Valid to H1(H3) Asserted (setup time) 15 H1(H3) Asserted to Port Input Data Invalid ...
Page 53
Figure 6.4 : Peripheral Input Timing Diagram. 7. CLK refers to the actual frequency of the CLK pin, not the maximum allowable CLK frequency. Note :Timing measurements are referenced to and from a low voltage of 0.8volt and a high ...
Page 54
AC ELECTRICAL SPECIFICATIONS (V = 5.0Vdc 5 0Vdc Peripheral Output Timings (figures 6.5) Number 16 Handshake Input H1(H4) Pulse Width Asserted 17 Handshake Input H1(H4) Pulse Width Negated 18 H1(H3) Asserted to ...
Page 55
Figure 6.5 : Peripheral Ouput Timing Diagram. Notes : 1. Timing diagram shows H1, H2, H3, and H4 asserted low. 2. Timing measurements are referenced to and from a low voltage of 0.8volt and a high voltage of 2.0volts, unless ...
Page 56
AC ELECTRICAL SPECIFICATIONS (V = 5.0Vdc 5 0Vdc Iack Timings (figure 6.6) Number PIACK or TIACK High to Data Out Invalid (hold time PIACK or TIACK ...
Page 57
This specification applies only when a pulsed handshake option is chosen and the pulse is not shortened due to an early asserted edge of H1(H3). 3. The maximum value is caused by a peripheral access (H1(H3) asserted) and bus ...
Page 58
PACKAGE MECHANICAL DATA mm mm 58/61 ...
Page 59
Table 1.3 : Register Model (sheet 2 of 2). Register Select Bits TOUT/TIACK Control Bit Bit ...
Page 60
Table 1.3 : Register Model (sheet 1 of 2). Register Select Bits Port Mode Control Enable SVCRQ Select ...
Page 61
... TS68230CP8 TS68230CP10 TS68230CFN8 TS68230CFN10 Information furnished is believed to be accurate and reliable. However, SGS-THOMSON Microelectronics assumes no responsability for the consequences of use of such information nor for any infringement of patents or other rights of third parties which may result from its use. No license is granted by implication or otherwise under any patent or patent rights of SGS-THOMSON Microelectronics ...