ATmega32 Atmel Corporation, ATmega32 Datasheet - Page 222

ATmega32
Manufacturer Part Number
ATmega32
Description
Manufacturer
Atmel Corporation
Specifications of ATmega32
Flash (kbytes)
32 Kbytes
Pin Count
44
Max. Operating Frequency
16 MHz
Cpu
8-bit AVR
# Of Touch Channels
16
Hardware Qtouch Acquisition
No
Max I/o Pins
32
Ext Interrupts
3
Usb Speed
No
Usb Interface
No
Spi
1
Twi (i2c)
1
Uart
1
Graphic Lcd
No
Video Decoder
No
Camera Interface
No
Adc Channels
8
Adc Resolution (bits)
10
Adc Speed (ksps)
15
Analog Comparators
1
Resistive Touch Screen
No
Temp. Sensor
No
Crypto Engine
No
Sram (kbytes)
2
Eeprom (bytes)
1024
Self Program Memory
YES
Dram Memory
No
Nand Interface
No
Picopower
No
Temp. Range (deg C)
-40 to 85
I/o Supply Class
2.7 to 5.5
Operating Voltage (vcc)
2.7 to 5.5
Fpu
No
Mpu / Mmu
no / no
Timers
3
Output Compare Channels
4
Input Capture Channels
1
Pwm Channels
4
32khz Rtc
Yes
Calibrated Rc Oscillator
Yes
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Company:
Part Number:
ATmega32-16AC
Manufacturer:
COMPAL
Quantity:
500
Part Number:
ATmega32-16AU
Manufacturer:
ATMEL
Quantity:
20 000
Part Number:
ATmega32-16PI
Manufacturer:
ATMEL/爱特梅尔
Quantity:
20 000
Part Number:
ATmega32-16PU
Manufacturer:
ATMEL/爱特梅尔
Quantity:
20 000
Using the
Boundary-scan
Chain
Using the On-chip
Debug System
2503Q–AVR–02/11
•
•
•
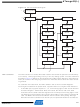
As shown in the state diagram, the Run-Test/Idle state need not be entered between selecting
JTAG instruction and using Data Registers, and some JTAG instructions may select certain
functions to be performed in the Run-Test/Idle, making it unsuitable as an Idle state.
Note:
For detailed information on the JTAG specification, refer to the literature listed in
on page
A complete description of the Boundary-scan capabilities are given in the section
(JTAG) Boundary-scan” on page
As shown in
•
•
•
All read or modify/write operations needed for implementing the Debugger are done by applying
AVR instructions via the internal AVR CPU Scan Chain. The CPU sends the result to an I/O
memory mapped location which is part of the communication interface between the CPU and the
JTAG system.
The Break Point Unit implements Break on Change of Program Flow, Single Step Break, 2 Pro-
gram Memory Break Points, and 2 combined Break Points. Together, the 4 Break Points can be
configured as either:
•
•
•
•
•
on the TDO pin. The JTAG Instruction selects a particular Data Register as path between
TDI and TDO and controls the circuitry surrounding the selected Data Register.
Apply the TMS sequence 1, 1, 0 to re-enter the Run-Test/Idle state. The instruction is
latched onto the parallel output from the Shift Register path in the Update-IR state. The Exit-
IR, Pause-IR, and Exit2-IR states are only used for navigating the state machine.
At the TMS input, apply the sequence 1, 0, 0 at the rising edges of TCK to enter the Shift
Data Register – Shift-DR state. While in this state, upload the selected Data Register
(selected by the present JTAG instruction in the JTAG Instruction Register) from the TDI
input at the rising edge of TCK. In order to remain in the Shift-DR state, the TMS input must
be held low during input of all bits except the MSB. The MSB of the data is shifted in when
this state is left by setting TMS high. While the Data Register is shifted in from the TDI pin,
the parallel inputs to the Data Register captured in the Capture-DR state is shifted out on the
TDO pin.
Apply the TMS sequence 1, 1, 0 to re-enter the Run-Test/Idle state. If the selected Data
Register has a latched parallel-output, the latching takes place in the Update-DR state. The
Exit-DR, Pause-DR, and Exit2-DR states are only used for navigating the state machine.
A scan chain on the interface between the internal AVR CPU and the internal peripheral
units
Break Point unit
Communication interface between the CPU and JTAG system
4 single Program Memory Break Points
3 Single Program Memory Break Point + 1 single Data Memory Break Point
2 single Program Memory Break Points + 2 single Data Memory Break Points
2 single Program Memory Break Points + 1 Program Memory Break Point with mask (“range
Break Point”)
2 single Program Memory Break Points + 1 Data Memory Break Point with mask (“range
Break Point”)
Independent of the initial state of the TAP Controller, the Test-Logic-Reset state can always be
entered by holding TMS high for five TCK clock periods.
224.
Figure
112, the hardware support for On-chip Debugging consists mainly of:
225.
ATmega32(L)
“Bibliography”
“IEEE 1149.1
222