BGX7101HN/1,118 NXP Semiconductors, BGX7101HN/1,118 Datasheet
BGX7101HN/1,118
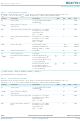
Specifications of BGX7101HN/1,118
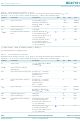
Related parts for BGX7101HN/1,118
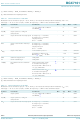
BGX7101HN/1,118 Summary of contents
Page 1
BGX7101 3D Transmitter IQ modulator Rev. 4 — 10 January 2013 1. General description The BGX7101 device combines high performance, high linearity I and Q modulation paths for use in radio frequency up-conversion. It supports RF frequency outputs in the ...
Page 2
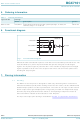
... NXP Semiconductors 5. Ordering information Table 1. Ordering information Type number Package Name BGX7101HN HVQFN24 6. Functional diagram Fig 1. Differential I and Q baseband inputs are each fed to an associated upconverter mixer. The Local Oscillator (LO) carrier input is buffered and split into 0 degree and 90 degree signals. The in-phase signal is passed to the I mixer and the 90 degree phase-changed signal is passed to the Q mixer ...
Page 3
... NXP Semiconductors Fig 2. 7.2 Pin description Table 2. Symbol POFF_P LOGND LO_P LO_N LOGND LOGND RFGND RFGND MODQ_N MODQ_P RFGND RFGND i.c. RFGND i.c. RFOUT RFGND V CC_RF(5V0) i.c. RFGND MODI_P MODI_N BGX7101 Product data sheet terminal 1 index area 1 POFF_P 2 LOGND LO_P 3 LO_N 4 LOGND 5 6 LOGND Transparent top view ...
Page 4
... NXP Semiconductors Table 2. Symbol i.c. V CC_LO(5V0) Exposed die pad [ ground input output power. [2] AC coupling required as shown in 8. Functional description 8.1 General Each IQ baseband input has a 100 differential input impedance allowing straightforward matching, from the DAC output through the baseband filter. The device allows operation with IQ input common-mode voltages between 0.25 V and 3.3 V allowing direct connection to a broad family of DACs. The LO and RF ports provide broadband 50 ...
Page 5
... NXP Semiconductors Fig 3. 9. Limiting values Table 4. In accordance with the Absolute Maximum Rating System (IEC 60134). Symbol i(lo) P o(RF stg V ESD BGX7101 Product data sheet -13.55 S11 (dB) -13.57 -13.59 -13.61 on -13.63 -13. input return loss variation (S11_LO) Limiting values Parameter Conditions supply voltage ...
Page 6
... NXP Semiconductors Table 4. In accordance with the Absolute Maximum Rating System (IEC 60134). Symbol Pin POFF_P V i Pins MODI_N, MODI_P, MODQ_N and MODQ_P 10. Thermal characteristics Table 5. Symbol Parameter R th(j-mb) 11. Characteristics Table 6. Characteristics Modulation source resistance per pin = 50 ...
Page 7
... NXP Semiconductors Table 7. Characteristics at 750 MHz Modulation source resistance per pin = 50 T range = + i(lo) Symbol Parameter P output power o P output power gain L(1dB) compression IP3 output third-order intercept point IQ frequency 1 = 4.5 MHz; o IP2 output second-order intercept o point ...
Page 8
... NXP Semiconductors Table 8. Characteristics at 910 MHz Modulation source resistance per pin = 50 T range = + i(lo) Symbol Parameter N output noise floor flr(o) SBS sideband suppression CF carrier feedthrough baseband harmonic distortion HD(bb) level MODI = MODI_P MODI_N and MODQ = MODQ_P MODQ_N. ...
Page 9
... NXP Semiconductors MODI = MODI_P MODI_N and MODQ = MODQ_P MODQ_N. [1] [2] Measurements done in supradyne mode. Table 10. Characteristics at 1.960 GHz Modulation source resistance per pin = 50 T range = + i(lo) Symbol Parameter P output power o P output power gain ...
Page 10
... NXP Semiconductors Table 11. Characteristics at 2.140 GHz Modulation source resistance per pin = 50 T range = + i(lo) Symbol Parameter IP2 output second-order intercept o point N output noise floor flr(o) SBS sideband suppression CF carrier feedthrough baseband harmonic distortion HD(bb) level MODI = MODI_P MODI_N and MODQ = MODQ_P MODQ_N. ...
Page 11
... NXP Semiconductors Table 12. Characteristics at 2.650 GHz Modulation source resistance per pin = 50 T range = + i(lo) Symbol Parameter CF carrier feedthrough baseband harmonic distortion HD(bb) level MODI = MODI_P MODI_N and MODQ = MODQ_P MODQ_N. [1] [2] Measurements done in supradyne mode. ...
Page 12
... NXP Semiconductors 12. Application information input O O PRIMARY 0.3 pF TC1-1-43A Fig 4. Typical wideband application diagram Figure 4 the application note for narrowband optimum component values. 12.1 External DAC interfacing Nominal DAC single-ended output currents are between mA. When driving into 25 impedance, this creates 250 mV peak-single signal (1 V (p-p) differential). Half of the impedance is placed at the DAC outputs as 50 ...
Page 13
... NXP Semiconductors Fig 5. 12.2 RF Good RF port matching typically requires some reactive components to tune-out residual inductance or capacitance. As the LO inputs and RF output are internally DC biased, both pins need a series AC-coupling capacitor. BGX7101 Product data sheet I DAC 50 Ω Q Typical interface All information provided in this document is subject to legal disclaimers. ...
Page 14
... NXP Semiconductors 13. Test information Parameters for the following drawings frequency = 5 MHz; IQ amplitude = 0.42 V (p-p) differential sine wave; V broadband output match; unless otherwise specified. = +25 C. ( 40 C. ( +85 C. ( Fig 6. Current consumption versus f BGX7101 Product data sheet 0.22 Current consumption (mA) ...
Page 15
... NXP Semiconductors Parameters for the five following drawings frequency = 5 MHz; IQ amplitude = 0.42 V (p-p) differential sine wave; V broadband output match; unless otherwise specified. 1 output power (dBm -11 -15 400 1600 = +25 C. ( 40 C. ( +85 C. ( Fig 7. P versus f and ...
Page 16
... NXP Semiconductors ( 2140 MHz. lo Fig 11. P versus baseband voltage at 2140 MHz o BGX7101 Product data sheet 20 output power (dBm) 0 -20 - baseband voltage differential (V (p-p)) All information provided in this document is subject to legal disclaimers. Rev. 4 — 10 January 2013 BGX7101 Transmitter IQ modulator ...
Page 17
... NXP Semiconductors Parameters for the four following drawings frequency = 5 MHz; IQ amplitude = 0.42 V (p-p) differential sine wave; V broadband output match; unless otherwise specified L(1dB) (dBm 400 1600 = +25 C. ( 40 C. ( +85 C. ( Fig 12. P versus f and T ...
Page 18
... NXP Semiconductors Parameters for the four following drawings: V tones; tone 1: IQ frequency = 4.5 MHz and tone 2: IQ frequency = 5.5 MHz; P tone = 10 dBm IP3 O (dBm) (1) ( 400 1600 = +25 C. ( 40 C. ( +85 C. ( Fig 16. IP3 versus f and T ...
Page 19
... NXP Semiconductors Parameters for the four following drawings: V tones; tone 1: IQ frequency = 4.5 MHz and tone 2: IQ frequency = 5.5 MHz; P tone = 10 dBm; V 100 IP2 O (dBm 400 1600 = +25 C. ( 40 C. ( +85 C. ( Fig 20. IP2 versus f and ...
Page 20
... NXP Semiconductors Parameters for the five following drawings frequency = 5 MHz; IQ amplitude = 0.42 V (p-p) differential sine wave; V broadband output match; unless otherwise specified. 0 unadjusted carrier feedthrough (dBm) -20 -40 -60 (1) (2) (3) -80 400 1600 = +25 C. ( 40 C. ( +85 C. ( Fig 24. Unadjusted CF versus f ...
Page 21
... NXP Semiconductors = +25 C. ( 40 C. ( +85 C. ( Fig 28. Adjusted CF versus f BGX7101 Product data sheet 0 adjusted carrier feedthrough (dBm) -20 -40 (1) (2) (3) -60 -80 -100 495 1695 after nulling at 25 C and All information provided in this document is subject to legal disclaimers. ...
Page 22
... NXP Semiconductors Parameters for the five following drawings frequency = 5 MHz; IQ amplitude = 0.42 V (p-p) differential sine wave; V broadband output match; unless otherwise specified. 80 unadjusted sideband suppression (dBc) 60 (1) ( 400 1600 = +25 C. ( 40 C. ( +85 C. ( Fig 29. Unadjusted SBS versus f ...
Page 23
... NXP Semiconductors = +25 C. ( 40 C. ( +85 C. ( Fig 33. Adjusted SBS versus f BGX7101 Product data sheet 100 unadjusted sideband suppression (dBc 495 1695 after nulling at 25 C and All information provided in this document is subject to legal disclaimers. ...
Page 24
... NXP Semiconductors Parameters for the six following drawings frequency = 5 MHz; IQ amplitude = 0.25 V (p-p) single-ended sine wave 0.5 V; broadband output match; unless otherwise specified. i(cm) -10 adjusted carrier feedthrough (dBm) -30 -50 -70 -90 670 710 750 Adjusted at 750 MHz and after nulling T = +25 C. ( 40 C. ...
Page 25
... NXP Semiconductors -10 adjusted carrier feedthrough (dBm) -30 (1) -50 (2) (3) -70 -90 2500 2540 2580 Adjusted at 2600 MHz and after nulling T = +25 C. ( 40 C. ( +85 C. ( Fig 38. Adjusted CF versus f band) BGX7101 Product data sheet aaa-002955 adjusted carrier feedthrough 2620 2660 ...
Page 26
... NXP Semiconductors Parameters for the six following drawings frequency = 5 MHz; IQ amplitude = 0.25 V (p-p) single-ended sine wave 0.5 V; broadband output match; unless otherwise specified. i(cm) 90 adjusted sideband suppression (dB (1) (2) ( 670 710 750 Adjusted at 750 MHz and after nulling T = +25 C. ( ...
Page 27
... NXP Semiconductors 90 adjusted sideband suppression (dB 2500 2540 2580 Adjusted at 2600 MHz and after nulling T = +25 C. ( 40 C. ( +85 C. ( Fig 44. Adjusted SBS versus f band) BGX7101 Product data sheet aaa-002961 adjusted sideband (1) (2) (3) 2620 2660 2700 LO frequency (MHz ...
Page 28
... NXP Semiconductors Parameters for the three following drawings: noise floor without baseband ; unless otherwise specified. -144 output noise floor (dBm/Hz) -154 -164 -174 400 1600 = +25 C. ( 40 C. ( +85 C. ( Fig 46. N versus f ...
Page 29
... NXP Semiconductors Parameters for the two following drawings: noise floor with baseband MODI_N, MODI_P and MODQ_N; DC signal on MODQ_P; unless otherwise specified. -148 RFoutput noise floor (dBm/Hz) -152 (1) (2) (3) -156 -160 -30 -20 -10 ( dBm. i(lo) = 3 dBm. (2) P i(lo) ( dBm. ...
Page 30
... NXP Semiconductors Parameters for the following drawing: T wanted and IP3 V = 0.5 V; for noise floor measurement see preceding conditions; noise floor i(cm) measurement has been integrated in 3.84 MHz bandwidth; unless otherwise specified. noise floor contribution no more negligeable BGX7101 (1) Measured IP3 . o (2) Pout/Tone 1 dB step. ...
Page 31
... NXP Semiconductors 16. Package outline HVQFN24: plastic thermal enhanced very thin quad flat package; no leads; 24 terminals; body 0.85 mm terminal 1 index area terminal 1 24 index area DIMENSIONS (mm are the original dimensions) (1) A UNIT max. 0.05 0. 0.2 0.00 0.18 Note 1. Plastic or metal protrusions of 0.075 mm maximum per side are not included. ...
Page 32
... NXP Semiconductors 17. Soldering of SMD packages This text provides a very brief insight into a complex technology. A more in-depth account of soldering ICs can be found in Application Note AN10365 “Surface mount reflow soldering description”. 17.1 Introduction to soldering Soldering is one of the most common methods through which packages are attached to Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs), to form electrical circuits ...
Page 33
... NXP Semiconductors 17.4 Reflow soldering Key characteristics in reflow soldering are: • Lead-free versus SnPb soldering; note that a lead-free reflow process usually leads to higher minimum peak temperatures (see reducing the process window • Solder paste printing issues including smearing, release, and adjusting the process window for a mix of large and small components on one board • ...
Page 34
... NXP Semiconductors Fig 53. Temperature profiles for large and small components For further information on temperature profiles, refer to Application Note AN10365 “Surface mount reflow soldering description”. 18. Abbreviations Table 17. Acronym DAC DC ESD FCDM HBM IF LO PCB RF TDD BGX7101 Product data sheet maximum peak temperature ...
Page 35
... NXP Semiconductors 19. Revision history Table 18. Revision history Document ID Release date BGX7101 v.4 20130110 • Modifications: Table • Table • Table • Table • Table • Table • Table BGX7101 v.3 20120903 BGX7101 v.2 20120809 BGX7101 v.1 20120425 BGX7101 Product data sheet Data sheet status Product data sheet ...
Page 36
... Terms and conditions of commercial sale of NXP Semiconductors. Right to make changes — NXP Semiconductors reserves the right to make changes to information published in this document, including without limitation specifications and product descriptions, at any time and without notice ...
Page 37
... Product data sheet NXP Semiconductors’ specifications such use shall be solely at customer’s own risk, and (c) customer fully indemnifies NXP Semiconductors for any liability, damages or failed product claims resulting from customer design and use of the product for automotive applications beyond NXP Semiconductors’ ...
Page 38
... NXP Semiconductors 22. Tables Table 1. Ordering information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2 Table 2. Pin description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3 Table 3. Shutdown control . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4 Table 4. Limiting values . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .5 Table 5. Thermal characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .6 Table 6. Characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .6 Table 7. Characteristics at 750 MHz . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7 Table 8. Characteristics at 910 MHz . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7 Table 9. Characteristics at 1.840 GHz . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8 Table 10. Characteristics at 1.960 GHz . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .9 Table 11. Characteristics at 2.140 GHz . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .9 Table 12. Characteristics at 2.650 GHz . . . . . . . . . . . . . .10 Table 13 ...
Page 39
... NXP Semiconductors 23. Figures Fig 1. Functional block diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2 Fig 2. Pin configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3 Fig 3. LO input return loss variation (S11_LO Fig 4. Typical wideband application diagram . . . . . . . . .12 Fig 5. Typical interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13 Fig 6. Current consumption versus f Fig 7. P versus f and . Fig 8. P versus f and . Fig 9 ...
Page 40
... NXP Semiconductors 24. Contents 1 General description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1 2 Features and benefits . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1 3 Applications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1 4 Device family . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1 5 Ordering information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2 6 Functional diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2 7 Pinning information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2 7.1 Pinning . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2 7.2 Pin description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3 8 Functional description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4 8.1 General . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4 8.2 Shutdown control . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4 9 Limiting values Thermal characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6 11 Characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6 12 Application information ...