ht82m73e Holtek Semiconductor Inc., ht82m73e Datasheet - Page 5

ht82m73e
Manufacturer Part Number
ht82m73e
Description
2.4ghz Mouse Tx 8-bit Otp Mcu
Manufacturer
Holtek Semiconductor Inc.
Datasheet
1.HT82M73E.pdf
(51 pages)
When executing instructions requiring jumps to
non-consecutive addresses such as a jump instruction,
a subroutine call, interrupt or reset, etc., the
microcontroller manages program control by loading the
required address into the Program Counter. For condi-
tional skip instructions, once the condition has been
met, the next instruction, which has already been
fetched during the present instruction execution, is dis-
carded and a dummy cycle takes its place while the cor-
rect instruction is obtained.
The lower byte of the Program Counter, known as the
Program Counter Low register or PCL, is available for
program control and is a readable and writeable regis-
ter. By transferring data directly into this register, a short
program jump can be executed directly, however, as
only this low byte is available for manipulation, the
jumps are limited to the present page of memory, that is
256 locations. When such program jumps are executed
it should also be noted that a dummy cycle will be in-
serted.
The lower byte of the Program Counter is fully accessi-
ble under program control. Manipulating the PCL might
cause program branching, so an extra cycle is needed
to pre-fetch. Further information on the PCL register can
be found in the Special Function Register section.
Stack
This is a special part of the memory which is used to
save the contents of the Program Counter only. The
stack has 2 levels and is neither part of the data nor part
of the program space, and is neither readable nor
writeable. The activated level is indexed by the Stack
Pointer, SP, and is neither readable nor writeable. At a
subroutine call or interrupt acknowledge signal, the con-
tents of the Program Counter are pushed onto the stack.
At the end of a subroutine or an interrupt routine, sig-
naled by a return instruction, RET or RETI, the Program
Note:
Rev. 1.00
Initial Reset
SPI Interrupt
Timer/Event Counter Overflow
Skip
Loading PCL
Jump, Call Branch
Return from Subroutine
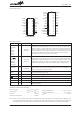
PC10~PC8: Current Program Counter bits
@7~@0: PCL bits
#10~#0: Instruction code address bits
S10~S0: Stack register bits
Mode
PC10
b10
S10
#10
0
0
0
PC9
S9
b9
#9
0
0
0
Program Counter
PC8
b8
S8
#8
0
0
0
@7
5
b7
#7
S7
0
0
0
Counter is restored to its previous value from the stack.
After a device reset, the Stack Pointer will point to the
top of the stack.
If the stack is full and an enabled interrupt takes place,
the interrupt request flag will be recorded but the ac-
knowledge signal will be inhibited. When the Stack
Pointer is decremented, by RET or RETI, the interrupt
will be serviced. This feature prevents stack overflow al-
lowing the programmer to use the structure more easily.
However, when the stack is full, a CALL subroutine in-
struction can still be executed which will result in a stack
overflow. Precautions should be taken to avoid such
cases which might cause unpredictable program
branching.
Arithmetic and Logic Unit - ALU
The arithmetic-logic unit or ALU is a critical area of the
microcontroller that carries out arithmetic and logic op-
erations of the instruction set. Connected to the main
microcontroller data bus, the ALU receives related in-
struction codes and performs the required arithmetic or
logical operations after which the result will be placed in
the specified register. As these ALU calculation or oper-
ations may result in carry, borrow or other status
changes, the status register will be correspondingly up-
dated to reflect these changes. The ALU supports the
following functions:
Program Counter Bits
Program Counter + 2
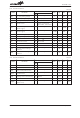
@6
S6
b6
#6
0
0
0
@5
b5
S5
#5
0
0
0
@4
S4
b4
#4
0
0
0
@3
b3
S3
#3
0
0
1
@2
b2
#2
S2
0
1
0
HT82M73E
May 14, 2008
@1
S1
b1
#1
0
0
0
@0
b0
#0
S0
0
0
0