PIC18F66K80-I/PT Microchip Technology, PIC18F66K80-I/PT Datasheet

PIC18F66K80-I/PT
Specifications of PIC18F66K80-I/PT
Available stocks
Related parts for PIC18F66K80-I/PT
PIC18F66K80-I/PT Summary of contents
Page 1
... Enhanced Flash 2011 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC18F66K80 Family Microcontrollers, with ECAN™ and nanoWatt XLP Technology Preliminary Data Sheet DS39977C ...
Page 2
... PICtail, REAL ICE, rfLAB, Select Mode, Total Endurance, TSHARC, UniWinDriver, WiperLock and ZENA are trademarks of Microchip Technology Incorporated in the U.S.A. and other countries. SQTP is a service mark of Microchip Technology Incorporated in the U.S.A. All other trademarks mentioned herein are property of their respective companies. ...
Page 3
... PIC18F66K80 64 Kbytes 3,648 PIC18LF66K80 64 Kbytes 3,648 2011 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC18F66K80 FAMILY ECAN Bus Module Features (Continued): • 16 Full, 29-Bit Acceptance Filters with Dynamic Association • Three Full, 29-Bit Acceptance Masks • Automatic Remote Frame Handling • Advanced Error Management Features Special Microcontroller Features: • ...
Page 4
... PIC18F66K80 FAMILY Peripheral Highlights: • Five CCP/ECCP modules: - Four Capture/Compare/PWM (CCP) modules - One Enhanced Capture/Compare/PWM (ECCP) module • Five 8/16-Bit Timer/Counter modules: - Timer0: 8/16-bit timer/counter with 8-bit programmable prescaler - Timer1, 3: 16-bit timer/counter - Timer2, 4: 8-bit timer/counter • Two Analog Comparators • Configurable Reference Clock Output • ...
Page 5
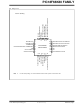
... Pin Diagrams (1) 28-Pin QFN RA2/V REF RA3/V +/AN3 REF V DDCORE RA5/AN4/C2INB/HLVDIN/T1CKI/SS/CTMUI OSC1/CLKIN/RA7 OSC2/CLKOUT/RA6 For the QFN package recommended that the bottom pad be connected to V Note 1: 2011 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC18F66K80 FAMILY -/AN2 PIC18F2XK80 CAP PIC18LF2XK80 Preliminary RB3/CANRX/C2OUT/P1D/CTED2/INT3 RB2/CANTX/C1OUT/P1C/CTED1/INT2 RB1/AN8/C1INB/P1B/CTDIN/INT1 RB0/AN10/C1INA/FLT0/INT0 ...
Page 6
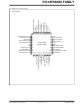
... PIC18F66K80 FAMILY Pin Diagrams (Continued) 28-Pin SSOP/SPDIP/SOIC MCLR/RE3 RA0/CV /AN0/ULPWU REF RA1/AN1 RA2/V -/AN2 REF RA3/V +/AN3 REF V /V DDCORE RA5/AN4/C2INB/HLVDIN/T1CKI/SS/CTMUI OSC1/CLKIN/RA7 OSC2/CLKOUT/RA6 RC0/SOSCO/SCLKI RC1/ISOSCI RC2/T1G/CCP2 RC3/REFO/SCL/SCK 40-Pin PDIP MCLR/RE3 RA0/CV /AN0/ULPWU REF RA1/AN1/C1INC RA2/V -/AN2/C2INC REF RA3/V +/AN3 REF V /V DDCORE ...
Page 7
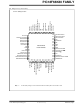
... Pin Diagrams (Continued) 44-Pin TQFP RC7/CANRX/RX1/DT1/CCP4 RD4/ECCP1/P1A/PSP4 RD5/P1B/PSP5 RD6/TX2/CK2/P1C/PSP6 RD7/RX2/DT2/P1D/PSP7 RB0/AN10/FLT0/INT0 RB1/AN8/CTDIN/INT1 RB2/CANTX/CTED1/INT2 RB3/CANRX/CTED2/INT3 2011 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC18F66K80 FAMILY PIC18F4XK80 5 29 PIC18LF4XK80 Preliminary N/C RC0/SOSCO/SCLKI OSC2/CLKOUT/RA6 OSC1/CLKIN/RA7 RE2/AN7/C2OUT/CS RE1/AN6/C1OUT/WR RE0/AN5/RD RA5/AN4/HLVDIN/T1CKI/ DDCORE CAP DS39977C-page 7 ...
Page 8
... PIC18F66K80 FAMILY Pin Diagrams (Continued) (1) 44-Pin QFN RC7/CANRX/RX1/DT1/CCP4 RD4/ECCP1/P1A/PSP4 RD5/P1B/PSP5 RD6/TX2/CK2/P1C/PSP6 RD7/RX2/DT2/P1D/PSP7 RB0/AN10/FLT0/INT0 RB1/AN8/CTDIN/INT1 RB2/CANTX/CTED1/INT2 RB3/CANRX/CTED2/INT3 For the QFN package recommended that the bottom pad be connected to V Note 1: DS39977C-page PIC18F4XK80 5 29 PIC18LF4XK80 Preliminary N/C RC0/SOSCO/SCLKI OSC2/CLKOUT/RA6 OSC1/CLKIN/RA7 RE2/AN7/C2OUT/CS RE1/AN6/C1OUT/WR RE0/AN5/RD RA5/AN4/HLVDIN/T1CKI/SS ...
Page 9
... RD7/P1D/PSP7 5 RG0/RX1/DT1 6 RG1/CANTX2 RG2/T3CKI 11 RG3/TX1/CK1 12 RB0/AN10/FLT0/INT0 13 14 RB1/AN8/CTDIN/INT1 RB2/CANTX/CTED1/INT2 15 RB3/CANRX/CTED2/INT3 16 For the QFN package recommended that the bottom pad be connected to V Note 1: 2011 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC18F66K80 FAMILY RC0/SOSCO/SCLKI 48 OSC2/CLKOUT/RA6 47 OSC1/CLKIN/RA7 46 RF5 45 RF4/MDCIN2 VSS V PIC18F6XK80 VDD 40 PIC18LF6XK80 RE2/AN7/C2OUT/CS 39 RE1/AN6/C1OUT/WR 38 RE0/AN5/RD ...
Page 10
... Instruction Set Summary .......................................................................................................................................................... 487 30.0 Development Support............................................................................................................................................................... 537 31.0 Electrical Characteristics .......................................................................................................................................................... 541 32.0 Packaging Information.............................................................................................................................................................. 589 Appendix A: Revision History............................................................................................................................................................. 609 Appendix B: Migration to PIC18F66K80 Family................................................................................................................................. 609 Index ................................................................................................................................................................................................. 611 The Microchip Web Site ..................................................................................................................................................................... 625 Customer Change Notification Service .............................................................................................................................................. 625 Customer Support .............................................................................................................................................................................. 625 Reader Response ...
Page 11
... When contacting a sales office, please specify which device, revision of silicon and data sheet (include literature number) you are using. Customer Notification System Register on our web site at www.microchip.com to receive the most current information on all of our products. 2011 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC18F66K80 FAMILY Preliminary DS39977C-page 11 ...
Page 12
... PIC18F66K80 FAMILY NOTES: DS39977C-page 12 Preliminary 2011 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 13
... Core Features 1.1.1 nanoWatt TECHNOLOGY All of the devices in the PIC18F66K80 family incorpo- rate a range of features that can significantly reduce power consumption during operation. Key items include: • Alternate Run Modes: By clocking the controller from the Timer1 source or the Internal RC oscilla- tor, power consumption during code execution can be reduced ...
Page 14
... See Section 31.0 “Electrical Characteristics” time-out periods. 1.3 Details on Individual Family Members Devices in the PIC18F66K80 family are available in 28-pin, 40/44-pin and 64-pin packages. Block diagrams for each package are shown in and Figure 1-3, respectively. The devices are differentiated from each other in these ways: • ...
Page 15
... Comparators CTMU Capture/Compare/PWM (CCP) Modules Enhanced CCP (ECCP) Modules Serial Communications 12-Bit Analog-to-Digital Module Resets (and Delays) Instruction Set Packages 2011 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC18F66K80 FAMILY PIC18F25K80 DC – 64 MHz 32K 16,384 3.6K 31 Ports Parallel Slave Port (PSP) Five Two Yes ...
Page 16
... PIC18F66K80 FAMILY TABLE 1-3: DEVICE FEATURES FOR THE PIC18F6XK80 (64-PIN DEVICES) Features Operating Frequency Program Memory (Bytes) Program Memory (Instructions) Data Memory (Bytes) Interrupt Sources I/O Ports Parallel Communications Timers Comparators CTMU Capture/Compare/PWM (CCP) Modules Enhanced CCP (ECCP) Modules DSM Serial Communications ...
Page 17
... RA6 and RA7 are only available as digital I/O in select oscillator modes. For more information, see 2: Configurations”. RE3 is only available when the MCLRE Configuration bit is cleared (MCLRE = 0). 3: 2011 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC18F66K80 FAMILY Data Bus<8> Data Latch 8 8 Data Memory ...
Page 18
... PIC18F66K80 FAMILY FIGURE 1-2: PIC18F4XK80 (40/44-PIN) BLOCK DIAGRAM Table Pointer<21> inc/dec logic 21 20 Address Latch Program Memory Data Latch 8 Instruction Bus<16> Timing OSC2/CLKO Generation OSC1/CLKI INTOSC Oscillator 16 MHz Oscillator Precision Band Gap Reference Voltage Regulator DDCORE CAP DD Timer2/4 Timer0 Timer1 CCP ...
Page 19
... RA6 and RA7 are only available as digital I/O in select oscillator modes. For more information, see 2: Configurations”. RE3 is only available when the MCLRE Configuration bit is cleared (MCLRE = 0). 3: 2011 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC18F66K80 FAMILY Data Bus<8> Data Latch 8 8 Data Memory ...
Page 20
... PIC18F66K80 FAMILY TABLE 1-4: PIC18F2XK80 I/O DESCRIPTIONS Pin Number SSOP/ Pin Name QFN SPDIP/ SOIC MCLR/RE3 26 1 MCLR RE3 OSC1/CLKIN/RA7 6 9 OSC1 CLKIN RA7 OSC2/CLKOUT/RA6 7 10 OSC2 CLKOUT RA6 Legend: CMOS = CMOS compatible input or output ST = Schmitt Trigger input with CMOS levels ...
Page 21
... T1CKI SS CTMUI Legend: CMOS = CMOS compatible input or output ST = Schmitt Trigger input with CMOS levels I = Input P = Power 2011 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC18F66K80 FAMILY Pin Buffer Type Type PORTA is a bidirectional I/O port. I/O ST/ General purpose I/O pin. CMOS O Analog Comparator reference voltage output. ...
Page 22
... PIC18F66K80 FAMILY TABLE 1-4: PIC18F2XK80 I/O DESCRIPTIONS (CONTINUED) Pin Number SSOP/ Pin Name QFN SPDIP/ SOIC RB0/AN10/C1INA/FLT0 INT0 RB0 AN10 C1INA FLT0 INT0 RB1/AN8/C1INB/P1B CTDIN/INT1 RB1 AN8 C1INB P1B CTDIN INT1 RB2/CANTX/C1OUT P1C/CTED1/INT2 RB2 CANTX C1OUT P1C CTED1 INT2 RB3/CANRX/C2OUT P1D/CTED2/INT3 ...
Page 23
... PGD T3G RX2 DT2 KBI3 Legend: CMOS = CMOS compatible input or output ST = Schmitt Trigger input with CMOS levels I = Input P = Power 2011 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC18F66K80 FAMILY Pin Buffer Type Type I/O ST/ Digital I/O. CMOS I Analog Analog Input 9. I Analog Comparator 2 Input A. ...
Page 24
... PIC18F66K80 FAMILY TABLE 1-4: PIC18F2XK80 I/O DESCRIPTIONS (CONTINUED) Pin Number SSOP/ Pin Name QFN SPDIP/ SOIC RC0/SOSCO/SCLKI 8 11 RC0 SOSCO SCLKI RC1/SOSCI 9 12 RC1 SOSCI RC2/T1G/CCP2 10 13 RC2 T1G CCP2 RC3/REFO/SCL/SCK 11 14 RC3 REFO SCL SCK RC4/SDA/SDI 12 15 RC4 SDA SDI ...
Page 25
... DDCORE V CAP Legend: CMOS = CMOS compatible input or output ST = Schmitt Trigger input with CMOS levels I = Input P = Power 2011 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC18F66K80 FAMILY Pin Buffer Type Type I/O ST/ Digital I/O. CMOS I ST CAN bus RX EUSART asynchronous receive. I/O ST EUSART synchronous data (see related TX2/CK2). ...
Page 26
... PIC18F66K80 FAMILY TABLE 1-5: PIC18F4XK80 PINOUT I/O DESCRIPTIONS Pin Number Pin Name QFN/ PDIP TQFP MCLR/RE3 1 18 MCLR RE3 OSC1/CLKIN/RA7 13 30 OSC1 CLKIN RA7 OSC2/CLKOUT/RA6 14 31 OSC2 CLKOUT RA6 2 2 Legend: I C™ C/SMBus input buffer ST = Schmitt Trigger input with CMOS levels ...
Page 27
... Legend: I C™ C/SMBus input buffer ST = Schmitt Trigger input with CMOS levels I = Input P = Power 2011 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC18F66K80 FAMILY Pin Buffer Type Type PORTA is a bidirectional I/O port. I/O ST/ General purpose I/O pin. CMOS O Analog Comparator reference voltage output. ...
Page 28
... PIC18F66K80 FAMILY TABLE 1-5: PIC18F4XK80 PINOUT I/O DESCRIPTIONS (CONTINUED) Pin Number Pin Name QFN/ PDIP TQFP RB0/AN10/FLT0/INT0 33 8 RB0 AN10 FLT0 INT0 RB1/AN8/CTDIN/INT1 34 9 RB1 AN8 CTDIN INT1 RB2/CANTX/CTED1 INT2 RB2 CANTX CTED1 INT2 RB3/CANRX/CTED2 INT3 RB3 CANRX CTED2 INT3 RB4/AN9/CTPLS/KBI0 ...
Page 29
... KBI3 2 2 Legend: I C™ C/SMBus input buffer ST = Schmitt Trigger input with CMOS levels I = Input P = Power 2011 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC18F66K80 FAMILY Pin Buffer Type Type I/O ST/ Digital I/O. CMOS I ST In-Circuit Debugger and ICSP™ programming clock input pin. ...
Page 30
... PIC18F66K80 FAMILY TABLE 1-5: PIC18F4XK80 PINOUT I/O DESCRIPTIONS (CONTINUED) Pin Number Pin Name QFN/ PDIP TQFP RC0/SOSCO/SCLKI 15 32 RC0 SOSCO SCLKI RC1/SOSCI 16 35 RC1 SOSCI RC2/T1G/CCP2 17 36 RC2 T1G CCP2 RC3/REFO/SCL/SCK 18 37 RC3 REFO SCL SCK RC4/SDA/SDI 23 42 RC4 SDA SDI ...
Page 31
... CANRX RX1 DT1 CCP4 2 2 Legend: I C™ C/SMBus input buffer ST = Schmitt Trigger input with CMOS levels I = Input P = Power 2011 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC18F66K80 FAMILY Pin Buffer Type Type I/O ST/ Digital I/O. CMOS I ST CAN bus RX EUSART asynchronous receive. I/O ST EUSART synchronous data (see related TX2/CK2) ...
Page 32
... PIC18F66K80 FAMILY TABLE 1-5: PIC18F4XK80 PINOUT I/O DESCRIPTIONS (CONTINUED) Pin Number Pin Name QFN/ PDIP TQFP RD0/C1INA/PSP0 19 38 RD0 C1INA PSP0 RD1/C1INB/PSP1 20 39 RD1 C1INB PSP1 RD2/C2INA/PSP2 21 40 RD2 C2INA PSP2 RD3/C2INB/CTMUI PSP3 RD3 C2INB CTMUI PSP3 RD4/ECCP1/P1A/PSP4 27 2 RD4 ECCP1 ...
Page 33
... CS RE3 2 2 Legend: I C™ C/SMBus input buffer ST = Schmitt Trigger input with CMOS levels I = Input P = Power 2011 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC18F66K80 FAMILY Pin Buffer Type Type I/O ST/ Digital I/O. CMOS I ST EUSART asynchronous transmit. I/O ST EUSART synchronous clock (see related RX2/DT2). ...
Page 34
... PIC18F66K80 FAMILY TABLE 1-5: PIC18F4XK80 PINOUT I/O DESCRIPTIONS (CONTINUED) Pin Number Pin Name QFN/ PDIP TQFP DDCORE CAP V DDCORE V CAP Legend: I C™ C/SMBus input buffer ST = Schmitt Trigger input with CMOS levels I = Input P = Power DS39977C-page 34 Pin Buffer Type Type P Ground reference for logic and I/O pins. ...
Page 35
... Legend: I C™ C/SMBus input buffer ST = Schmitt Trigger input with CMOS levels I = Input P = Power 2011 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC18F66K80 FAMILY Buffer Description Type ST Master Clear (input) or programming voltage (input).This pin is an active-low Reset to the device. ST General purpose, input only pin. ST Oscillator crystal input ...
Page 36
... PIC18F66K80 FAMILY TABLE 1-6: PIC18F6XK80 PINOUT I/O DESCRIPTIONS (CONTINUED) Pin Pin Pin Name Num Type RA0/CV /AN0/ 29 REF ULPWU RA0 I REF AN0 I ULPWU I RA1/AN1/C1INC 30 RA1 I/O AN1 I C1INC I RA2/V -/AN2/C2INC 31 REF RA2 I REF AN2 I C2INC I RA3/V +/AN3 32 REF RA3 I REF AN3 ...
Page 37
... Legend: I C™ C/SMBus input buffer ST = Schmitt Trigger input with CMOS levels I = Input P = Power 2011 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC18F66K80 FAMILY Buffer Description Type PORTB is a bidirectional I/O port. ST/ Digital I/O. CMOS Analog Analog Input 10. ST Enhanced PWM Fault input for ECCP1. ...
Page 38
... PIC18F66K80 FAMILY TABLE 1-6: PIC18F6XK80 PINOUT I/O DESCRIPTIONS (CONTINUED) Pin Pin Pin Name Num Type RB6/PGC/KBI2 22 RB6 I/O PGC I KBI2 I RB7/PGD/T3G/KBI3 23 RB7 I/O PGD I/O T3G I KBI3 Legend: I C™ C/SMBus input buffer ST = Schmitt Trigger input with CMOS levels I = Input P = Power ...
Page 39
... CCP4 I Legend: I C™ C/SMBus input buffer ST = Schmitt Trigger input with CMOS levels I = Input P = Power 2011 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC18F66K80 FAMILY Buffer Description Type PORTC is a bidirectional I/O port. ST/ Digital I/O. CMOS ST Timer1 oscillator output. ST Digital SOSC input. ST/ Digital I/O. ...
Page 40
... PIC18F66K80 FAMILY TABLE 1-6: PIC18F6XK80 PINOUT I/O DESCRIPTIONS (CONTINUED) Pin Pin Pin Name Num Type RD0/C1INA/PSP0 54 RD0 I/O C1INA I PSP0 I/O RD1/C1INB/PSP1 55 RD1 I/O C1INB I PSP1 I/O RD2/C2INA/PSP2 58 RD2 I/O C2INA I PSP2 I/O RD3/C2INB/CTMUI/ 59 PSP3 RD3 I/O C2INB I CTMUI O PSP3 I/O ...
Page 41
... PSP7 I Legend: I C™ C/SMBus input buffer ST = Schmitt Trigger input with CMOS levels I = Input P = Power 2011 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC18F66K80 FAMILY Buffer Description Type ST/ Digital I/O. CMOS CMOS Enhanced PWM1 Output C. ST/ Parallel Slave Port data. CMOS ST/ Digital I/O. CMOS CMOS Enhanced PWM1 Output D ...
Page 42
... PIC18F66K80 FAMILY TABLE 1-6: PIC18F6XK80 PINOUT I/O DESCRIPTIONS (CONTINUED) Pin Pin Pin Name Num Type RE0/AN5/RD 37 RE0 I/O AN5 RE1/AN6/C1OUT/WR 38 RE1 I/O AN6 I C1OUT RE2/AN7/C2OUT/CS 39 RE2 I/O AN7 I C2OUT RE3 RE4/CANRX 27 RE4 I/O CANRX I RE5/CANTX 24 RE5 I/O CANTX O RE6/RX2/DT2 60 RE6 I/O ...
Page 43
... Legend: I C™ C/SMBus input buffer ST = Schmitt Trigger input with CMOS levels I = Input P = Power 2011 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC18F66K80 FAMILY Buffer Description Type PORTF is a bidirectional I/O port. ST/ Digital I/O. CMOS CMOS Modulator source input. ST/ Digital I/O. CMOS ST/ Digital I/O ...
Page 44
... PIC18F66K80 FAMILY TABLE 1-6: PIC18F6XK80 PINOUT I/O DESCRIPTIONS (CONTINUED) Pin Pin Pin Name Num Type RG0/RX1/DT1 6 RG0 I/O RX1 I DT1 I/O RG1/CANTX2 7 RG1 I/O CANTX2 O RG2/T3CKI 11 RG2 I/O T3CKI I RG3/TX1/CK1 12 RG3 I/O TX1 O CK1 I/O RG4/T0CKI 18 RG4 I/O T0CKI Legend: I C™ ...
Page 45
... C™ C/SMBus input buffer ST = Schmitt Trigger input with CMOS levels I = Input P = Power 2011 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC18F66K80 FAMILY Buffer Description Type P Ground reference for logic and I/O pins. P Ground reference for logic and I/O pins. P Ground reference for analog modules. ...
Page 46
... PIC18F66K80 FAMILY NOTES: DS39977C-page 46 Preliminary 2011 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 47
... GUIDELINES FOR GETTING STARTED WITH PIC18FXXKXX MICROCONTROLLERS 2.1 Basic Connection Requirements Getting started with the PIC18F66K80 family family of 8-bit microcontrollers requires attention to a minimal set of device pin connections before proceeding with development. The following pins must always be connected: • All V ...
Page 48
... PIC18F66K80 FAMILY 2.2 Power Supply Pins 2.2.1 DECOUPLING CAPACITORS The use of decoupling capacitors on every pair of power supply pins, such required. SS Consider the following criteria when using decoupling capacitors: • Value and type of capacitor: A 0.1 F (100 nF), 10-20V capacitor is recommended. The capacitor should be a low-ESR device, with a resonance frequency in the range of 200 MHz and higher ...
Page 49
... PIC18FXXKXX devices permanently enable the voltage regulator. These devices require a 10 F capacitor on the V /V pin. CAP DDCORE For details on all members of the PIC18F66K80 family, see Section 28.3 “On-Chip Voltage Regulator”. 2011 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC18F66K80 FAMILY FIGURE 2- ...
Page 50
... PIC18F66K80 FAMILY TABLE 2-1 SUITABLE CAPACITOR EQUIVALENTS Make Part # TDK C3216X7R1C106K TDK C3216X5R1C106K Panasonic ECJ-3YX1C106K Panasonic ECJ-4YB1C106K Murata GRM32DR71C106KA01L Murata GRM31CR61C106KC31L 2.6 External Oscillator Pins Many microcontrollers have options for at least two oscillators: a high-frequency primary oscillator and a low-frequency secondary oscillator Section 3.0 “Oscillator Configurations” ...
Page 51
... Unused I/O pins should be configured as outputs and driven to a logic low state. Alternatively, connect a 1 kΩ kΩ resistor unused pins and drive the SS output to logic low. 2011 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC18F66K80 FAMILY FIGURE 2-4: Single-Sided and In-Line Layouts: Copper Pour (tied to ground) Devices” Primary ...
Page 52
... PIC18F66K80 FAMILY NOTES: DS39977C-page 52 Preliminary 2011 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 53
... OSCILLATOR CONFIGURATIONS 3.1 Oscillator Types The PIC18F66K80 family of devices can be operated in the following oscillator modes: • EC External Clock, RA6 Available • ECIO External Clock, Clock Out RA6 (F on RA6) • HS High-Speed Crystal/Resonator • XT Crystal/Resonator • LP Low-Power Crystal • RC External Resistor/Capacitor, RA6 Available • ...
Page 54
... EC1IO) EC2 (medium power) (EC2 & EC2IO) EC3 (high power) (EC3 & EC3IO) HS1 (medium power) HS2 (high power (External) INTIO FIGURE 3-1: PIC18F66K80 FAMILY CLOCK DIAGRAM SOSCO SOSCI OSC2 OSC1 HF-INTOSC 16 MHz to 31 kHz MF-INTOSC 500 kHz to 31 kHz LF-INTOSC ...
Page 55
... INTSRC = OSCTUNE<7> and MFIOSEL = OSCCON2<0>. 5: Lowest power option for an internal source. 6: 2011 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC18F66K80 FAMILY The OSCTUNE register tuning and operation of the internal oscillator block. It also implements the PLLEN bit which controls the operation of the Phase Locked Loop (PLL) (see Frequency Multiplier” ...
Page 56
... PIC18F66K80 FAMILY REGISTER 3-1: OSCCON: OSCILLATOR CONTROL REGISTER (CONTINUED) bit 2 HFIOFS: HF-INTOSC Frequency Stable bit 1 = HF-INTOSC oscillator frequency is stable 0 = HF-INTOSC oscillator frequency is not stable bit 1-0 SCS<1:0>: System Clock Select bits 1x = Internal oscillator block (LF-INTOSC, MF-INTOSC or HF-INTOSC SOSC oscillator 00 = Default primary oscillator (OSC1/OSC2 or HF-INTOSC with or without PLL. Defined by the FOSC< ...
Page 57
... Center frequency; fast RC oscillator is running at the calibrated frequency 111111 • • • • 100000 = Minimum frequency 2011 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC18F66K80 FAMILY R/W-0 R/W-0 R/W-0 TUN4 TUN3 TUN2 U = Unimplemented bit, read as ‘0’ ‘0’ = Bit is cleared Preliminary ...
Page 58
... Monitor. The internal oscillator block is discussed in more detail in Section 3.6 “Internal Oscillator Block”. The PIC18F66K80 family includes features that allow the device clock source to be switched from the main oscillator, chosen by device configuration, to one of the alternate clock sources. When an alternate clock source is enabled, various power-managed operating modes are available ...
Page 59
... SCS<1:0> bits, at any given time. 3.3.3 OSCILLATOR TRANSITIONS PIC18F66K80 family devices contain circuitry to prevent clock “glitches” when switching between clock sources. A short pause in the device clock occurs during the clock switch. The length of this pause is the sum of two cycles of the old clock source and three to four cycles of the new clock source ...
Page 60
... PIC18F66K80 FAMILY 3.5 External Oscillator Modes 3.5.1 CRYSTAL OSCILLATOR/CERAMIC RESONATORS (HS MODES HSPLL Oscillator modes, a crystal or ceramic resonator is connected to the OSC1 and OSC2 pins to establish oscillation. Figure 3-4 shows connections. The oscillator design requires the use of a crystal rated for parallel resonant operation. ...
Page 61
... EMI due to high-frequency crystals or users who require higher clock speeds from an internal oscillator. 2011 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC18F66K80 FAMILY 3.5.3.1 HSPLL and ECPLL Modes The HSPLL and ECPLL modes provide the ability to selectively run the device at four times the external oscillating source to produce frequencies MHz ...
Page 62
... PIC18F66K80 FAMILY 3.6 Internal Oscillator Block The PIC18F66K80 family of devices includes an internal oscillator block which generates two different clock signals. Either clock can be used as the microcontroller’s clock source, which may eliminate the need for an external oscillator circuit on the OSC1 and/or OSC2 pins. ...
Page 63
... Reference Clock Output or tempera addition to the F oscillator modes, the device clock in the PIC18F66K80 family can also be configured to provide a reference clock output signal to a port pin. This feature is avail- able in all oscillator configurations and allows the user to select a greater range of clock submultiples to drive external devices in the application ...
Page 64
... PIC18F66K80 FAMILY REGISTER 3-4: REFOCON: REFERENCE OSCILLATOR CONTROL REGISTER R/W-0 U-0 R/W-0 ROON — ROSSLP bit 7 Legend Readable bit W = Writable bit -n = Value at POR ‘1’ = Bit is set bit 7 ROON: Reference Oscillator Output Enable bit 1 = Reference oscillator output available on REFO pin 0 = Reference oscillator output disabled bit 6 Unimplemented: Read as ‘ ...
Page 65
... I/O pin, RA6, direction controlled by TRISA<6> See Note: Section 5.0 “Reset” 2011 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC18F66K80 FAMILY 3.9 Power-up Delays Power-up delays are controlled by two timers, so that no external Reset circuitry is required for most applica- tions. The delays ensure that the device is kept in ...
Page 66
... PIC18F66K80 FAMILY NOTES: DS39977C-page 66 Preliminary 2011 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 67
... POWER-MANAGED MODES The PIC18F66K80 family of devices offers a total of seven operating modes for more efficient power man- agement. These modes provide a variety of options for selective power conservation in applications where resources may be limited (such as battery-powered devices). There are three categories of power-managed mode: • ...
Page 68
... PIC18F66K80 FAMILY 4.1.3 CLOCK TRANSITIONS AND STATUS INDICATORS The length of the transition between clock sources is the sum of two cycles of the old clock source and three to four cycles of the new clock source. This formula assumes that the new clock source is stable. The HF- INTOSC and MF-INTOSC are termed as INTOSC in this chapter ...
Page 69
... PRI_RUN and RC_RUN modes during execution. Entering or exiting RC_RUN mode, how- ever, causes a clock switch delay. Therefore, if the primary clock source is the internal oscillator block, using RC_RUN mode is not recommended. 2011 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC18F66K80 FAMILY n-1 n (1) ...
Page 70
... PIC18F66K80 FAMILY If the IRCF bits and the INTSRC bit are all clear, the INTOSC output (HF-INTOSC/MF-INTOSC) is not enabled and the HFIOFS and MFIOFS bits will remain clear. There will be no indication of the current clock source. The LF-INTOSC source is providing the device clocks ...
Page 71
... Output CPU Clock Peripheral Clock Program Counter SCS<1:0> Bits Changed Note1 1024 (approx). These intervals are not shown to scale. OST OSC PLL 2: Clock transition typically occurs within 2-4 T 2011 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC18F66K80 FAMILY n-1 n (1) Clock Transition OSC (1) OST ...
Page 72
... PIC18F66K80 FAMILY 4.3 Sleep Mode The power-managed Sleep mode in the PIC18F66K80 family of devices is identical to the legacy Sleep mode offered in all other PIC devices entered by clearing the IDLEN bit (the default state on device Reset) and executing the SLEEP instruction. This shuts down the ...
Page 73
... Peripheral Clock Program Counter Wake Event 2011 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC18F66K80 FAMILY 4.4.2 SEC_IDLE MODE In SEC_IDLE mode, the CPU is disabled but the peripherals continue to be clocked from the SOSC oscillator. This mode is entered from SEC_RUN by set- ting the IDLEN bit and executing a SLEEP instruction. If the device is in another Run mode, set the IDLEN bit first, then set the SCS< ...
Page 74
... Many peripheral modules have a corresponding PMD bit. There are three PMD registers in PIC18F66K80 family devices: PMD0, PMD1 and PMD2. These registers have bits associated with each module for disabling or enabling a particular peripheral ...
Page 75
... CMP1MD: Comparator 1 Module Disable bit 1 = The Comparator 1 module is disabled. All Comparator 1 registers are held in Reset and are not writable The Comparator 1 module is enabled Only implemented on devices with 64 pins (PIC18F6XK80, PIC18LF6XK80). Note 1: 2011 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC18F66K80 FAMILY U-0 R/W-0 R/W-0 — MODMD ECANMD U = Unimplemented bit, read as ‘ ...
Page 76
... PIC18F66K80 FAMILY REGISTER 4-2: PMD1: PERIPHERAL MODULE DISABLE REGISTER 1 R/W-0 R/W-0 R/W-0 (1) PSPMD CTMUMD ADCMD bit 7 Legend Readable bit W = Writable bit -n = Value at POR ‘1’ = Bit is set bit 7 PSPMD: Peripheral Module Disable bit 1 = The PSP module is disabled. All PSP registers are held in Reset and are not writable. ...
Page 77
... The USART1 module is enabled bit 0 SSPMD: MSSP Module Disable bit 1 = The MSSP module is disabled. All SSP registers are held in Reset and are not writable The MSSP module is enabled 2011 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC18F66K80 FAMILY R/W-0 R/W-0 R/W-0 CCP2MD CCP1MD UART2MD U = Unimplemented bit, read as ‘ ...
Page 78
... PIC18F66K80 FAMILY 4.6 Exiting Idle and Sleep Modes An exit from Sleep mode or any of the Idle modes is triggered by an interrupt, a Reset or a WDT time-out. This section discusses the triggers that cause exits from power-managed modes. The clocking subsystem actions are discussed in each of the power-managed modes (see Section 4.2 “ ...
Page 79
... Sleep OSCCONbits.IDLEN = 0; //Enter Sleep Mode // Sleep(); //for sleep, execution will //resume here 2011 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC18F66K80 FAMILY A series resistor, between RA0 and the external capacitor, provides overcurrent protection for the RA0/ CV /AN0/ULPWU REF calibration of the time-out (see FIGURE 4-9: ...
Page 80
... PIC18F66K80 FAMILY TABLE 4-4: EXIT DELAY ON WAKE-UP BY RESET FROM SLEEP MODE OR ANY IDLE MODE (BY CLOCK SOURCES) Power-Managed Mode PRI_IDLE mode SEC_IDLE mode RC_IDLE mode Sleep mode T (Parameter 38, Table Note 1: CSD runs concurrently with any other required delays (see Includes postscaler derived frequencies. On Reset, INTOSC defaults to HF-INTOSC at 8 MHz. ...
Page 81
... RESET The PIC18F66K80 family devices differentiate between various kinds of Reset: a) Power-on Reset (POR) b) MCLR Reset during Normal Operation c) MCLR Reset during Power-Managed modes d) Watchdog Timer (WDT) Reset (during execution) e) Configuration Mismatch (CM) Reset f) Programmable Brown-out Reset (BOR) g) RESET Instruction h) Stack Full Reset ...
Page 82
... PIC18F66K80 FAMILY REGISTER 5-1: RCON: RESET CONTROL REGISTER (1) R/W-0 R/W-1 R/W-1 IPEN SBOREN CM bit 7 Legend Readable bit W = Writable bit -n = Value at POR ‘1’ = Bit is set bit 7 IPEN: Interrupt Priority Enable bit 1 = Enable priority levels on interrupts 0 = Disable priority levels on interrupts (PIC16CXXX Compatibility mode) ...
Page 83
... The MCLR pin is not driven low by any internal Resets, including the WDT. In PIC18F66K80 family devices, the MCLR input can be disabled with the MCLRE Configuration bit. When MCLR is disabled, the pin becomes a digital input. See Section 11.6 “PORTE, TRISE and LATE Registers” ...
Page 84
... PIC18F66K80 FAMILY 5.4 Brown-out Reset (BOR) The PIC18F66K80 family has four BOR Power modes: • High-Power BOR • Medium Power BOR • Low-Power BOR • Zero-Power BOR Each power mode is selected by the BORPWR<1:0> setting (CONFIG2L<6:5>). For low, medium and high-power BOR, the module monitors the V ing on the BORV< ...
Page 85
... Oscillator Start-up Timer (OST) • PLL Lock Time-out 5.6.1 POWER-UP TIMER (PWRT) The Power-up Timer (PWRT) of the PIC18F66K80 family devices is an 11-bit counter which uses the INTOSC source as the clock input. This yields an approximate time interval of 2048 x 32 65.6 ms. ...
Page 86
... PIC18F66K80 FAMILY 5.6.2 OSCILLATOR START-UP TIMER (OST) The Oscillator Start-up Timer (OST) provides a 1024 oscillator cycle (from OSC1 input) delay after the PWRT delay is over (Parameter 33). This ensures that the crystal oscillator or resonator has started and stabilized. The OST time-out is invoked only for XT, LP, HS and HSPLL modes and only on Power-on Reset or on exit from most power-managed modes ...
Page 87
... TIME-OUT SEQUENCE ON POWER-UP (MCLR NOT TIED MCLR INTERNAL POR PWRT TIME-OUT OST TIME-OUT INTERNAL RESET FIGURE 5-6: SLOW RISE TIME (MCLR TIED MCLR INTERNAL POR PWRT TIME-OUT OST TIME-OUT INTERNAL RESET 2011 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC18F66K80 FAMILY T PWRT T OST T PWRT T OST , V RISE > PWRT ...
Page 88
... PIC18F66K80 FAMILY FIGURE 5-7: TIME-OUT SEQUENCE ON POR W/PLL ENABLED (MCLR TIED MCLR INTERNAL POR PWRT TIME-OUT OST TIME-OUT PLL TIME-OUT INTERNAL RESET T = 1024 clock cycles. Note: OST max. First three stages of the PWRT timer. T PLL DS39977C-page 88 T PWRT T OST T PLL Preliminary ...
Page 89
... Reset state is ‘ 1 ’ for POR and unchanged for all other Resets when software BOR is enabled 2: (BOREN<1:0> Configuration bits = 01 and SBOREN = 1 ); otherwise, the Reset state is ‘ 0 ’. 2011 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC18F66K80 FAMILY ferent Reset situations, as indicated in These bits are used in software to determine the nature of the Reset. ...
Page 90
... PIC18F66K80 FAMILY TABLE 5-4: INITIALIZATION CONDITIONS FOR ALL REGISTERS Register Applicable Devices TOSU PIC18F2XK80 PIC18F4XK80 TOSH PIC18F2XK80 PIC18F4XK80 TOSL PIC18F2XK80 PIC18F4XK80 STKPTR PIC18F2XK80 PIC18F4XK80 PCLATU PIC18F2XK80 PIC18F4XK80 PCLATH PIC18F2XK80 PIC18F4XK80 PCL PIC18F2XK80 PIC18F4XK80 TBLPTRU PIC18F2XK80 PIC18F4XK80 TBLPTRH PIC18F2XK80 PIC18F4XK80 TBLPTRL PIC18F2XK80 ...
Page 91
... PORTA pins, they are disabled and read ‘0’. This register reads all ‘0’s until the ECAN™ technology is set up in Mode 1 or Mode 2. 6: 2011 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC18F66K80 FAMILY Power-on MCLR Resets, Reset, WDT Reset, Brown-out ...
Page 92
... PIC18F66K80 FAMILY TABLE 5-4: INITIALIZATION CONDITIONS FOR ALL REGISTERS (CONTINUED) Register Applicable Devices TXSTA2 PIC18F2XK80 PIC18F4XK80 BAUDCON2 PIC18F2XK80 PIC18F4XK80 IPR4 PIC18F2XK80 PIC18F4XK80 PIR4 PIC18F2XK80 PIC18F4XK80 PIE4 PIC18F2XK80 PIC18F4XK80 CVRCON PIC18F2XK80 PIC18F4XK80 CMSTAT PIC18F2XK80 PIC18F4XK80 TMR3H PIC18F2XK80 PIC18F4XK80 TMR3L PIC18F2XK80 PIC18F4XK80 T3CON ...
Page 93
... PORTA pins, they are disabled and read ‘0’. This register reads all ‘0’s until the ECAN™ technology is set up in Mode 1 or Mode 2. 6: 2011 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC18F66K80 FAMILY Power-on MCLR Resets, Reset, WDT Reset, Brown-out ...
Page 94
... PIC18F66K80 FAMILY TABLE 5-4: INITIALIZATION CONDITIONS FOR ALL REGISTERS (CONTINUED) Register Applicable Devices TXREG2 PIC18F2XK80 PIC18F4XK80 IPR5 PIC18F2XK80 PIC18F4XK80 PIR5 PIC18F2XK80 PIC18F4XK80 PIE5 PIC18F2XK80 PIC18F4XK80 EEADRH PIC18F2XK80 PIC18F4XK80 EEADR PIC18F2XK80 PIC18F4XK80 EEDATA PIC18F2XK80 PIC18F4XK80 ECANCON PIC18F2XK80 PIC18F4XK80 COMSTAT PIC18F2XK80 PIC18F4XK80 CIOCON ...
Page 95
... PORTA pins, they are disabled and read ‘0’. This register reads all ‘0’s until the ECAN™ technology is set up in Mode 1 or Mode 2. 6: 2011 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC18F66K80 FAMILY Power-on MCLR Resets, Reset, WDT Reset, Brown-out ...
Page 96
... PIC18F66K80 FAMILY TABLE 5-4: INITIALIZATION CONDITIONS FOR ALL REGISTERS (CONTINUED) Register Applicable Devices RXB1EIDL PIC18F2XK80 PIC18F4XK80 RXB1EIDH PIC18F2XK80 PIC18F4XK80 RXB1SIDL PIC18F2XK80 PIC18F4XK80 RXB1SIDH PIC18F2XK80 PIC18F4XK80 RXB1CON PIC18F2XK80 PIC18F4XK80 CANCON_RO1 PIC18F2XK80 PIC18F4XK80 CANSTAT_RO1 PIC18F2XK80 PIC18F4XK80 TXB0D7 PIC18F2XK80 PIC18F4XK80 TXB0D6 PIC18F2XK80 PIC18F4XK80 TXB0D5 ...
Page 97
... PORTA pins, they are disabled and read ‘0’. This register reads all ‘0’s until the ECAN™ technology is set up in Mode 1 or Mode 2. 6: 2011 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC18F66K80 FAMILY Power-on MCLR Resets, Reset, WDT Reset, Brown-out ...
Page 98
... PIC18F66K80 FAMILY TABLE 5-4: INITIALIZATION CONDITIONS FOR ALL REGISTERS (CONTINUED) Register Applicable Devices RXF4SIDH PIC18F2XK80 PIC18F4XK80 RXF3EIDL PIC18F2XK80 PIC18F4XK80 RXF3EIDH PIC18F2XK80 PIC18F4XK80 RXF3SIDL PIC18F2XK80 PIC18F4XK80 RXF3SIDH PIC18F2XK80 PIC18F4XK80 RXF2EIDL PIC18F2XK80 PIC18F4XK80 RXF2EIDH PIC18F2XK80 PIC18F4XK80 RXF2SIDL PIC18F2XK80 PIC18F4XK80 RXF2SIDH PIC18F2XK80 PIC18F4XK80 RXF1EIDL ...
Page 99
... PORTA pins, they are disabled and read ‘0’. This register reads all ‘0’s until the ECAN™ technology is set up in Mode 1 or Mode 2. 6: 2011 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC18F66K80 FAMILY Power-on MCLR Resets, Reset, WDT Reset, Brown-out ...
Page 100
... PIC18F66K80 FAMILY TABLE 5-4: INITIALIZATION CONDITIONS FOR ALL REGISTERS (CONTINUED) Register Applicable Devices B2D5 PIC18F2XK80 PIC18F4XK80 B2D4 PIC18F2XK80 PIC18F4XK80 B2D3 PIC18F2XK80 PIC18F4XK80 B2D2 PIC18F2XK80 PIC18F4XK80 B2D1 PIC18F2XK80 PIC18F4XK80 B2D0 PIC18F2XK80 PIC18F4XK80 B2DLC PIC18F2XK80 PIC18F4XK80 B2EIDL PIC18F2XK80 PIC18F4XK80 B2EIDH PIC18F2XK80 PIC18F4XK80 B2SIDL ...
Page 101
... PORTA pins, they are disabled and read ‘0’. This register reads all ‘0’s until the ECAN™ technology is set up in Mode 1 or Mode 2. 6: 2011 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC18F66K80 FAMILY Power-on MCLR Resets, Reset, WDT Reset, Brown-out ...
Page 102
... PIC18F66K80 FAMILY TABLE 5-4: INITIALIZATION CONDITIONS FOR ALL REGISTERS (CONTINUED) Register Applicable Devices RXF13EIDH PIC18F2XK80 PIC18F4XK80 RXF13SIDL PIC18F2XK80 PIC18F4XK80 RXF13SIDH PIC18F2XK80 PIC18F4XK80 RXF12EIDL PIC18F2XK80 PIC18F4XK80 RXF12EIDH PIC18F2XK80 PIC18F4XK80 RXF12SIDL PIC18F2XK80 PIC18F4XK80 RXF12SIDH PIC18F2XK80 PIC18F4XK80 RXF11EIDL PIC18F2XK80 PIC18F4XK80 RXF11EIDH PIC18F2XK80 PIC18F4XK80 RXF11SIDL ...
Page 103
... PORTA pins, they are disabled and read ‘0’. This register reads all ‘0’s until the ECAN™ technology is set up in Mode 1 or Mode 2. 6: 2011 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC18F66K80 FAMILY Power-on MCLR Resets, Reset, WDT Reset, Brown-out ...
Page 104
... PIC18F66K80 FAMILY NOTES: DS39977C-page 104 Preliminary 2011 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 105
... MEMORY ORGANIZATION PIC18F66K80 family devices have these types of memory: • Program Memory • Data RAM • Data EEPROM As Harvard architecture devices, the data and program memories use separate busses. concurrent access of the two memory spaces. FIGURE 6-1: MEMORY MAPS FOR PIC18F66K80 FAMILY DEVICES ...
Page 106
... Accessing a location between the upper boundary of the physically implemented memory and the 2-Mbyte address will return all ‘ 0 ’s (a NOP instruction). The entire PIC18F66K80 family offers a range of on-chip Flash program memory sizes, from 32 Kbytes (16,384 single-word instructions Kbytes (32,768 single-word instructions). ...
Page 107
... Microchip Technology Inc. PIC18F66K80 FAMILY The stack operates as a 31-word by 21-bit RAM and a 5-bit Stack Pointer, STKPTR. The stack space is not part of either program or data space. The Stack Pointer is readable and writable and the address on the top of the stack is readable and writable through the Top-of-Stack (TOS) Special Function Registers ...
Page 108
... PIC18F66K80 FAMILY 6.1.3.2 Return Stack Pointer (STKPTR) The STKPTR register (Register 6-1) contains the Stack Pointer value, the STKFUL (Stack Full) status bit and the STKUNF (Stack Underflow) status bits. The value of the Stack Pointer can be 0 through 31. The Stack Pointer increments before values are pushed onto the stack and decrements after values are popped off of the stack ...
Page 109
... SUB1 RETURN FAST ;RESTORE VALUES SAVED ;IN FAST REGISTER STACK 2011 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC18F66K80 FAMILY 6.1.5 LOOK-UP TABLES IN PROGRAM MEMORY There may be programming situations that require the creation of data structures, or look-up tables, in program memory. For PIC18 devices, look-up tables can be implemented in two ways: • ...
Page 110
... PIC18F66K80 FAMILY 6.2 PIC18 Instruction Cycle 6.2.1 CLOCKING SCHEME The microcontroller clock input, whether from an internal or external source, is internally divided by four to generate four non-overlapping quadrature clocks (Q1, Q2, Q3 and Q4). Internally, the program counter is incremented on every Q1, with the instruction fetched from the program memory and latched into the Instruction Register (IR) during Q4 ...
Page 111
... ADDWF 2011 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC18F66K80 FAMILY The CALL and GOTO instructions have the absolute program memory address embedded into the instruc- tion. Since instructions are always stored on word boundaries, the data contained in the instruction is a word address. The word address is written to PC< ...
Page 112
... PIC18F66K80 FAMILY 6.3 Data Memory Organization The operation of some aspects of data Note: memory are changed when the PIC18 extended instruction set is enabled. See Section 6.6 “Data Memory and the Extended Instruction Set” information. The data memory in PIC18 devices is implemented as static RAM. Each register in the data memory has a 12-bit address, allowing up to 4,096 bytes of data memory ...
Page 113
... Addresses, E41h through F5Fh, are also used by SFRs, but are not part of the Access RAM. Note 1: Users must always use the complete address, or load the proper BSR value, to access these registers. 2011 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC18F66K80 FAMILY Data Memory Map 000h Access RAM 05Fh ...
Page 114
... PIC18F66K80 FAMILY FIGURE 6-7: USE OF THE BANK SELECT REGISTER (DIRECT ADDRESSING) (1) BSR (2) Bank Select The Access RAM bit of the instruction can be used to force an override of the selected bank (BSR<3:0>) Note 1: to the registers of the Access Bank. The MOVFF instruction embeds the entire 12-bit address in the instruction. ...
Page 115
... RAM. SFRs start at the top of data memory (FFFh) and extend downward to occupy all of Bank 15 (F00h to FFFh) and the top part of Bank 14 (EF4h to EFFh). A list of these registers is given in Table 6-2. TABLE 6-1: SPECIAL FUNCTION REGISTER MAP FOR PIC18F66K80 FAMILY Name Name Addr. Addr. FFFh TOSU FDFh ...
Page 116
... PIC18F66K80 FAMILY TABLE 6-1: SPECIAL FUNCTION REGISTER MAP FOR PIC18F66K80 FAMILY (CONTINUED) Name Name Addr. Addr. (5) F3Fh CANCON_RO0 F0Fh CANCON_RO3 F3Eh CANSTAT_RO0 (5) F0Eh CANSTAT_RO3 (5) (5) F3Dh RXB1D7 F0Dh TXB2D7 (5) (5) F3Ch RXB1D6 F0Ch TXB2D6 (5) (5) F3Bh RXB1D5 F0Bh TXB2D5 (5) (5) F3Ah ...
Page 117
... TABLE 6-2: PIC18F66K80 FAMILY REGISTER FILE SUMMARY Addr. File Name Bit 7 Bit 6 FFFh TOSU — — FFEh TOSH Top-of-Stack High Byte (TOS<15:8>) FFDh TOSL Top-of-Stack Low Byte (TOS<7:0>) FFCh STKPTR STKFUL STKUNF FFBh PCLATU — — FFAh PCLATH Holding Register for PC<15:8> ...
Page 118
... PIC18F66K80 FAMILY TABLE 6-2: PIC18F66K80 FAMILY REGISTER FILE SUMMARY (CONTINUED) Addr. File Name Bit 7 Bit 6 FCFh TMR1H Timer1 Register High Byte FCEh TMR1L Timer1 Register Low Bytes FCDh T1CON TMR1CS1 TMR1CS0 FCCh TMR2 Timer2 Register FCBh PR2 Timer2 Period Register FCAh T2CON — ...
Page 119
... TABLE 6-2: PIC18F66K80 FAMILY REGISTER FILE SUMMARY (CONTINUED) Addr. File Name Bit 7 Bit 6 F9Fh IPR1 PSPIP ADIP F9Eh PIR1 PSPIF ADIF F9Dh PIE1 PSPIE ADIE F9Ch PSTR1CON CMPL1 CMPL0 F9Bh OSCTUNE INTSRC PLLEN F9Ah REFOCON ROON — F99h CCPTMRS — — ...
Page 120
... PIC18F66K80 FAMILY TABLE 6-2: PIC18F66K80 FAMILY REGISTER FILE SUMMARY (CONTINUED) Addr. File Name Bit 7 Bit 6 F6Dh RXB0D7 RXB0D77 RXB0D76 F6Ch RXB0D6 RXB0D67 RXB0D66 F6Bh RXB0D5 RXB0D57 RXB0D56 F6Ah RXB0D4 RXB0D47 RXB0D46 F69h RXB0D3 RXB0D37 RXB0D36 F68h RXB0D2 RXB0D27 RXB0D26 F67h RXB0D1 ...
Page 121
... TABLE 6-2: PIC18F66K80 FAMILY REGISTER FILE SUMMARY (CONTINUED) Addr. File Name Bit 7 Bit 6 F3Bh RXB1D5 RXB1D57 RXB1D56 F3Ah RXB1D4 RXB1D47 RXB1D46 F39h RXB1D3 RXB1D37 RXB1D36 F38h RXB1D2 RXB1D27 RXB1D26 F37h RXB1D1 RXB1D17 RXB1D16 F36h RXB1D0 RXB1D07 RXB1D06 F35h RXB1DLC — RXRTR ...
Page 122
... PIC18F66K80 FAMILY TABLE 6-2: PIC18F66K80 FAMILY REGISTER FILE SUMMARY (CONTINUED) Addr. File Name Bit 7 Bit 6 F09h TXB2D3 TXB2D37 TXB2D36 F08h TXB2D2 TXB2D27 TXB2D26 F07h TXB2D1 TXB2D17 TXB2D16 F06h TXB2D0 TXB2D07 TXB2D06 F05h TXB2DLC — TXRTR F04h TXB2EIDL EID7 EID6 F03h TXB2EIDH ...
Page 123
... TABLE 6-2: PIC18F66K80 FAMILY REGISTER FILE SUMMARY (CONTINUED) Addr. File Name Bit 7 Bit 6 ED6h B5D0 B5D07 B5D06 ED5h B5DLC — TXRTR ED4h B5EIDL EID7 EID6 ED3h B5EIDH EID15 EID14 ED2h B5SIDL SID2 SID1 ED1h B5SIDH SID10 SID9 ED0h B5CON TXBIF TXABT ...
Page 124
... PIC18F66K80 FAMILY TABLE 6-2: PIC18F66K80 FAMILY REGISTER FILE SUMMARY (CONTINUED) Addr. File Name Bit 7 Bit 6 EA3h B2EIDH EID15 EID14 EA2h B2SIDL SID2 SID1 EA1h B2SIDH SID10 SID9 EA0h B2CON TXBIF TXABT E9Fh CANCON_RO8 CANCON_RO8 E9Eh CANSTAT_RO8 CANSTAT_RO8 E9Dh B1D7 B1D77 B1D76 ...
Page 125
... TABLE 6-2: PIC18F66K80 FAMILY REGISTER FILE SUMMARY (CONTINUED) Addr. File Name Bit 7 Bit 6 E72h RXFBCON1 CAN Buffer 3/2 Pointer Register 2011 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC18F66K80 FAMILY Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Preliminary Value on Bit 1 Bit 0 POR, BOR on page 101 DS39977C-page 125 ...
Page 126
... PIC18F66K80 FAMILY TABLE 6-2: PIC18F66K80 FAMILY REGISTER FILE SUMMARY (CONTINUED) Addr. File Name Bit 7 Bit 6 E71h RXFBCON0 CAN Buffer 1/0 Pointer Register E70h SDFLC — — E6Fh RXF15EIDL EID7 EID6 E6Eh RXF15EIDH EID15 EID14 E6Dh RXF15SIDL SID2 SID1 E6Ch RXF15SIDH SID10 ...
Page 127
... For rotate ( RRF, RLF ) instructions, this bit is loaded with either the high or low-order bit of the source register. 2011 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC18F66K80 FAMILY It is recommended, therefore, that only BCF, BSF, SWAPF, MOVFF and MOVWF instructions be used to 6-2, contains alter the STATUS register because these instructions do not affect the bits in the STATUS register ...
Page 128
... PIC18F66K80 FAMILY 6.4 Data Addressing Modes The execution of some instructions in the Note: core PIC18 instruction set are changed when the PIC18 extended instruction set is enabled. For more information, see Section 6.6 “Data Memory and the Extended Instruction Set” While the program memory can be addressed in only ...
Page 129
... FCCh will be added to that of the W register and stored back in FCCh. 2011 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC18F66K80 FAMILY mapped in the SFR space, but are not physically imple- mented. Reading or writing to a particular INDF register actually accesses its corresponding FSR register pair. ...
Page 130
... PIC18F66K80 FAMILY 6.4.3.2 FSR Registers and POSTINC, POSTDEC, PREINC and PLUSW In addition to the INDF operand, each FSR register pair also has four additional indirect operands. Like INDF, these are “virtual” registers that cannot be indirectly read or written to. Accessing these registers actually accesses the associated FSR register pair, but also performs a specific action on its stored value ...
Page 131
... Enabling the extended instruction set adds five additional two-word commands to the existing PIC18 instruction set: ADDFSR , CALLW , MOVSF , MOVSS and SUBFSR . These instructions are executed as described in Section 6.2.4 “Two-Word Instructions” 2011 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC18F66K80 FAMILY . Preliminary DS39977C-page 131 ...
Page 132
... PIC18F66K80 FAMILY 6.6 Data Memory and the Extended Instruction Set Enabling the PIC18 extended instruction set (XINST Configuration bit = 1 ) significantly changes certain aspects of data memory and its addressing. Using the Access Bank for many of the core PIC18 instructions introduces a new addressing mode for the data memory space ...
Page 133
... The bank is designated by the Bank Select Register (BSR). The address can be in any implemented bank in the data memory space. 2011 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC18F66K80 FAMILY 000h 060h Bank 0 100h Bank 1 through Bank 14 F00h ...
Page 134
... PIC18F66K80 FAMILY 6.6.3 MAPPING THE ACCESS BANK IN INDEXED LITERAL OFFSET MODE The use of Indexed Literal Offset Addressing mode effectively changes how the lower part of Access RAM (00h to 5Fh) is mapped. Rather than containing just the contents of the bottom part of Bank 0, this mode maps the contents from Bank 0 and a user-defined “ ...
Page 135
... Program Memory (TBLPTR) Note 1: Table Pointer register points to a byte in program memory. 2011 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC18F66K80 FAMILY 7.1 Table Reads and Table Writes In order to read and write program memory, there are two operations that allow the processor to move bytes ...
Page 136
... PIC18F66K80 FAMILY FIGURE 7-2: TABLE WRITE OPERATION (1) Table Pointer TBLPTRU TBLPTRH TBLPTRL Program Memory (TBLPTR) Note 1: Table Pointer actually points to one of 64 holding registers, the address of which is determined by TBLPTRL<5:0>. The process for physically writing data to the program memory array is discussed in Section 7.5 “Writing to Flash Program 7 ...
Page 137
... RD bit cannot be set when EEPGD = 1 or CFGS = Does not initiate an EEPROM read When a WRERR occurs, the EEPGD and CFGS bits are not cleared. This allows tracing of the error Note 1: condition. 2011 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC18F66K80 FAMILY R/W-0 R/W-x R/W-0 (1) FREE ...
Page 138
... PIC18F66K80 FAMILY 7.2.2 TABLAT – TABLE LATCH REGISTER The Table Latch (TABLAT eight-bit register mapped into the SFR space. The Table Latch register is used to hold 8-bit data during data transfers between program memory and data RAM. 7.2.3 TBLPTR – TABLE POINTER ...
Page 139
... MOVF TABLAT, W MOVF WORD_ODD 2011 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC18F66K80 FAMILY TBLPTR points to a byte address in program space. Executing TBLRD places the byte pointed to into TABLAT. In addition, TBLPTR can be modified automatically for the next table read operation. The internal program memory is typically organized by words ...
Page 140
... PIC18F66K80 FAMILY 7.4 Erasing Flash Program Memory The erase blocks are 32 words or 64 bytes. Word erase in the Flash array is not supported. When initiating an erase sequence from the micro- controller itself, a block of 64 bytes of program memory is erased. The Most Significant 16 bits of the TBLPTR< ...
Page 141
... Set the WREN to enable byte writes 8. Disable the interrupts. 2011 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC18F66K80 FAMILY The EEPROM on-chip timer controls the write time. The write/erase voltages are generated by an on-chip charge pump, rated to operate over the voltage range of the device. ...
Page 142
... PIC18F66K80 FAMILY EXAMPLE 7-3: WRITING TO FLASH PROGRAM MEMORY MOVLW SIZE_OF_BLOCK MOVWF COUNTER MOVLW BUFFER_ADDR_HIGH MOVWF FSR0H MOVLW BUFFER_ADDR_LOW MOVWF FSR0L MOVLW CODE_ADDR_UPPER MOVWF TBLPTRU MOVLW CODE_ADDR_HIGH MOVWF TBLPTRH MOVLW CODE_ADDR_LOW MOVWF TBLPTRL READ_BLOCK TBLRD*+ MOVF TABLAT, W MOVWF POSTINC0 DECFSZ COUNTER BRA ...
Page 143
... Legend: — = unimplemented, read as ‘ 0 ’. Shaded cells are not used during Flash/EEPROM access. Bit 21 of the TBLPTRU allows access to the device Configuration bits. Note 1: 2011 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC18F66K80 FAMILY ; point to Flash program memory ; access Flash program memory ; enable write to memory ...
Page 144
... PIC18F66K80 FAMILY NOTES: DS39977C-page 144 Preliminary 2011 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 145
... EEADRH holds the two MSbs of the address; the upper 6 bits are ignored. The 10-bit range of the pair can address a memory range of 1024 bytes (00h to 3FFh). 2011 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC18F66K80 FAMILY 8.2 EECON1 and EECON2 Registers Access to the data EEPROM is controlled by two registers: EECON1 and EECON2 ...
Page 146
... PIC18F66K80 FAMILY REGISTER 8-1: EECON1: DATA EEPROM CONTROL REGISTER 1 R/W-x R/W-x U-0 EEPGD CFGS — bit Settable bit Legend Readable bit W = Writable bit -n = Value at POR ‘1’ = Bit is set bit 7 EEPGD: Flash Program or Data EEPROM Memory Select bit 1 = Access Flash program memory ...
Page 147
... EEPROM. The WREN bit is not cleared by hardware. 2011 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC18F66K80 FAMILY After a write sequence has been initiated, EECON1, EEADRH:EEADR and EEDATA cannot be modified. The WR bit will be inhibited from being set unless the WREN bit is set ...
Page 148
... PIC18F66K80 FAMILY EXAMPLE 8-1: DATA EEPROM READ MOVLW DATA_EE_ADDRH MOVWF EEADRH MOVLW DATA_EE_ADDR MOVWF EEADR BCF EECON1, EEPGD BCF EECON1, CFGS BSF EECON1, RD NOP MOVF EEDATA, W EXAMPLE 8-2: DATA EEPROM WRITE MOVLW DATA_EE_ADDRH MOVWF EEADRH MOVLW DATA_EE_ADDR MOVWF EEADR MOVLW DATA_EE_DATA ...
Page 149
... BRA LOOP BCF EECON1, WREN BSF INTCON, GIE 2011 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC18F66K80 FAMILY 8.8 Using the Data EEPROM The data EEPROM is a high-endurance, byte- and write addressable array that has been optimized for the storage of frequently changing information (e.g., pro- gram variables or other data that are updated often) ...
Page 150
... PIC18F66K80 FAMILY TABLE 8-1: REGISTERS ASSOCIATED WITH DATA EEPROM MEMORY Name Bit 7 Bit 6 INTCON GIE/GIEH PEIE/GIEL EEADRH EEPROM Address Register High Byte EEADR EEPROM Address Register Low Byte EEDATA EEPROM Data Register EECON2 EEPROM Control Register 2 (not a physical register) EECON1 EEPGD ...
Page 151
... Hardware multiply Without hardware multiply signed Hardware multiply Without hardware multiply unsigned Hardware multiply Without hardware multiply signed Hardware multiply 2011 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC18F66K80 FAMILY EXAMPLE 9-1: MOVF ARG1, W MULWF ARG2 EXAMPLE 9-2: MOVF ARG1, W MULWF ARG2 BTFSC ARG2, SB ...
Page 152
... PIC18F66K80 FAMILY Example 9-3 shows the sequence unsigned multiplication. Equation 9-1 algorithm that is used. The 32-bit result is stored in four registers (RES3:RES0). EQUATION 9- UNSIGNED MULTIPLICATION ALGORITHM ARG1H:ARG1L ARG2H:ARG2L RES3:RES0 = 16 (ARG1H ARG2H (ARG1H ARG2L (ARG1L ARG2H 2 (ARG1L ...
Page 153
... INTERRUPTS Members of the PIC18F66K80 family of devices have multiple interrupt sources and an interrupt priority feature that allows most interrupt sources to be assigned a high-priority level or a low-priority level. The high-priority interrupt vector is at 0008h and the low-priority interrupt vector is at 0018h. High-priority interrupt events will interrupt any low-priority interrupts that may be in progress ...
Page 154
... PIC18F66K80 FAMILY FIGURE 10-1: PIC18F66K80 FAMILY INTERRUPT LOGIC PIR1<7:0> PIE1<7:0> IPR1<7:0> PIR2<7,5:0> PIE2<7,5:0> IPR2<7,5:0> PIR3<7,5> PIE3<7,5> IPR3<7,5> PIR4<7:0> PIE4<7:0> IPR4<7:0> PIR5<7:0> PIE5<7:0> IPR5<7:0> High-Priority Interrupt Generation Low-Priority Interrupt Generation PIR1<7:0> PIE1<7:0> IPR1<7:0> PIR2<7, 5:0> PIE2<7, 5:0> IPR2<7, 5:0> PIR3<7, 5:0> PIE3<7, 5:0> ...
Page 155
... Each pin on PORTB for interrupt-on-change is individually enabled and disabled in the IOCB register default, all pins are enabled. 2011 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC18F66K80 FAMILY Interrupt flag bits are set when an interrupt Note: condition occurs regardless of the state of its corresponding enable bit or the global interrupt enable bit ...
Page 156
... PIC18F66K80 FAMILY REGISTER 10-2: INTCON2: INTERRUPT CONTROL REGISTER 2 R/W-1 R/W-1 R/W-1 RBPU INTEDG0 INTEDG1 bit 7 Legend Readable bit W = Writable bit -n = Value at POR ‘1’ = Bit is set bit 7 RBPU: PORTB Pull-up Enable bit 1 = All PORTB pull-ups are disabled 0 = PORTB pull-ups are enabled by individual port latch values ...
Page 157
... Interrupt flag bits are set when an interrupt condition occurs regardless of the state of its corresponding Note: enable bit or the global interrupt enable bit. User software should ensure the appropriate interrupt flag bits are clear prior to enabling an interrupt. This feature allows for software polling. 2011 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC18F66K80 FAMILY R/W-0 R/W-0 R/W-x INT2IE ...
Page 158
... PIC18F66K80 FAMILY 10.2 PIR Registers The PIR registers contain the individual flag bits for the peripheral interrupts. Due to the number of peripheral interrupt sources, there are six Peripheral Interrupt Request (Flag) registers (PIR1 through PIR5). REGISTER 10-4: PIR1: PERIPHERAL INTERRUPT REQUEST (FLAG) REGISTER 1 ...
Page 159
... TMR3 register overflowed (bit must be cleared in software TMR3 register did not overflow bit 0 TMR3GIF: TMR3 Gate Interrupt Flag bit 1 = Timer gate interrupt occurred (bit must be cleared in software timer gate interrupt occurred 2011 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC18F66K80 FAMILY U-0 R/W-0 R/W-0 — BCLIF HLVDIF U = Unimplemented bit, read as ‘ ...
Page 160
... PIC18F66K80 FAMILY REGISTER 10-6: PIR3: PERIPHERAL INTERRUPT REQUEST (FLAG) REGISTER 3 U-0 U-0 R-0 — — RC2IF bit 7 Legend Readable bit W = Writable bit -n = Value at POR ‘1’ = Bit is set bit 7-6 Unimplemented: Read as ‘ 0 ’ bit 5 RC2IF: EUSART Receive Interrupt Flag bit ...
Page 161
... No TMR register capture occurred Compare Mode TMR register compare match occurred (must be cleared in software TMR register compare match occurred PWM Mode Not used in PWM mode. 2011 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC18F66K80 FAMILY R/W-0 U-0 R/W-0 CMP1IF — CCP5IF U = Unimplemented bit, read as ‘0’ ...
Page 162
... PIC18F66K80 FAMILY REGISTER 10-8: PIR5: PERIPHERAL INTERRUPT REQUEST (FLAG) REGISTER 5 R/W-0 R/W-0 R/W-0 IRXIF WAKIF ERRIF bit 7 Legend Readable bit W = Writable bit -n = Value at POR ‘1’ = Bit is set bit 7 IRXIF: Invalid Message Received Interrupt Flag bits invalid message occurred on the CAN bus ...
Page 163
... Enables the TMR2 to PR2 match interrupt 0 = Disables the TMR2 to PR2 match interrupt bit 0 TMR1IE: TMR1 Overflow Interrupt Enable bit 1 = Enables the TMR1 overflow interrupt 0 = Disables the TMR1 overflow interrupt 2011 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC18F66K80 FAMILY R/W-0 R/W-0 R/W-0 TX1IE SSPIE TMR1GIE U = Unimplemented bit, read as ‘ ...
Page 164
... PIC18F66K80 FAMILY REGISTER 10-10: PIE2: PERIPHERAL INTERRUPT ENABLE REGISTER 2 R/W-0 U-0 U-0 OSCFIE — — bit 7 Legend Readable bit W = Writable bit -n = Value at POR ‘1’ = Bit is set bit 7 OSCFIE: Oscillator Fail Interrupt Enable bit 1 = Enabled 0 = Disabled bit 6-4 Unimplemented: Read as ‘ 0 ’ ...
Page 165
... CCP2IE: CCP2 Interrupt Enable bit 1 = Enabled 0 = Disabled bit 1 CCP1IE: ECCP1 Interrupt Enable bit 1 = Enabled 0 = Disabled bit 0 Unimplemented: Read as ‘ 0 ’ 2011 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC18F66K80 FAMILY R-0 R/W-0 R/W-0 TX2IE CTMUIE CCP2IE U = Unimplemented bit, read as ‘0’ ‘0’ = Bit is cleared Preliminary ...
Page 166
... PIC18F66K80 FAMILY REGISTER 10-12: PIE4: PERIPHERAL INTERRUPT ENABLE REGISTER 4 R/W-0 R/W-0 R/W-0 TMR4IE EEIE CMP2IE bit 7 Legend Readable bit W = Writable bit -n = Value at POR ‘1’ = Bit is set bit 7 TMR4IE: TMR4 Overflow Interrupt Flag bit 1 = Interrupt enabled 0 = Interrupt disabled bit 6 EEIE: Data EEDATA/Flash Write Operation Interrupt Flag bit ...
Page 167
... Interrupt enabled 0 = Interrupt disabled Mode 1: Unimplemented: Read as ‘ 0 ’ Mode 2: FIFOFIE: FIFO Full Interrupt Flag bit 1 = Interrupt enabled 0 = Interrupt disabled 2011 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC18F66K80 FAMILY R/W-0 R/W-0 R/W-0 TXB2IE TXB1IE TXB0IE U = Unimplemented bit, read as ‘0’ ‘0’ = Bit is cleared ...
Page 168
... PIC18F66K80 FAMILY 10.4 IPR Registers The IPR registers contain the individual priority bits for the peripheral interrupts. Due to the number of peripheral interrupt sources, there are six Peripheral Interrupt Priority registers (IPR1 through IPR6). Using the priority bits requires that the Interrupt Priority Enable (IPEN) bit (RCON< ...
Page 169
... TMR3IP: TMR3 Overflow Interrupt Priority bit 1 = High priority 0 = Low priority bit 0 TMR3GIP: TMR3 Gate Interrupt Priority bit 1 = High priority 0 = Low priority 2011 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC18F66K80 FAMILY U-0 R/W-1 R/W-1 — BCLIP HLVDIP U = Unimplemented bit, read as ‘0’ ‘0’ = Bit is cleared ...
Page 170
... PIC18F66K80 FAMILY REGISTER 10-16: IPR3: PERIPHERAL INTERRUPT PRIORITY REGISTER 3 U-0 U-0 R/W-1 — — RC2IP bit 7 Legend Readable bit W = Writable bit -n = Value at POR ‘1’ = Bit is set bit 7-6 Unimplemented: Read as ‘ 0 ’ bit 5 RC2IP: EUSART Receive Priority Flag bit 1 = High priority ...
Page 171
... CCP4IP: CCP4 Interrupt Priority bit 1 = High priority 0 = Low priority bit CCP3IP: CCP3 Interrupt Priority bits 1 = High priority 0 = Low priority 2011 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC18F66K80 FAMILY R/W-1 U-0 R/W-1 CMP1IP — CCP5IP U = Unimplemented bit, read as ‘0’ ‘0’ = Bit is cleared ...
Page 172
... PIC18F66K80 FAMILY REGISTER 10-18: IPR5: PERIPHERAL INTERRUPT PRIORITY REGISTER 5 R/W-1 R/W-1 R/W-1 IRXIP WAKIP ERRIP bit 7 Legend Readable bit W = Writable bit -n = Value at POR ‘1’ = Bit is set bit 7 IRXIP: Invalid Message Received Interrupt Priority bits 1 = High priority 0 = Low priority bit 6 WAKIP: Bus Wake Up Activity Interrupt Priority bit ...
Page 173
... For details of bit operation, see bit 1 POR: Power-on Reset Status bit For details of bit operation, see bit 0 BOR: Brown-out Reset Status bit For details of bit operation, see 2011 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC18F66K80 FAMILY R/W-1 R-1 R Unimplemented bit, read as ‘0’ ...
Page 174
... PIC18F66K80 FAMILY 10.6 INTx Pin Interrupts External interrupts on the RB0/INT0, RB1/INT1, RB2/INT2 and RB3/INT3 pins are edge-triggered. If the corresponding INTEDGx bit in the INTCON2 register is set (= 1 ), the interrupt is triggered by a rising edge. If that bit is clear, the trigger is on the falling edge. When a valid edge appears on the RBx/INTx pin, the corresponding flag bit, INTxIF, is set ...
Page 175
... IPEN SBOREN Legend: Shaded cells are not used by the interrupts. 2011 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC18F66K80 FAMILY If a fast return from interrupt is not used (see Section 6.3 “Data Memory Organization” may need to save the WREG, STATUS and BSR regis- ters on entry to the Interrupt Service Routine (ISR). ...
Page 176
... PIC18F66K80 FAMILY NOTES: DS39977C-page 176 Preliminary 2011 Microchip Technology Inc. ...
Page 177
... EN RD PORT I/O pins have diode protection to V Note 1: 2011 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC18F66K80 FAMILY 11.1 I/O Port Pin Capabilities When developing an application, the capabilities of the port pins must be considered. Outputs on some pins have higher output drive strength than others. Similarly, some pins can tolerate higher than V All of the digital ports are 5 ...
Page 178
... PIC18F66K80 FAMILY REGISTER 11-1: PADCFG1: PAD CONFIGURATION REGISTER R/W-0 R/W-0 R/W-0 (1) (1) RDPU REPU RFPU bit 7 Legend Readable bit W = Writable bit -n = Value at POR ‘1’ = Bit is set bit 7 RDPU: PORTD Pull-up Enable bit 1 = PORTD pull-up resistors are enabled by individual port latch values ...
Page 179
... U2OD: UART2 Open-Drain Output Enable bit 1 = Open-drain capability enabled 0 = Open-drain capability disabled bit 0 U1OD: UART1 Open-Drain Output Enable bit 1 = Open-drain capability enabled 0 = Open-drain capability disabled 2011 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC18F66K80 FAMILY FIGURE 11-2: 3.3V PIC18F66K80 V DD (at logic ‘1’) R/W-0 ...
Page 180
... ANALOG AND DIGITAL PORTS Many of the ports multiplex analog and digital function- ality, providing a lot of flexibility for hardware designers. PIC18F66K80 family devices can make any analog pin analog or digital, depending on an application’s needs. The ports’ analog/digital functionality is controlled by the registers: ANCON0 and ANCON1. ...
Page 181
... RA5 and RA<3:0> are configured as Note: analog inputs on any Reset and are read as ‘ 0 ’. 2011 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC18F66K80 FAMILY OSC2/CLKO/RA6 and serve as the external circuit connections for the exter- nal (primary) oscillator circuit (HS Oscillator modes) or the external clock input and output (EC Oscillator modes) ...
Page 182
... PIC18F66K80 FAMILY TABLE 11-1: PORTA FUNCTIONS TRIS Pin Name Function Setting RA0/CV /AN0/ RA0 REF 0 ULPWU 1 CV REF x AN0 1 ULPWU 1 RA1/AN1/C1INC RA1 0 1 AN1 1 (1) C1INC x RA2/V -/AN2/ RA2 REF 0 C2INC REF 1 AN2 1 (1) C2INC x RA3/V +/AN3 RA3 REF REF 1 AN3 ...
Page 183
... Legend: — = unimplemented, read as ‘ 0 ’. Shaded cells are not used by PORTA. These bits are enabled depending on the oscillator mode selected. When not enabled as PORTA pins, Note 1: they are disabled and read as ‘ x ’. 2011 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC18F66K80 FAMILY Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 RA5 — ...
Page 184
... PIC18F66K80 FAMILY 11.3 PORTB, TRISB and LATB Registers PORTB is an eight-bit wide, bidirectional port. The corresponding Data Direction and Output Latch registers are TRISB and LATB. All pins on PORTB are digital only. EXAMPLE 11-2: INITIALIZING PORTB CLRF PORTB ; Initialize PORTB by ; clearing output ...
Page 185
... Default pin assignment for T0CKI when the T0CKMX Configuration bit is set. 3: Default pin assignment for T3CKI for 28, 40 and 44-pin devices. Alternate pin assignment for T3CKI for 64-pin devices 4: when T3CKMX is cleared. 2011 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC18F66K80 FAMILY I/O I/O Type O DIG LATB<0> data output. ...
Page 186
... PIC18F66K80 FAMILY TABLE 11-3: PORTB FUNCTIONS (CONTINUED) TRIS Pin Name Function Setting RB5/T0CKI/T3CKI/ RB5 0 CCP5/KBI1 1 (3) T0CKI x (4) T3CKI x CCP5 0 1 KBI1 1 RB6/PGC/TX2/CK2/ RB6 0 KBI2 1 PGC x (1) TX2 0 CK2 ( KBI2 1 RB7/PGD/T3G/RX2/ RB7 0 DT2/KBI3 1 PGD x x T3G x (1) RX2 1 (1) DT2 1 1 KBI3 ...
Page 187
... CCP2OD (ODCON<3>). 2011 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC18F66K80 FAMILY When enabling peripheral functions, use care in defin- ing TRIS bits for each PORTC pin. Some peripherals can override the TRIS bit to make a pin an output or input. Consult the corresponding peripheral section for the correct TRIS bit settings ...
Page 188
... PIC18F66K80 FAMILY TABLE 11-5: PORTC FUNCTIONS TRIS Pin Name Function I/O Setting RC0/SOSCO/ RC0 O 0 SCLKI I 1 SOSCO I 1 SCLKI I 1 RC1/SOSCI RC1 SOSCI I x RC2/T1G/ RC2 O 0 CCP2 I 1 T1G I x CCP2 RC3/REFO/ RC3 O 0 SCL/SCK I 1 REFO O x SCL ...
Page 189
... LATC LATC7 LATBC6 TRISC TRISC7 TRISC6 ODCON SSPOD CCP5OD Legend: Shaded cells are not used by PORTC. 2011 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC18F66K80 FAMILY I/O Description Type DIG LATC<7> data output. ST PORTC<7> data input. ST CAN bus RX. ST Asynchronous serial receive data input (EUSART module). ...
Page 190
... PIC18F66K80 FAMILY 11.5 PORTD, TRISD and LATD Registers PORTD is an 8-bit wide, bidirectional port. The corresponding Data Direction and Output Latch registers are TRISD and LATD. PORTD is unavailable on 28-pin devices. Note: All pins on PORTD are implemented with Schmitt Trigger input buffers. Each pin is individually configurable as an input or output ...
Page 191
... O = Output Input, ANA = Analog Signal, DIG = CMOS Output Schmitt Trigger Buffer Input, Legend Don’t care (TRIS bit does not affect port direction or is overridden for this option) Pin assignment for 40 and 44-pin devices (PIC18F4XK80). Note 1: 2011 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC18F66K80 FAMILY I/O I/O Type O DIG LATD<0> data output. ...
Page 192
... PIC18F66K80 FAMILY TABLE 11-7: PORTD FUNCTIONS (CONTINUED) TRIS Pin Name Function Setting RD7/RX2/DT2/ RD7 0 P1D/PSP7 1 (1) RX2 1 (1) DT2 1 1 P1D 0 PSP7 Output Input, ANA = Analog Signal, DIG = CMOS Output Schmitt Trigger Buffer Input, Legend Don’t care (TRIS bit does not affect port direction or is overridden for this option) Pin assignment for 40 and 44-pin devices (PIC18F4XK80) ...
Page 193
... Alternate pin assignment for CANRX and CANTX on 64-pin devices (PIC18F6XK80) when the CANMX Configuration 2: bit is cleared. 2011 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC18F66K80 FAMILY weak pull-up is automatically turned off when the port pin is configured as an output. The pull-ups are disabled on any device Reset. ...
Page 194
... PIC18F66K80 FAMILY TABLE 11-9: PORTE FUNCTIONS (CONTINUED) TRIS Pin Name Function Setting (1) RE5/CANTX RE5 0 1 (1,2) CANTX 0 (1) RE6/RX2/DT2 RE6 0 1 (1) RX2 1 (1) DT2 1 1 (1) RE7/TX2/CK2 RE7 0 1 (1) TX2 0 (1) CK2 Output Input, ANA = Analog Signal, DIG = CMOS Output Schmitt Trigger Buffer Input, Legend Don’ ...
Page 195
... REPU Legend: — = unimplemented, read as ‘ 0 ’. Shaded cells are not used by PORTF. Unimplemented on 28-pin devices; read as ‘ 0 ’. Note 1: 2011 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC18F66K80 FAMILY On device Resets, pins, RF<7:1>, are Note: configured as analog inputs and are read as ‘ 0 ’. ...
Page 196
... PIC18F66K80 FAMILY 11.8 PORTG, TRISG and LATG Registers PORTG is a 5-bit wide, bidirectional port. The corresponding Data Direction and Output Latch registers are TRISG and LATG. PORTG is only available on 64-pin Note: devices. PORTG is multiplexed with EUSART and CCP, ECCP, Analog, Comparator and Timer input functions (Table 11-13) ...
Page 197
... PADCFG1 RDPU REPU Legend: — = unimplemented, read as ‘ 0 ’. Shaded cells are not used by PORTG. Unimplemented on 28-pin devices. Read as ‘ 0 ’. Note 1: 2011 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC18F66K80 FAMILY I/O I/O Type O DIG LATG<4> data output PORTG<4> data input. ...
Page 198
... PIC18F66K80 FAMILY 11.9 Parallel Slave Port PORTD can function as an 8-bit-wide Parallel Slave Port (PSP), or microprocessor port, when control bit, PSPMODE (PSPCON<4>), is set. The port is asyn- chronously readable and writable by the external world through the RD control input pin (RE0/AN5/RD) and WR control input pin (RE1/AN6/C1OUT/WR). ...
Page 199
... General Purpose I/O mode bit 3-0 Unimplemented: Read as ‘ 0 ’ FIGURE 11-4: PARALLEL SLAVE PORT WRITE WAVEFORMS PORTD<7:0> IBF OBF PSPIF 2011 Microchip Technology Inc. PIC18F66K80 FAMILY R/W-0 U-0 PSPMODE — Unimplemented bit, read as ‘0’ ‘0’ = Bit is cleared Preliminary U-0 U-0 U-0 — ...
Page 200
... PIC18F66K80 FAMILY FIGURE 11-5: PARALLEL SLAVE PORT READ WAVEFORMS PORTD<7:0> IBF OBF PSPIF TABLE 11-15: REGISTERS ASSOCIATED WITH PARALLEL SLAVE PORT Name Bit 7 Bit 6 PORTD RD7 RD6 LATD LATD7 LATD6 TRISD TRISD7 TRISD6 PORTE RE7 RE6 LATE LATE7 LATE6 TRISE TRISE7 ...