MICRF505YML Micrel Inc, MICRF505YML Datasheet

MICRF505YML
Specifications of MICRF505YML
Available stocks
Related parts for MICRF505YML
MICRF505YML Summary of contents
Page 1
MICRF505 General Description The MICRF505 is a true single chip, frequency shift keying (FSK) transceiver intended for use in half-duplex, bidirec- tional RF links. The multi-channeled FSK transceiver is intended for UHF radio equipment in compliance with the North American ...
Page 2
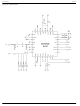
MICRF505 Typical Application M9999-051304 2 Micrel May 13, 2004 ...
Page 3
MICRF505 Pin Configuration Pin Description Pin Number Pin Name 1 RFGND 2 PTATBIAS 3 RFVDD 4 RFGND 5 ANT 6 RFGND 7 RFGND CIBIAS 10 IFVDD 11 IFGND 12 ICHOUT 13 QCHOUT 14 RSSI ...
Page 4
MICRF505 Absolute Maximum Ratings Supply Voltage (V ) ................................................. +3.3V DD Voltage on any pin (GND = 0V) ................. –0.3V to 2.7V Lead Temperature (soldering, 4 sec.) ...................... TBD∞C Storage Temperature (T ) ....................... –55∞C to +150∞C S (3) ............................................................................... ...
Page 5
MICRF505 Symbol Parameter Receive Section Rx Current Consumption Rx Current Consumption Variation Receiver Sensitivity Receiver Maximum Input Power Receiver Sensitivity Tolerance Receiver Bandwidth Co-Channel Rejection Adjacent Channel Rejection Blocking Noise Figure, Cascade 1dB Compression Input IP3 Input IP2 LO Leakage ...
Page 6
MICRF505 Symbol Parameter Digital Inputs/Outputs V Logic Input High IH V Logic Input Low IL (5) Clock/Data Frequency (5) Clock/Data Duty Cycle Notes: 1. Exceeding the absolute maximum ratings may damage the device. 2. The device is not guaranteed to ...
Page 7
MICRF505 Programming General The MICRF505 functions are enabled through a number of programming bits. The programming bits are organized as a set of addressable control registers, each register holding 8 bits. There are 23 control registers in total in the ...
Page 8
MICRF505 Adr A6.. 0000000 LNA_by PA2 0000001 Modulation1 Modulation0 0000010 CP_HI ‘0’ 0000011 ‘1’ ‘1’ 0000100 Mod_F2 Mod_F1 0000101 - - 0000110 - Mod_clkS2 0000111 BitRate_clkS1 BitRate_clkS0 0001000 ‘1’ ScClk_X2 0001001 ‘0’ ‘0’ 0001010 - - 0001011 - ...
Page 9
MICRF505 How to write: Bring CS active to start a write sequence. The active state of the CS line is “high.” Use the SCLK/IO serial interface to clock “Address” and “R/W bit and “Values” into the MICRF505. MICRF505 will sample ...
Page 10
MICRF505 How to write: • Bring CS high • Use SCLK and IO to clock in the 23 octets • Bring CS low Refer to the figure in the next section, “Writing to n registers having incremental addresses”. What to ...
Page 11
MICRF505 Writing to n Registers having Non- Incremental Addresses Registers with non-incremental addresses can be written to in one write-sequence as well. Example of non-incremental addresses: “0,1,3”. However, this requires more overhead, and the user should consider the possibility to ...
Page 12
MICRF505 Programming interface timing Figure 4 and Table 6 shows the timing specification for the 3-wire serial programming interface. SCLK CS IO Symbol Parameter Tper Min. period of SCLK Thigh Min. high time of SCLK Tlow Min. low time of ...
Page 13
MICRF505 Frequency Synthesizer A6.. 0001010 - - 0001011 - - 0001100 N0_7 N0_6 0001101 - - 0001110 M0_7 M0_6 0001111 - - 0010000 - - 0010001 N1_7 N1_6 0010010 - - 0010011 M1_7 M1_6 The frequency synthesizer consists ...
Page 14
MICRF505 parasitic The parasitic capacitance is the pin input capacitance and PCB stray capacitance. Typically the total parasitic capaci- tance is around 6pF. For instance, for a ...
Page 15
MICRF505 Charge Pump A6.. 0000011 CP_HI ‘0’ ‘0’ ‘0’ OUTS3 OUTS2 OUTS1 OUTS0 The charge pump current can be set to either 125mA or 500mA by CP_HI (‘1’ D 500mA). This will affect the loop ...
Page 16
MICRF505 Lock Detect A6..A0 D7 0000001 Modulation1 Modulation0 A lock detector can be enabled by setting LD_en = 1. When pin LD is high, it indicates that the PLL is in lock. Modes of Operation A6..A0 D7 0000000 LNA_by PA2 ...
Page 17
MICRF505 Data Interface The MICRF505 interface can be divided in to two separate interfaces, a “programming interface” and a “Data interface”. The “programming interface” has a three wire serial program- mable interface and is described in chapter Programming. The “data ...
Page 18
MICRF505 Sallen-Key Filters A6.. 0000001 Modulation1 Modulation0 Each channel includes a pre-amplifier and a prefilter, which is a three-pole Sallen-Key lowpass filter. It protects the following switched-capacitor filter from strong adjacent chan- nel signals, and it also works ...
Page 19
MICRF505 RSSI A6.. 0000001 Modulation1 Modulation0 RSSI 2,5 2 1,5 1 0,5 0 -110 -100 -90 -80 -70 Pin Pin (dBm) (dBm) Figure 12. RSSI Voltage Pin 14 RSSI R2 33k Figure 13. RSSI Network May 13, 2004 ...
Page 20
MICRF505 FEE A6.. 0000001 — 0000001 FEE_7 FEE_6 The Frequency Error Estimator (FEE) uses information from the demodulator to calculate the frequency offset between its receive frequency and the transmitter frequency. The output of the FEE can be ...
Page 21
MICRF505 Bit Synchronizer A6.. 0000110 — ModclkS2 0000111 BitRate_clkS1 BitRate_clkS0 A bit synchronizer can be enabled in receive mode by selecting the synchronous mode (Sync_en=1). The DataClk- pin will output a clock with twice the frequency of the ...
Page 22
MICRF505 Frequency Modulation A6.. 0000001 Modulation1 Modulation0 Modulation1 Modulation0 Modulation Type 0 0 Closed loop modulation using modulator 0 1 Not in use 1 0 FSK applied using two sets of dividers 1 1 Not in use Table ...
Page 23
MICRF505 When Modulation1 Modulation0 is 10, two sets of divider values need to be programmed. The formula for calculating the M,N and A values is given in chapter Frequency synthe- sizer. The divider values stored in the M0-, N0- and ...
Page 24
MICRF505 Modulator Current The current used during the rise- and fall times can be programmed with the Mod_I4..Mod_I0 bit, the last one being LSB. Figure 15 shows two waveforms generated with two different currents, where Mod_Ia > Mod_Ib. Higher current ...
Page 25
MICRF505 The modulator filter will not influence on the frequency deviation as long as the programmed cut-off frequency is above the actual bit rate. The frequency deviation must be programmed so that the modulation index (2 x single sided frequency ...
Page 26
MICRF505 XCO_Present (5-bit) holds present value in XCO_tune bits XCO_Step (4-bit) holds Increment/decrement of XCO_tune bits XCO_Sign (1 bit) holds POS or NEG (increment/decrement) increasing LO is done by reducing the XCO_tune value XCO TUNE PROCEDURE INIT: XCO_Present = 0 ...
Page 27
MICRF505 MICREL, INC. 1849 FORTUNE DRIVE SAN JOSE, CA 95131 USA + 1 (408) 944-0800 TEL The information furnished by Micrel in this data sheet is believed to be accurate and reliable. However, no responsibility is assumed by Micrel for ...