ht82k68e Holtek Semiconductor Inc., ht82k68e Datasheet - Page 11

ht82k68e
Manufacturer Part Number
ht82k68e
Description
Ht82k68e -- Multimedia Keyboard Encoder 8-bit Otp Mcu
Manufacturer
Holtek Semiconductor Inc.
Datasheet
1.HT82K68E.pdf
(39 pages)
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Part Number:
HT82K68E
Manufacturer:
HOLTEK/合泰
Quantity:
20 000
Company:
Part Number:
ht82k68e(PB-FREE)
Manufacturer:
MICROCHIP
Quantity:
11
Company:
Part Number:
ht82k68e20
Manufacturer:
SOY
Quantity:
17
(8-stages) to get the nominal time-out period of approxi-
mately 20ms. This time-out period may vary with tem-
perature, VDD and process variations. By invoking the
WDT prescaler, longer time-out periods can be realized.
Writing data to WS2, WS1, WS0 (bit 2,1,0 of the WDTS)
can give different time-out periods. If WS2, WS1, WS0
are all equal to 1, the division ratio is up to 1:128, and the
maximum time-out period is 2.6 seconds.
If the WDT oscillator is disabled, the WDT clock may still
come from the instruction clock and operate in the same
manner except that in the HALT state the WDT may stop
counting and lose its protecting purpose. In this situation
the WDT logic can be restarted by external logic. The
high nibble and bit 3 of the WDTS are reserved for user
defined flags, which can be used to indicate some speci-
fied status.
If the device operates in a noisy environment, using the
on-chip RC oscillator (WDT OSC) is strongly recom-
mended, since the HALT will stop the system clock.
The WDT overflow under normal operation will initialize
HALT mode, initializes a warm reset only when the pro-
gram counter and stack pointer are reset to zero. To
clear the contents of the WDT (including the WDT
prescaler ), three methods are adopted; external reset
(a low level to RESET), software instruction(s), or a HALT
instruction. There are two types of software instructions;
CLR WDT and CLR WDT1/CLR WDT2. Of these two
types of instruction, only one can be active depending
on the mask option
If the CLR WDT is selected (ie. CLR WDT times equal
one), any execution of the CLR WDT instruction will
clear the WDT. In case CLR WDT1 and CLR WDT2
are chosen (ie. CLRWDT times equal two), these two in-
structions must be executed to clear the WDT; otherwise,
the WDT may reset the chip because of the time-out.
Power Down Operation - HALT
The HALT mode is initialized by the HALT instruction
and results in the following...
Rev. 2.00
chip reset and set the status bit TO. An overflow in the
The system oscillator will turn off but the WDT oscilla-
tor keeps running (if the WDT oscillator is selected).
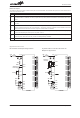
WS2
0
0
0
0
1
1
1
1
WS1
0
0
1
1
0
0
1
1
WDTS (09H) Register
CLR WDT times selection option .
WS0
0
1
0
1
0
1
0
1
Division Ratio
1:128
1:16
1:32
1:64
1:1
1:2
1:4
1:8
11
The system can leave the HALT mode by means of an
external reset, interrupt, and external falling edge signal
on port A and port C [0:3] or a WDT overflow. An exter-
nal reset causes a device initialization and the WDT
overflow performs a warm reset . Examining the TO
and PDF flags, the reason for chip reset can be deter-
mined. The PDF flag is cleared when system power-up
or executing the CLR WDT instruction and is set when
the HALT instruction is executed. The TO flag is set if the
WDT time-out occurs, and causes a wake-up that only
resets the program counter and stack pointer, the others
keep their original status.
On the other hand, awakening from an external interrupt
(PC2), two sequences may happen. If the interrupt is
disabled or the interrupt is enabled but the stack is full,
the program will resume execution at the next instruc-
tion. But if the interrupt is enabled and the stack is not
full, the regular interrupt response takes place.
The port A or port C [0:3] wake-up can be considered as
a continuation of normal execution. Each bit in port A
can be independently selected to wake up the device by
mask option. Awakening from an I/O port stimulus, the
program will resume execution of the next instruction.
Once a wake-up event occurs, and the system clock co-
mes from a crystal, it takes 1024 t
riod) to resume normal operation. In other words, the
HT82K68E will insert a dummy period after the
wake-up. If the system clock comes from an RC oscilla-
tor, it continues operating immediately. If the wake-up
results in next instruction execution, this will execute im-
mediately after the dummy period is completed.
To minimize power consumption, all I/O pins should be
carefully managed before entering the HALT status.
Reset
There are three ways in which a reset can occur:
The WDT time-out during HALT is different from other
chip reset conditions, since it can perform a warm reset
that just resets the program counter and stack pointer,
leaving the other circuits to remain in their original state.
Some registers remain unchanged during other reset
conditions. Most registers are reset to the initial condi-
tion when the reset conditions are met. By examining
the PDF and TO flags, the program can distinguish be-
tween different chip resets .
The contents of the on–chip RAM and registers re-
main unchanged.
WDT and WDT prescaler will be cleared and recount
again (if the WDT clock has come from the WDT oscil-
lator).
All I/O ports maintain their original status.
The PDF flag is set and the TO flag is cleared.
RESET reset during normal operation
RESET reset during HALT
WDT time-out reset during normal operation
SYS
(system clock pe-
HT82K68E
July 10, 2007