SAA4951WP Philips Semiconductors, SAA4951WP Datasheet
SAA4951WP
Related parts for SAA4951WP
SAA4951WP Summary of contents
Page 1
DATA SHEET SAA4951 Memory controller Preliminary specification File under Integrated Circuits, IC02 INTEGRATED CIRCUITS April 1994 ...
Page 2
... T operating ambient amb temperature ORDERING INFORMATION EXTENDED TYPE NUMBER PINS SAA4951WP Note 1. SOT187-2; 1996 December 13. April 1994 GENERAL DESCRIPTION The memory controller SAA4951 has been designed for high end TV sets using 2f The circuit provides all necessary write, read and clock pulses to control different field memory concepts. ...
Page 3
... Philips Semiconductors Memory controller April 1994 3 Preliminary specification SAA4951 ...
Page 4
... Philips Semiconductors Memory controller PINNING SYMBOL PIN HRD SWC1 3 SRC 4 SWC2 5 WEXT 6 IE1 7 WE1 8 STROBE HRA 11 BLNA LLA 13 IE2 14 WE2 15 CLV 16 ALDUV/VB 17 RE1 18 RE2 19 BLND 20 ALE 21 WRD LLDFL HRDFL 35 April 1994 (1) TYPE O horizontal reference signal, display part positive supply voltage O serial write clock, memory 1 ...
Page 5
... I vertical synchronization signal, acquisition part I test input O reset write signal, memory 2 O reset write signal, memory 1 I line-locked clock signal, display part ground SAA4951WP Fig.2 Pin configuration. 5 Preliminary specification SAA4951 DESCRIPTION 39 VACQ 38 VDFL 37 HDFL V DD ...
Page 6
... Philips Semiconductors Memory controller FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION Block diagram and short description The SAA4951 is a memory controller intended to be used for scan conversion in TV receivers. This conversion is done from 50 to 100 Hz or from 60 to 120 Hz. The device supports three separate PLL circuits: the acquisition PLL can run on 12, 13 ...
Page 7
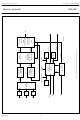
... Philips Semiconductors Memory controller handbook, full pagewidth 6 WEXT 13 LLA 39 VACQ 9 STROBE 21 ALE 22 WRD LLD 33 LLDFL April 1994 SAA4951 ACQ H-TIMING ACQ-CLOCK GENERATOR ACQ V-TIMING MICRO- PROCESSOR- INTERFACE DSP V-TIMING DSP H-TIMING DSP-CLOCK GENERATOR DFL DFL-CLOCK TIMING GENERATOR Fig.3 Block diagram. 7 Preliminary specification ...
Page 8
... Philips Semiconductors Memory controller Microcontroller interface The SAA4951 is connected to a microcontroller via pins P0 to P7, ALE and WRD. This controller receives commands 2 from the I C-bus and sets the registers of the SAA4951 accordingly. Fig.4 shows the timing of these signals. Address and data are transmitted sequentially on the bus with the falling edge of ALE denoting a valid address and the falling edge of WRD indicating valid data ...
Page 9
... Philips Semiconductors Memory controller ADDRESS REGISTER (HEX) Horizontal pulses generated from the display clock 48 BLNDSTA 49 BLNDSTO 4A HWE2STA 4B HWE2STO 4C HRESTA 4D HRESTO 4E HDMSB 4F HDDEL Vertical pulses generated from the acquisition clock 50 VWE1STA 51 VWE1STO 52 VAMSB Horizontal pulses generated from the acquisition clock 58 CLVSTA 59 CLVSTO ...
Page 10
... Philips Semiconductors Memory controller ADDRESS REGISTER (HEX) Registers to turn on different modes 60 MODE0 61 MODE1 80 READ As it can be seen from the above table the registers form groups which are reflected in the addressing scheme according to Table 2. Table 2 Internal register addressing scheme Note don’t care data bit ...
Page 11
... Philips Semiconductors Memory controller Table 3 Mode registers. REGISTER BIT NAME MODE0 0 (LSB) FSA0 1 FSA1 2 FSD0 3 FSD1 4 FORMAT0 MODE0 5 FORMAT1 6 HDEL0 7 (MSB) HDEL1 April 1994 frequency select acquisition bit 0 frequency select acquisition bit 1 frequency select display bit 0 frequency select display bit 1 FSA1 ...
Page 12
... Philips Semiconductors Memory controller REGISTER BIT NAME MODE1 0 (LSB STPWM1 2 STPWM2 3 MC1 4 GSC 5 CCIR60 6 EXTLLA 7 VFS Description of acquisition part LLA This is the main input clock pulse for the acquisition side of the memory controller generated by an external PLL circuit. Depending on the chosen system application LLA runs on the different frequencies of 12/13 ...
Page 13
... Philips Semiconductors Memory controller handbook, full pagewidth LLA HRA ALDUV (format 4:1:1) ALDUV (format 4:2:2) ALDUV (format 4:4:4) In case of an external write enable signal WEXT this output provides a vertical blanking signal, which can be used to generate a sandcastle pulse. The settings for the blanking signal are done with the registers VWE1STA (falling edge) and VWE1STO (rising edge) ...
Page 14
... Philips Semiconductors Memory controller handbook, full pagewidth HRA CLV CLV f WE1 r WE1 Table 4 Horizontal programming range of CLV and WE1 (see also Fig.6). 13.5 MHz CLV CLV WE1 WE1 13.5 MHz CLV CLV WE1 WE1 18 MHz CLV CLV WE1 WE1 16 MHz CLV ...
Page 15
... Philips Semiconductors Memory controller VACQ This is the 50 Hz vertical synchronization input signal derived from a suitable vertical synchronization circuit (i. e. TDA2579). The LOW-to-HIGH transition of this pulse is the timing reference of all vertical control signals of the SAA4951. handbook, full pagewidth VACQ V rWE1 WE1 RSTW1 Table 5 Vertical programming range of WE1 (see also Fig ...
Page 16
... Philips Semiconductors Memory controller BLND The output signal BLND is a horizontal blanking pulse and is used for the peripheral circuits NORIC and BENDIC. A LOW level indicates the blanking interval, a HIGH level indicates valid data from the memories possible to delay the horizontal timing of BLND up to three steps of LLD clock pulses ...
Page 17
... Philips Semiconductors Memory controller RE1 The output RE1 is the read enable signal for field memory 1. A HIGH level enables the picture data to be read from the memory. RE1 is a composite signal and includes the horizontal read enable timing as well as the vertical timing possible to delay the horizontal timing of RE1 up to three steps of LLD clock pulses ...
Page 18
... Philips Semiconductors Memory controller Description of deflection part LLDFL The input signal LLDFL is the main line-locked clock pulse for the deflection side of the memory controller generated by an external PLL circuit. The frequency of LLDFL is always 27 MHz and is independent of the chosen feature modes. The PLL circuit operates on the video clamping ...
Page 19
... Philips Semiconductors Memory controller Timing specification The internal delays of the output signals referred to the respective clock are given in Table 8. handbook, full pagewidth CLK OUT Table 8 Delay table. Conditions +4 =+70 C (worst case CLK OUT LLA SWC1 LLD SRC LLDFL SRC SRC ...
Page 20
... Philips Semiconductors Memory controller LIMITING VALUES In accordance with the Absolute Maximum Rating System (IEC 134). SYMBOL V supply voltage DD V input voltage I T operating ambient temperature amb T storage temperature stg CHARACTERISTICS Recommended operating conditions SYMBOL V DC supply voltage input voltage output voltage ...
Page 21
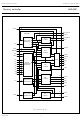
... Philips Semiconductors Memory controller APPLICATION INFORMATION Fig.12 shows a block diagram of the application environment of the memory controller SAA4951. The full option chip set of the new TV-feature system (third generation) controlled by the I TDA8709 3 ADC (8-bit) with clamp and gain setting, 30 MHz or TDA8755 1 ADC ...
Page 22
... Philips Semiconductors Memory controller book, full pagewidth April 1994 RE2 RE1 BLND SRC RSTW2 SWC2 WE2 IE2 RSTW1 WE1 IE1 SWC1 CLV 22 Preliminary specification SAA4951 ...
Page 23
... Philips Semiconductors Memory controller PACKAGE OUTLINE PLCC44: plastic leaded chip carrier; 44 leads pin 1 index DIMENSIONS (millimetre dimensions are derived from the original inch dimensions UNIT min. max. 4.57 0.53 mm 0.51 0.25 3.05 4.19 0.33 0.180 0.021 inches 0.020 0.01 0.12 0.165 ...
Page 24
... Philips Semiconductors Memory controller SOLDERING Introduction There is no soldering method that is ideal for all IC packages. Wave soldering is often preferred when through-hole and surface mounted components are mixed on one printed-circuit board. However, wave soldering is not always suitable for surface mounted ICs, or for printed-circuits with high population densities ...
Page 25
... Philips Semiconductors Memory controller DEFINITIONS Data sheet status Objective specification This data sheet contains target or goal specifications for product development. Preliminary specification This data sheet contains preliminary data; supplementary data may be published later. Product specification This data sheet contains final product specifications. ...