LM1084IT-ADJ/NOPB National Semiconductor, LM1084IT-ADJ/NOPB Datasheet - Page 9
LM1084IT-ADJ/NOPB
Manufacturer Part Number
LM1084IT-ADJ/NOPB
Description
IC REG POSITIVE 5A LDO TO220-3
Manufacturer
National Semiconductor
Datasheet
1.LM1084IS-5.0NOPB.pdf
(13 pages)
Specifications of LM1084IT-ADJ/NOPB
Regulator Topology
Positive Adjustable
Voltage - Output
1.2 ~ 15 V
Voltage - Input
Up to 29V
Voltage - Dropout (typical)
1.3V @ 5A
Number Of Regulators
1
Current - Output
5A
Current - Limit (min)
5.5A
Operating Temperature
-40°C ~ 125°C
Mounting Type
Through Hole
Package / Case
TO-220-3 (Straight Leads)
Voltage Regulator Type
Linear
Topology
LDO
Regulator Output Type
Adjustable
Polarity Type
Positive
Number Of Outputs
Single
Input Voltage (min)
2.6V
Input Voltage (max)
29V
Output Voltage
1.2 to 15V
Package Type
TO-220
Output Current
5A
Power Dissipation
30W
Load Regulation
0.3%
Line Regulation
0.2%
Operating Temp Range
-40C to 125C
Operating Temperature Classification
Automotive
Dropout Voltage@current (max)
1.5@5A
Dropout Voltage@current (typ)
1.3@5A
Pin Count
3 +Tab
Mounting
Through Hole
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Lead free / RoHS Compliant
Other names
*LM1084IT-ADJ
*LM1084IT-ADJ/NOPB
LM1084IT-ADJ
*LM1084IT-ADJ/NOPB
LM1084IT-ADJ
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Application Note
must be added, one for case to heat-sink (θ
heatsink to ambient (θ
predicted as follows:
T
T
P
consumption is calculated as follows:
Once the devices power is determined, the maximum allow-
able (θ
θ
The LM1084 has different temperature specifications for two
different sections of the IC: the control section and the output
section. The Electrical Characteristics table shows the junc-
tion to case thermal resistances for each of these sections,
while the maximum junction temperatures (T
section is listed in the Absolute Maximum section of the
datasheet. T
T
θ
follows:
θ
θ
The required heat sink is determined by calculating its re-
quired thermal resistance (θ
JA (max)
JA (max)
JA
JA
J
J
J(max)
D
= T
is junction temperature, T
is the power consumption of the device. Device power
(max, CONTROL SECTION) = (125˚C - T
(max, OUTPUT SECTION) = (150˚C - T
A
JA (max)
is 150˚C for the output section.
+ P
should be calculated separately for each section as
= T
D
R(max)
J(max)
(θ
) is calculated as:
JC
/P
+ θ
is 125˚C for the control section, while
D
CH
HA
= T
). The junction temperature can be
+ θ
J(max)
HA (max)
HA
A
(Continued)
) = T
is ambient temperature, and
− T
A(max)
).
A
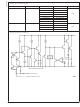
FIGURE 7. Heat sink thermal Resistance vs Area
+ P
/P
D
FIGURE 6. Power Dissipation Diagram
D
θ
CH
A(max)
JA
J(max)
A(max)
) and one for
) for each
)/P
)/P
D
D
9
Figure 6 shows the voltages and currents which are present
in the circuit.
θ
(θ
(θ
TROL SECTION) + θ
(θ
SECTION) + θ
If thermal compound is used, θ
C/W. If the case is soldered to the heat sink, then a θ
be estimated as 0 C/W.
After, θ
lower of the two θ
ate heat sink.
If PC board copper is going to be used as a heat sink, then
Figure 7 can be used to determine the appropriate area
(size) of copper foil required.
HA (max)
HA (max)
HA (max)
HA (max)
I
P
IN
D
HA (max)
= I
= (V
= θ
) should also be calculated twice as follows:
) = θ
) = θ
L
10094664
+ I
IN
JA (max)
JA
−V
JA
G
CH
(max, OUTPUT SECTION) - (θ
is calculated for each section, choose the
OUT
(max, CONTROL SECTION) - (θ
)
10094616
HA (max)
− (θ
) I
CH
L
)
+ V
JC
values to determine the appropri-
+ θ
IN
I
G
CH
CH
)
can be estimated at 0.2
JC
www.national.com
(OUTPUT
JC
CH
(CON-
can