ATmega32 Atmel Corporation, ATmega32 Datasheet - Page 271

ATmega32
Manufacturer Part Number
ATmega32
Description
Manufacturer
Atmel Corporation
Specifications of ATmega32
Flash (kbytes)
32 Kbytes
Pin Count
44
Max. Operating Frequency
16 MHz
Cpu
8-bit AVR
# Of Touch Channels
16
Hardware Qtouch Acquisition
No
Max I/o Pins
32
Ext Interrupts
3
Usb Speed
No
Usb Interface
No
Spi
1
Twi (i2c)
1
Uart
1
Graphic Lcd
No
Video Decoder
No
Camera Interface
No
Adc Channels
8
Adc Resolution (bits)
10
Adc Speed (ksps)
15
Analog Comparators
1
Resistive Touch Screen
No
Temp. Sensor
No
Crypto Engine
No
Sram (kbytes)
2
Eeprom (bytes)
1024
Self Program Memory
YES
Dram Memory
No
Nand Interface
No
Picopower
No
Temp. Range (deg C)
-40 to 85
I/o Supply Class
2.7 to 5.5
Operating Voltage (vcc)
2.7 to 5.5
Fpu
No
Mpu / Mmu
no / no
Timers
3
Output Compare Channels
4
Input Capture Channels
1
Pwm Channels
4
32khz Rtc
Yes
Calibrated Rc Oscillator
Yes
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Company:
Part Number:
ATmega32-16AC
Manufacturer:
COMPAL
Quantity:
500
Part Number:
ATmega32-16AU
Manufacturer:
ATMEL
Quantity:
20 000
Part Number:
ATmega32-16PI
Manufacturer:
ATMEL/爱特梅尔
Quantity:
20 000
Part Number:
ATmega32-16PU
Manufacturer:
ATMEL/爱特梅尔
Quantity:
20 000
SPI Serial
Programming
Algorithm
Data Polling Flash
2503Q–AVR–02/11
tion. The Chip Erase operation turns the content of every memory location in both the Program
and EEPROM arrays into $FF.
Depending on CKSEL Fuses, a valid clock must be present. The minimum low and high periods
for the serial clock (SCK) input are defined as follows:
Low:> 2 CPU clock cycles for f
High:> 2 CPU clock cycles for f
When writing serial data to the ATmega32, data is clocked on the rising edge of SCK.
When reading data from the ATmega32, data is clocked on the falling edge of SCK. See
137
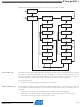
To program and verify the ATmega32 in the SPI Serial Programming mode, the following
sequence is recommended (See four byte instruction formats in
1. Power-up sequence:
2. Wait for at least 20ms and enable SPI Serial Programming by sending the Programming
3. The SPI Serial Programming instructions will not work if the communication is out of syn-
4. The Flash is programmed one page at a time (page size found in
5. The EEPROM array is programmed one byte at a time by supplying the address and data
6. Any memory location can be verified by using the Read instruction which returns the con-
7. At the end of the programming session, RESET can be set high to commence normal
8. Power-off sequence (if needed):
When a page is being programmed into the Flash, reading an address location within the page
being programmed will give the value $FF. At the time the device is ready for a new page, the
programmed value will read correctly. This is used to determine when the next page can be writ-
Apply power between V
tems, the programmer can not guarantee that SCK is held low during power-up. In this
case, RESET must be given a positive pulse of at least two CPU clock cycles duration
after SCK has been set to “0”.
Enable serial instruction to pin MOSI.
chronization. When in sync. the second byte ($53), will echo back when issuing the third
byte of the Programming Enable instruction. Whether the echo is correct or not, all four
bytes of the instruction must be transmitted. If the $53 did not echo back, give RESET a
positive pulse and issue a new Programming Enable command.
258). The memory page is loaded one byte at a time by supplying the 6LSB of the
address and data together with the Load Program Memory Page instruction. To ensure
correct loading of the page, the data low byte must be loaded before data high byte is
applied for a given address. The Program Memory Page is stored by loading the Write
Program Memory Page instruction with the 8MSB of the address. If polling is not used,
the user must wait at least t
Accessing the SPI Serial Programming interface before the Flash write operation com-
pletes can result in incorrect programming.
together with the appropriate Write instruction. An EEPROM memory location is first
automatically erased before new data is written. If polling is not used, the user must wait
at least t
no $FFs in the data file(s) need to be programmed.
tent at the selected address at serial output MISO.
operation.
Set RESET to “1”.
Turn V
for timing details.
CC
WD_EEPROM
power off.
before issuing the next byte. (See
CC
ck
and GND while RESET and SCK are set to “0”. In some sys-
ck
WD_FLASH
< 12MHz, 3 CPU clock cycles for f
< 12MHz, 3 CPU clock cycles for f
before issuing the next page. (See
Table
114). In a chip erased device,
Table
ck
ck
≥ 12MHz
“Page Size” on page
≥ 12MHz
ATmega32(L)
115):
Table
114).
Figure
271