M34506E4FP Renesas Electronics Corporation., M34506E4FP Datasheet

M34506E4FP
Available stocks
Related parts for M34506E4FP
M34506E4FP Summary of contents
Page 1
... FEATURES Minimum instruction execution time ................................ 0.68 s (at 4.4 MHz oscillation frequency, in high-speed mode) Supply voltage .......................................................... 2 5.5 V (It depends on the oscillation frequency and operating mode.) Part number M34506M2-XXXFP M34506M4-XXXFP M34506E4FP (Note) Note: Shipped in blank. PIN CONFIGURATION ...
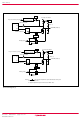
Page 2
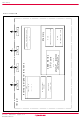
Group BLOCK DIAGRAM Block diagram (4506 Group) Rev.3.01 2005.02.07 page 2 of 111 REJ03B0106-0301 ...
Page 3
Group PERFORMANCE OVERVIEW Parameter Number of basic instructions Minimum instruction execution time Memory sizes ROM M34506M2 M34506M4/E4 RAM M34506M2 M34506M4/E4 Input/Output D –D I ports P0 –P0 I –P1 I ...
Page 4
Group PIN DESCRIPTION Pin Name V Power supply DD V Ground SS CNV CNV SS SS RESET Reset input/output X System clock input IN X System clock output OUT D –D I/O port –P0 I/O ...
Page 5
Group DEFINITION OF CLOCK AND CYCLE Operation source clock The operation source clock is the source clock to operate this product. In this product, the following clocks are used. • External ceramic resonator • External RC oscillation • Clock ...
Page 6
Group CONNECTIONS OF UNUSED PINS Connection Pin Connect Open. X OUT Open. (Output latch is set to “1.” Open. (Output latch is set to “0.”) Connect to V ...
Page 7
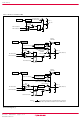
Group PORT BLOCK DIAGRAMS instruction ...
Page 8
Group ...
Page 9
Group Register ...
Page 10
Group Register ...
Page 11
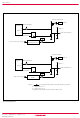
Group ( External interrupt circuit structure Rev.3.01 2005.02.07 page 11 of 111 REJ03B0106-0301 One-sided edge ...
Page 12
Group FUNCTION BLOCK OPERATIONS CPU (1) Arithmetic logic unit (ALU) The arithmetic logic unit ALU performs 4-bit arithmetic such as 4- bit data addition, comparison, AND operation, OR operation, and bit manipulation. (2) Register A and carry flag Register ...
Page 13
Group (5) Stack registers (SK ) and stack pointer (SP) S Stack registers (SKs) are used to temporarily store the contents of program counter (PC) just before branching until returning to the original routine when; • branching to an ...
Page 14
Group (8) Program counter (PC) Program counter (PC) is used to specify a ROM address (page and address). It determines a sequence in which instructions stored in ROM are read binary counter that increments the number ...
Page 15
Group PROGRAM MEMOY (ROM) The program memory is a mask ROM. 1 word of ROM is composed of 10 bits. ROM is separated every 128 words by the unit of page (addresses 0 to 127). Table 1 shows the ...
Page 16
Group DATA MEMORY (RAM) 1 word of RAM is composed of 4 bits, but 1-bit manipulation (with the and SZB j instructions) is enabled for the entire memory area. A RAM address is specified by ...
Page 17
Group INTERRUPT FUNCTION The interrupt type is a vectored interrupt branching to an individual address (interrupt address) according to each interrupt source. An interrupt occurs when the following 3 conditions are satisfied. • An interrupt activated condition is satisfied ...
Page 18
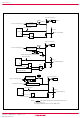
Group (4) Internal state during an interrupt The internal state of the microcomputer during an interrupt is as fol- lows (Figure 14). • Program counter (PC) An interrupt address is set in program counter. The address to be executed ...
Page 19
Group (6) Interrupt control registers • Interrupt control register V1 Interrupt enable bits of external 0, timer 1 and timer 2 are as- signed to register V1. Set the contents of this register through register A with the TV1A ...
Page 20
Group Fig. 16 Interrupt sequence Rev.3.01 2005.02.07 page 20 of 111 REJ03B0106-0301 ...
Page 21
Group EXTERNAL INTERRUPTS The 4506 Group has the external 0 interrupt. An external interrupt request occurs when a valid waveform is input to an interrupt input pin (edge detection). The external interrupt can be controlled with the interrupt control ...
Page 22
Group (2) External interrupt control registers • Interrupt control register I1 Register I1 controls the valid waveform for the external 0 inter- rupt. Set the contents of this register through register A with the TI1A instruction. The TAI1 instruction ...
Page 23
Group (3) Notes on interrupts Note [1] on bit 3 of register I1 When the input of the INT pin is controlled with the bit 3 of regis- ter I1 in software, be careful about the following notes. • ...
Page 24
Group TIMERS The 4506 Group has the following timers. • Programmable timer The programmable timer has a reload register and enables the frequency dividing ratio to be set decremented from a set- ting value n. When it ...
Page 25
Group Division circuit divided by 8 divided by 4 divided ...
Page 26
Group Table 10 Timer control registers Timer control register W1 W1 Prescaler control bit 3 W1 Prescaler dividing ratio selection bit 2 W1 Timer 1 control bit 1 Timer 1 count start synchronous circuit W1 0 control bit Timer ...
Page 27
Group (3) Timer 1 (interrupt function) Timer 8-bit binary down counter with the timer 1 reload reg- ister (R1). Data can be set simultaneously in timer 1 and the reload register (R1) with the T1AB instruction. ...
Page 28
Group (8) Timer input/output pin (P1 CNTR pin is used to input the timer 2 count source and output the timer 1 and timer 2 underflow signal divided by 2. The P1 /CNTR pin function can be selected by ...
Page 29
Group WATCHDOG TIMER Watchdog timer provides a method to reset the system when a pro- gram run-away occurs. Watchdog timer consists of timer WDT(16-bit binary counter), watchdog timer enable flag (WEF), and watchdog timer flags (WDF1, WDF2). The timer ...
Page 30
Group When the watchdog timer is used, clear the WDF1 flag at the pe- riod of 65534 machine cycles or less with the WRST instruction. When the watchdog timer is not used, execute the DWDT instruc- tion and the ...
Page 31
Group A/D CONVERTER The 4506 Group has a built-in A/D conversion circuit that performs conversion by 10-bit successive comparison method. Table 11 shows the characteristics of this A/D converter. This A/D converter can also be used as an 8-bit ...
Page 32
Group Table 12 A/D control registers A/D control register Q1 A/D operation mode selection bit Not used Analog input pin selection bits Q1 0 Note: “R” represents read enabled, and “W” represents write ...
Page 33
Group Table 13 Change of successive comparison register AD during A/D conversion At starting conversion Change of successive comparison register AD 1 1st comparison 1 2nd comparison 1 3rd comparison A/D conversion result After 10th comparison 1 completes 1: ...
Page 34
Group (9) Operation at comparator mode The A/D converter is set to comparator mode by setting bit 3 of the register Q1 to “1.” Below, the operation at comparator mode is described. (10) Comparator register In comparator mode, the ...
Page 35
Group (15) Definition of A/D converter accuracy The A/D conversion accuracy is defined below (refer to Figure 32). • Relative accuracy Zero transition voltage ( This means an analog input voltage when the actual A/D con- version ...
Page 36
Group RESET FUNCTION System reset is performed by applying “L” level to RESET pin for 1 machine cycle or more when the following condition is satisfied; the value of supply voltage is the minimum value or more of the ...
Page 37
Group (1) Power-on reset Reset can be performed automatically at power on (power-on re- set) by connecting a diode and a capacitor to RESET pin. Connect RESET pin and the external circuit at the shortest distance ...
Page 38
Group (2) Internal state at reset Figure 36 shows internal state at reset (they are the same after sys- tem is released from reset). The contents of timers, registers, flags and RAM except shown in Figure 36 are undefined, ...
Page 39
Group RAM BACK-UP MODE The 4506 Group has the RAM back-up mode. When the POF2 instruction is executed continuously after the EPOF instruction, system enters the RAM back-up state. The POF2 instruction is equal to the NOP instruction when ...
Page 40
Group (4) Return signal An external wakeup signal is used to return from the RAM back-up mode because the oscillation is stopped. Table 16 shows the return condition for each return source. (5) Control registers • Key-on wakeup control ...
Page 41
Group ...
Page 42
Group Table 17 Key-on wakeup control register Key-on wakeup control register K0 Port P0 key-on wakeup control bit Port P0 key-on wakeup control bit Port P0 key-on wakeup control bit ...
Page 43
Group Table 18 Pull-up control register and interrupt control register Pull-up control register PU0 Port P0 pull-up transistor 3 PU0 3 control bit Port P0 pull-up transistor 2 PU0 2 control bit Port P0 pull-up transistor 1 PU0 1 ...
Page 44
Group CLOCK CONTROL The clock control circuit consists of the following circuits. • On-chip oscillator (internal oscillator) • Ceramic resonator • RC oscillation circuit • Multi-plexer (clock selection circuit) • Frequency divider • Internal clock generating circuit O n ...
Page 45
Group (1) Selection of source oscillation (f(X The ceramic resonator or RC oscillation can be used for the source oscillation of the MCU. After system is released from reset, the MCU starts operation by the clock output from the ...
Page 46
Group (5) External clock When the external signal clock is used as the source oscillation (f(X )), connect the X pin to the clock source and leave open. Then, execute the CMCK instruction (Figure 45). Be ...
Page 47
Group LIST OF PRECAUTIONS Noise and latch-up prevention Connect a capacitor on the following condition to prevent noise and latch-up; • connect a bypass capacitor (approx. 0.1 F) between pins V and V at the shortest distance, SS • ...
Page 48
Group P1 /INT pin 3 15 Note [1] on bit 3 of register I1 When the input of the INT pin is controlled with the bit 3 of regis- ter I1 in software, be careful about the following notes. ...
Page 49
Group Notes for the use of A/D conversion 1 16 Note the following when using the analog input pins also for port P2 function: • Selection of analog input pins Even when P2 /A and IN0 ...
Page 50
Group Clock control 19 Execute the CMCK or the CRCK instruction in the initial setting routine of program (executing it in address 0 in page 0 is recom- mended). The oscillation circuit by the CMCK or CRCK instruction can ...
Page 51
Group CONTROL REGISTERS Interrupt control register V1 Timer 2 interrupt enable bit Timer 1 interrupt enable bit 2 Not used External 0 interrupt enable bit 0 Interrupt control register V2 Not used V2 ...
Page 52
Group Timer control register W1 Prescaler control bit Prescaler dividing ratio selection bit 2 W1 Timer 1 control bit 1 Timer 1 count start synchronous circuit W1 0 control bit Timer control register ...
Page 53
Group Key-on wakeup control register K0 Port P0 key-on wakeup control bit Port P0 key-on wakeup control bit Port P0 key-on wakeup control bit Port P0 key-on wakeup 0 K0 ...
Page 54
Group Pull-up control register PU0 Port P0 pull-up transistor 3 PU0 3 control bit Port P0 pull-up transistor 2 PU0 2 control bit Port P0 pull-up transistor 1 PU0 1 control bit Port P0 pull-up transistor 0 PU0 0 ...
Page 55
Group INSTRUCTIONS The 4506 Group has the 110 instructions. Each instruction is de- scribed as follows; (1) Index list of instruction function (2) Machine instructions (index by alphabet) (3) Machine instructions (index by function) (4) Instruction code table SYMBOL ...
Page 56
Group INDEX LIST OF INSTRUCTION FUNCTION Group- Mnemonic Function ing TAB (A) (B) TBA (B) (A) TAY (A) (Y) TYA (Y) (A) TEAB (E – – TABE (B) (E –E ...
Page 57
Group INDEX LIST OF INSTRUCTION FUNCTION (continued) Group- Mnemonic Function ing SB j (Mj(DP (Mj(DP SZB j (Mj(DP ...
Page 58
Group INDEX LIST OF INSTRUCTION FUNCTION (continued) Group- Mnemonic Function ing TR1AB (R1 – (R1 – SNZT1 (T1F After skipping, (T1F ...
Page 59
Group INDEX LIST OF INSTRUCTION FUNCTION (continued) Group- Mnemonic Function ing NOP (PC) (PC POF2 RAM back-up EPOF POF2 instructions valid SNZP ( DWDT Stop of watchdog timer func- tion enabled (WDF1 ...
Page 60
Group MACHINE INSTRUCTIONS (INDEX BY ALPHABET (Add n and accumulator) Instruction D 9 code Operation: (A) ( ADST (A/D conversion STart) Instruction D 9 code ...
Page 61
Group MACHINE INSTRUCTIONS (INDEX BY ALPHABET) (continued) AND (logical AND between accumulator and memory) Instruction D 9 code Operation: (A) (A) AND (M(DP (Branch to address a) Instruction D 9 code 0 ...
Page 62
Group MACHINE INSTRUCTIONS (INDEX BY ALPHABET) (continued (Branch and Mark to address a in page 2) Instruction D 9 code Operation: (SP) (SP (SK(SP)) (PC) ( ...
Page 63
Group MACHINE INSTRUCTIONS (INDEX BY ALPHABET) (continued) CMA (CoMplement of Accumulator) Instruction D 9 code Operation: (A) (A) CMCK (Clock select: ceraMic resonance ClocK) Instruction D 9 code Operation: ...
Page 64
Group MACHINE INSTRUCTIONS (INDEX BY ALPHABET) (continued) DI (Disable Interrupt) Instruction D 9 code Operation: (INTE) 0 DWDT (Disable WatchDog Timer) Instruction D 9 code Operation: Stop of watchdog ...
Page 65
Group MACHINE INSTRUCTIONS (INDEX BY ALPHABET) (continued) IAK (Input Accumulator from port K) Instruction D 9 code Operation ( – IAP0 (Input Accumulator from port P0) ...
Page 66
Group MACHINE INSTRUCTIONS (INDEX BY ALPHABET) (continued) INY (INcrement register Y) Instruction D 9 code Operation: (Y) ( (Load n in Accumulator) Instruction D 9 code ...
Page 67
Group MACHINE INSTRUCTIONS (INDEX BY ALPHABET) (continued) NOP (No OPeration) Instruction D 9 code Operation: (PC) (PC OKA (Output port K from Accumulator) Instruction D 9 code ...
Page 68
Group MACHINE INSTRUCTIONS (INDEX BY ALPHABET) (continued) OP2A (Output port P2 from Accumulator) Instruction D 9 code Operation: ( (logical OR between ...
Page 69
Group MACHINE INSTRUCTIONS (INDEX BY ALPHABET) (continued (Reset Bit) Instruction D 9 code Operation: (Mj(DP (Reset Carry flag) Instruction D 9 code ...
Page 70
Group MACHINE INSTRUCTIONS (INDEX BY ALPHABET) (continued) RT (ReTurn from subroutine) Instruction D 9 code Operation: (PC) (SK(SP)) (SP) (SP) – 1 RTI (ReTurn from Interrupt) Instruction D 9 code ...
Page 71
Group MACHINE INSTRUCTIONS (INDEX BY ALPHABET) (continued) SC (Set Carry flag) Instruction D 9 code Operation: (CY) 1 SCP (Set Port C) Instruction D 9 code Operation: (C) 1 ...
Page 72
Group MACHINE INSTRUCTIONS (INDEX BY ALPHABET) (continued) SEAM (Skip Equal, Accumulator with Memory) Instruction D 9 code Operation: (A) = (M(DP)) ? SNZ0 (Skip if Non Zero condition of external 0 interrupt request flag) ...
Page 73
Group MACHINE INSTRUCTIONS (INDEX BY ALPHABET) (continued) SNZI0 (Skip if Non Zero condition of external 0 Interrupt input pin) Instruction D 9 code Operation (INT) = “L” ...
Page 74
Group MACHINE INSTRUCTIONS (INDEX BY ALPHABET) (continued) SZB j (Skip if Zero, Bit) Instruction D 9 code Operation: (Mj(DP SZC (Skip if Zero, Carry flag) Instruction ...
Page 75
Group MACHINE INSTRUCTIONS (INDEX BY ALPHABET) (continued) T2AB (Transfer data to timer 2 and register R2 from Accumulator and register B) Instruction D 9 code Operation: (T2 – (R2 –R2 ...
Page 76
Group MACHINE INSTRUCTIONS (INDEX BY ALPHABET) (continued) TABAD (Transfer data to Accumulator and register B from register AD) Instruction D 9 code Operation: In A/D conversion mode (Q1 (B) (AD – ...
Page 77
Group MACHINE INSTRUCTIONS (INDEX BY ALPHABET) (continued) TADAB (Transfer data to register AD from Accumulator from register B) Instruction D 9 code Operation: (AD – (AD –AD ) (A) 3 ...
Page 78
Group MACHINE INSTRUCTIONS (INDEX BY ALPHABET) (continued) TAK2 (Transfer data to Accumulator from register K2) Instruction D 9 code Operation: (A) (K2) TALA (Transfer data to Accumulator from register LA) Instruction D 9 code ...
Page 79
Group MACHINE INSTRUCTIONS (INDEX BY ALPHABET) (continued) TAQ1 (Transfer data to Accumulator from register Q1) Instruction D 9 code Operation: (A) (Q1) TASP (Transfer data to Accumulator from Stack Pointer) Instruction D 9 code ...
Page 80
Group MACHINE INSTRUCTIONS (INDEX BY ALPHABET) (continued) TAW1 (Transfer data to Accumulator from register W1) Instruction D 9 code Operation: (A) (W1) TAW2 (Transfer data to Accumulator from register W2) Instruction D 9 code ...
Page 81
Group MACHINE INSTRUCTIONS (INDEX BY ALPHABET) (continued) TAY (Transfer data to Accumulator from register Y) Instruction D 9 code Operation: (A) (Y) TAZ (Transfer data to Accumulator from register Z) Instruction D 9 code ...
Page 82
Group MACHINE INSTRUCTIONS (INDEX BY ALPHABET) (continued) TEAB (Transfer data to register E from Accumulator and register B) Instruction D 9 code Operation: (E – –E ) (A) 3 ...
Page 83
Group MACHINE INSTRUCTIONS (INDEX BY ALPHABET) (continued) TK2A (Transfer data to register K2 from Accumulator) Instruction D 9 code Operation: (K2) (A) TMA j (Transfer data to Memory from Accumulator) Instruction D 9 code ...
Page 84
Group MACHINE INSTRUCTIONS (INDEX BY ALPHABET) (continued) TPU1A (Transfer data to register PU1 from Accumulator) Instruction D 9 code Operation: (PU1) (A) TPU2A (Transfer data to register PU2 from Accumulator) Instruction D 9 code ...
Page 85
Group MACHINE INSTRUCTIONS (INDEX BY ALPHABET) (continued) TV1A (Transfer data to register V1 from Accumulator) Instruction D 9 code Operation: (V1) (A) TV2A (Transfer data to register V2 from Accumulator) Instruction D 9 code ...
Page 86
Group MACHINE INSTRUCTIONS (INDEX BY ALPHABET) (continued) TW6A (Transfer data to register W6 from Accumulator) Instruction D 9 code Operation: (W6) (A) TYA (Transfer data to register Y from Accumulator) Instruction D 9 code ...
Page 87
Group MACHINE INSTRUCTIONS (INDEX BY ALPHABET) (continued) XAMD j (eXchange Accumulator and Memory data and Decrement register Y and skip) Instruction D 9 code Operation: (A) (M(DP)) (X) (X)EXOR( ...
Page 88
Group MACHINE INSTRUCTIONS (INDEX BY TYPES) Parameter Mnemonic Type instructions TAB TBA TAY TYA TEAB ...
Page 89
Group Skip condition – – Transfers the contents of register B to register A. – – Transfers the contents of register A to register B. – – Transfers the contents of register Y to register A. – – Transfers ...
Page 90
Group MACHINE INSTRUCTIONS (INDEX BY TYPES) (continued) Parameter Mnemonic Type instructions TABP AMC 0 0 ...
Page 91
Group Skip condition Continuous – Loads the value n in the immediate field to register A. description When the LA instructions are continuously coded and executed, only the first LA instruction is executed and other LA instructions coded continuously ...
Page 92
Group MACHINE INSTRUCTIONS (INDEX BY TYPES) (continued) Parameter Mnemonic Type instructions BLA p 0 ...
Page 93
Group Skip condition Branch within a page : Branches to address a in the identical page. – – Branch out of a page : Branches to address a in page p. – – Branch out of a page : ...
Page 94
Group MACHINE INSTRUCTIONS (INDEX BY TYPES) (continued) Parameter Mnemonic Type instructions SNZ0 SNZI0 ...
Page 95
Group Skip condition – – Clears (0) to interrupt enable flag INTE, and disables the interrupt. – – Sets (1) to interrupt enable flag INTE, and enables the interrupt (EXF0 – When V1 0 ...
Page 96
Group MACHINE INSTRUCTIONS (INDEX BY TYPES) (continued) Parameter Mnemonic Type instructions IAP0 OP0A IAP1 OP1A ...
Page 97
Group Skip condition – – Transfers the input of port P0 to register A. – – Outputs the contents of register A to port P0. – – Transfers the input of port P1 to register A. – – Outputs ...
Page 98
Group MACHINE INSTRUCTIONS (INDEX BY TYPES) (continued) Parameter Mnemonic Type instructions TABAD TALA TADAB TAQ1 ...
Page 99
Group Skip condition – – In the A/D conversion mode (Q1 B, and the middle-order 4 bits (AD In the comparator mode (Q1 ister B, and the low-order 4 bits (AD (Q1 : bit 3 of A/D control register ...
Page 100
Group INSTRUCTION CODE TABLE D –D 000000 000001 000010 000011 9 4 Hex – notation SZB 0000 0 NOP BLA BMLA 0 SZB 0001 1 – CLD 1 SZB 0010 2 – ...
Page 101
Group INSTRUCTION CODE TABLE (continued) D –D 100000 100001 100010 100011 9 4 Hex – notation 0 – – OP0A T1AB 0000 1 – – OP1A T2AB 0001 2 – – OP2A ...
Page 102
Group Electrical characteristics Absolute maximum ratings Parameter Symbol V Supply voltage DD Input voltage P0, P1, P2 RESET IN Input voltage A –A V IN0 IN1 I Output voltage P0, P1, P2 ...
Page 103
Group Recommended operating conditions 1 (Ta = –20 ° ° 2.0 to 5.5 V, unless otherwise noted) DD Symbol Parameter V Supply voltage DD (with a ceramic resonator) V Supply voltage DD (with RC oscillation) ...
Page 104
Group Ceramic resonator and high-speed mode selected f [MHz] 4.4 Recommended operating condition 2.2 2.0 2.7 RC oscillation circuit selected f [MHz] 4.4 Recommended operating condition 2.7 Except external clock input, high-speed mode (ceramic resonator selected) f [MHz] 3.2 ...
Page 105
Group Recommended operating conditions 2 (Ta = –20 ° ° 2.0 to 5.5 V, unless otherwise noted) DD Symbol Parameter f(X ) Oscillation frequency IN (with a ceramic resonator) f(X ) Oscillation frequency IN (with ...
Page 106
Group Electrical characteristics (Ta = –20 ° °C, V Symbol Parameter V “L” level output voltage OL P0 “L” level output voltage OL P2, RESET V “L” level output voltage ...
Page 107
Group A/D converter recommended operating conditions (Comparator mode included –20 ° °C, unless otherwise noted) Symbol Parameter V Supply voltage DD V Analog input voltage IA f(X ) Oscillation frequency IN A/D converter characteristcs (Comparator ...
Page 108
Group Basic timing diagram Parameter ...
Page 109
... Table 20 Product of built-in PROM version PROM size Part number ( 10 bits) M34506E4FP 4096 words (1) PROM mode The 4506 Group has a PROM mode in addition to a normal opera- tion mode. It has a function to serially input/output the command codes, addresses, and data required for operation (e.g., read and program) on the built-in PROM using only a few pins ...
Page 110
Group PIN CONFIGURATION (TOP VIEW Fig. 54 Pin configuration of built-in PROM version Rev.3.01 2005.02.07 page 110 of 111 REJ03B0106-0301 ...
Page 111
Group Package outline JEITA Package Code RENESAS Code P-SOP20-5.3x12.6-1.27 PRSP0020DA Index mark *2 e Rev.3.01 2005.02.07 page 111 of 111 REJ03B0106-0301 Previous Code MASS[Typ.] 20P2N-A 0. NOTE) 1. DIMENSIONS ...
Page 112
REVISION DESCRIPTION LIST Rev. No. 1.0 First Edition 1.1 Pages Character fonts errors revised 2.0 The 4506/4507 Group data sheet is separated. Page 10: Port block diagram (3); Block diagram of P1 Page 26: Fig. ...
Page 113
REVISION DESCRIPTION LIST Rev. No. 3.01 Page 1, 3: Package name revised. Page 28: •Timer 1 and timer 2 count start timing and count time when operation starts added. Page 47: Timer 1 and timer 2 count start timing and ...
Page 114
Keep safety first in your circuit designs! 1. Renesas Technology Corp. puts the maximum effort into making semiconductor products better and more reliable, but there is always the possibility that trouble may occur with them. Trouble with semiconductors may lead ...