CY7C63801-PXC Cypress Semiconductor Corp, CY7C63801-PXC Datasheet
CY7C63801-PXC
Specifications of CY7C63801-PXC
Related parts for CY7C63801-PXC
CY7C63801-PXC Summary of contents
Page 1
... Maskable interrupts on all I/O pins ❐ A dedicated 3.3 V regulator for the USB PHY. Aids in signalling ■ and D– line pull-up Cypress Semiconductor Corporation Document 38-08035 Rev. *N Low Speed USB Peripheral Controller 125 mA 3.3 V voltage regulator powers external 3.3 V devices ■ 3.3 V I/O pins ■ ...
Page 2
Contents Introduction ....................................................................... 4 Conventions ...................................................................... 4 Pinouts .............................................................................. 5 CPU Architecture .............................................................. 8 CPU Registers ................................................................... 9 Instruction Set Summary ............................................... 13 Memory Organization ..................................................... 14 Clocking .......................................................................... 20 Reset ................................................................................ 28 Sleep Mode ...................................................................... 29 Low Voltage Detect ...
Page 3
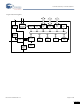
Logic Block Diagram Low-Speed USB/PS2 3.3V Transceiver Regulator and Pull up Internal 24 MHz Oscillator Clock Control External Clock POR / Low-Voltage Detect Document 38-08035 Rev Low-Speed Interrupt 4 3VIO/SPI Extended USB SIE Control Pins IO ...
Page 4
Introduction Cypress has reinvented its leadership position in the low speed USB market with a new family of innovative microcontrollers. Introducing enCoRe II USB - ‘enhanced Component Reduction.’ Cypress has leveraged its design expertise in USB solutions to advance ...
Page 5
... P0.1 8 P0.0 9 P2 CY7C63833 P0.6/TIO1 1 P0.5/TIO0 2 P0.4/INT2 3 P0.3/INT1 4 P0.2/INT0 5 P0.1 6 P0 Document 38-08035 Rev. *N Figure 5-1. Pin Diagrams Top View CY7C63801, CY7C63310 16-Pin SOIC P1.6/SMISO TIO1/P0 TIO0/P0.5 2 P1.5/SMOSI P1.4/SCLK INT2/P0 INT1/P0.3 13 P1.3/SSEL 4 12 P1.2 INT0/P0 P0 P1.1/D– P0 P1.0/ CY7C63813 18-Pin SOIC P1 ...
Page 6
Table 5-1. Die Pad Summary Pad Number Pad Name 1 P0.7 2 P0.6 3 P0.5 4 P0.4 5 P0.3 6 P0.2 7 P0.1 8 P0.0 CLKIN 9 P2.1 10 P2.0 11 VSS 12 PI P1.1 D– 14 VDD ...
Page 7
... P1.2/VREG GPIO Port 1 bit 2. Configured individually. 3.3V if regulator is enabled. (The 3.3 V regulator is not available in the CY7C63310 and CY7C63801.) A 1-μF min, 2-μF max capacitor is required on Vreg output P1.3/SSEL GPIO Port 1 bit 3. Configured individually. Alternate function is SSEL signal of the SPI bus TTL voltage thresholds ...
Page 8
Table 5-2. Pin Description (continued SOIC SIOC PDIP QFN QSOP – – – – ...
Page 9
CPU Registers The CPU registers in enCoRe II devices are in two banks with 256 registers in each bank. Bit[4]/XI/O bit in the CPU Flags register must be set/cleared to select between the two register banks 7.1 Flags Register ...
Page 10
Table 7-3. CPU X Register (CPU_X) Bit # 7 6 Field – – Read/Write 0 0 Default Bit [7:0]: X [7:0] 8-bit data value holds an index for any instruction that uses an indexed addressing mode. Table 7-4. CPU Stack ...
Page 11
Source Direct The result of an instruction using this addressing mode is placed in either the A register or the X register, which is specified as part of the instruction opcode. Operand address that points to ...
Page 12
Destination Direct Source Immediate The result of an instruction using this addressing mode is placed within the RAM memory space or the register space. Operand 1 is the address of the result. The source of the instruction is Operand ...
Page 13
Instruction Set Summary The instruction set is summarized in Table 8-1 Instruction Set Summary tables are described in detail in the PSoC Designer Assembly Language User Guide (available on the Cypress web site at http://www.cypress.com). Table 8-1. Instruction Set ...
Page 14
... Reserved 0x005C Reserved 0x0060 Reserved 0x0064 Sleep timer 0x0068 Program Memory begins here (if below interrupts not used, program memory can start lower) 0x0BFF 3 KB ends here (CY7C63310) 0x0FFF 4 KB ends here (CY7C63801) 0x1FFF 8 KB ends here (CY7C638x3) CY7C63310, CY7C638xx Page [+] Feedback ...
Page 15
Data Memory Organization The CY7C63310/638xx microcontrollers provide up to 256 bytes of data RAM. after reset 8-bit PSP Top of RAM Memory 9.3 Flash This section describes the flash block of the enCoRe II. Much of the user visible ...
Page 16
Two important variables that are used for all functions are KEY1 and KEY2. These variables are used to help discriminate between valid SSCs and inadvertent SSCs. KEY1 must always have a value of 3 Ah, while KEY2 must have the ...
Page 17
WriteBlock Function The WriteBlock function is used to store data in the flash. Data is moved 64 bytes at a time from SRAM to flash using this function. The WriteBlock function first checks the protection bits and determines if ...
Page 18
Table 9-8. ProtectBlock Parameters Name Address Description KEY1 0,F8h 3Ah KEY2 0,F9h Stack Pointer value when SSC is executed. CLOCK 0,FCh Clock divider used to set the write pulse width. DELAY 0,FEh For a CPU speed of 12 MHz set ...
Page 19
F8h Silicon ID Table 0 [15-8] Family/ Table 1 Die ID Table 2 Table 3 Table 4 Table 5 Table 6 Table 7 The Silicon IDs for enCoRe II devices are stored in SROM tables in the part, as shown ...
Page 20
Checksum Function The Checksum function calculates a 16-bit checksum over a user specifiable number of blocks, within a single flash macro (Bank) starting from block zero. The BLOCKID parameter is used to pass in the number of blocks to ...
Page 21
CLK_EXT CLK_24MHz Document 38-08035 Rev. *N Figure 10-1. Clock Block Diagram CPUCLK SEL n SCALE (divide MUX n = 0-5,7) EXT CLK_USB MUX 24 MHz SEL SCALE OUT SEL SCALE MHz ...
Page 22
Clock Architecture Description The enCoRe II clock selection circuitry allows the selection of independent clocks for the CPU, USB, Interval Timers and Capture Timers. The CPU clock CPUCLK is sourced from an external clock or the Internal 24 MHz ...
Page 23
Table 10-2. LPOSC Trim (LPOSCTR) [0x36] [R/W] Bit # kHz Low Reserved Field Power R/W – Read/Write 0 D Default This register is used to calibrate the 32 kHz Low speed Oscillator. The reset value is undefined ...
Page 24
Table 10-4. OSC Control 0 (OSC_CR0) [0x1E0] [R/W] Bit # 7 6 Reserved Field – – Read/Write 0 0 Default Bit [7:6]: Reserved Bit 5: No Buzz During sleep (the Sleep bit is set in the CPU_SCR on periodically to ...
Page 25
Table 10-5. USB Osclock Clock Configuration (OSCLCKCR) [0x39] [R/W] Bit # 7 6 Field – – Read/Write 0 0 Default This register is used to trim the Internal 24 MHz Oscillator using received low speed USB packets as a timing ...
Page 26
Interval Timer Clock (ITMRCLK) The Interval Timer Clock (TITMRCLK), is sourced from an external clock, the Internal 24 MHz Oscillator, the Internal 32 kHz Low power Oscillator, or the Timer Capture clock. A programmable prescaler ...
Page 27
Captimer Clock Table 10-1. Clock IO Config (CLKIOCR) [0x32] [R/W] Bit # 7 6 Field – – Read/Write 0 0 Default Bit [7:2]: Reserved Bit [1:0]: CLKOUT Select Internal 24 MHz Oscillator External clock ...
Page 28
Reset The microcontroller supports two types of resets: Power on Reset (POR) and Watchdog Reset (WDR). When reset is initiated, all registers are restored to their default states and all interrupts are disabled. The occurrence of a reset is ...
Page 29
Power on Reset POR occurs every time the power to the device is switched on. POR is released when the supply is typically 2.6V for the upward supply transition, with typically hysteresis during the power on ...
Page 30
Sleep Sequence The SLEEP bit is an input into the sleep logic circuit. This circuit is designed to sequence the device into and out of the hardware sleep state. The hardware sequence to put the device to sleep is ...
Page 31
Low Power in Sleep Mode To achieve the lowest possible power consumption during suspend or sleep, the following conditions must be observed in addition to considerations for the sleep timer: 1. All GPIOs must be set to outputs and ...
Page 32
Low Voltage Detect Control Table 13-1. Low Voltage Control Register (LVDCR) [0x1E3] [R/W] Bit # 7 6 Reserved Field – – Read/Write 0 0 Default This register controls the configuration of the Power on Reset/Low voltage Detection block. Note ...
Page 33
Table 13-2. Voltage Monitor Comparators Register (VLTCMP) [0x1E4] [R] Bit # 7 6 Field – – Read/Write 0 0 Default This read only register allows reading the current state of the Low-Voltage-Detection and Precision-Power-On-Reset compar- ators Bit [7:2]: Reserved Bit ...
Page 34
General Purpose I/O (GPIO) Ports 14.1 Port Data Registers Table 14-1. P0 Data Register (P0DATA)[0x00] [R/W] Bit # 7 6 P0.7 P0.6/TIO1 Field R/W R/W Read/Write 0 0 Default This register contains the data for Port 0. Writing to ...
Page 35
... Table 19-1 on page 58 is set), a 3.3V source is placed on the pin and the GPIO function of the pin is disabled. The VREG functionality is not present in the CY7C63310 and the CY7C63801 variants μF min, 2 μF max capacitor is required on VREG output. Bit [1:0]: P1.1–P1.0/D– and D+ When the USB mode is disabled (Bit 7 in the P1.0 and P1.1 pins. When the USB mode is enabled, the P1.1 and P1.0 pins are used as the D– ...
Page 36
... To enable the pin for GPIO, clear the corresponding VREG Output or SPI Use bit. The SPI function controls the output enable for its dedicated function pins when their GPIO enable bit is clear. The VREG output is not available on the CY7C63801 and CY7C63310. 14.2.9 3.3V Drive The P1 ...
Page 37
Drive Pull-Up Enable Output Enable Open Drain Port Data High Sink Data In TTL Threshold Table 14-1. P0.0/CLKIN Configuration (P00CR) [0x05] [R/W] Bit # 7 6 Reserved Int Enable Field – R/W Read/Write 0 0 Default This pin is ...
Page 38
Table 14-3. P0.2/INT0–P0.4/INT2 Configuration (P02CR–P04CR) [0x07–0x09] [R/W] Bit # 7 6 Reserved Field – – Read/Write 0 0 Default These registers control the operation of pins P0.2–P0.4 respectively. The pins are shared between the P0.2–P0.4 GPIOs and the INT0–INT2. These ...
Page 39
Table 14-5. P0.7 Configuration (P07CR) [0x0C] [R/W] Bit # 7 6 Reserved Int Enable Field – R/W Read/Write 0 0 Default This register controls the operation of pin P0.7. The P0.7 pin only exists in the CY7C638(1/2/3)3. Table 14-6. P1.0/D+ ...
Page 40
Table 14-9. P1.3 Configuration (P13CR) [0x10] [R/W] Bit # 7 6 Reserved Int Enable Field – R/W Read/Write 0 0 Default This register controls the operation of the P1.3 pin. This register exists in all enCoRe II parts. The P1.3 ...
Page 41
Table 14-13. P3 Configuration (P3CR) [0x16] [R/W] Bit # 7 6 Reserved Int Enable Field – R/W Read/Write 0 0 Default This register exists in CY7C638(2/3)3. This register controls the operation of pins P3.0–P3.1. 15. Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) The ...
Page 42
SPI Configure Register Table 15-2. SPI Configure Register (SPICR) [0x3D] [R/W] Bit # 7 6 Swap LSB First Field R/W R/W Read/Write 0 0 Default Bit 7: Swap 0 = Swap function disabled The SPI block swaps ...
Page 43
SPI Interface Pins The SPI interface uses the P1.3–P1.6 pins. These pins are configured using the P1.3 and P1.4–P1.6 Configuration. Table 15-4. SPI Mode Timing vs. LSB First, CPOL and CPHA LSB First CPHA CPOL ...
Page 44
Timer Registers All timer functions of the enCoRe II are provided by a single timer block. The timer block is asynchronous from the CPU clock. 16.1 Registers 16.1.1 Free Running Counter The 16 bit free-running counter is clocked by ...
Page 45
Table 16-3. Timer Capture 0 Rising (TIO0R) [0x22] [R/W] Bit # 7 6 Field R/W R/W Read/Write 0 0 Default Bit [7:0]: Capture 0 Rising [7:0] This register holds the value of the Free-running Timer when the last rising edge ...
Page 46
Table 16-8. Programmable Interval Timer High (PITMRH) [0x27] [R] Bit # 7 6 Reserved Field – – Read/Write 0 0 Default Bit [7:4]: Reserved Bit [3:0]: Prog Internal Timer [11:8] This register holds the high order nibble of the 12-bit ...
Page 47
Timer Capture Cypress enCoRe II has two 8-bit captures. Each capture has separate registers for the rising and falling time. The two eight bit captures can be configured as a single 16-bit capture. When configured, the capture 1 registers ...
Page 48
Table 16-2. Capture Interrupt Enable (TCAPINTE) [0x2B] [R/W] Bit # 7 6 Reserved Field – – Read/Write 0 0 Default Bit [7:4]: Reserved Bit 3: Cap1 Fall Enable 0 = Disable the capture 1 falling edge interrupt 1 = Enable ...
Page 49
Figure 16-3. Timer Functional Sequence Diagram Document 38-08035 Rev. *N CY7C63310, CY7C638xx Page [+] Feedback ...
Page 50
Figure 16-4. 16-Bit Free Running Counter Loading Timing Diagram clk_sys write valid addr write data FRT reload ready Clk Timer 12b Prog Timer 12b reload interrupt Capture timer clk 16b free running counter load 16b free 00A0 00A1 00A2 00A3 ...
Page 51
Interrupt Controller The interrupt controller and its associated registers allow the user’s code to respond to an interrupt from almost every functional block in the enCoRe II devices. The registers associated with the interrupt controller allow disabling interrupts globally ...
Page 52
Figure 17-1. Interrupt Controller Block Diagram Interrupt Taken or INT_CLRx Write Interrupt Source (Timer, GPIO, etc.) 17.2 Interrupt Processing The sequence of events that occur during interrupt processing follows interrupt becomes active, because: a. ...
Page 53
Interrupt Registers The Interrupt Clear Registers (INT_CLRx) are used to enable the individual interrupt sources’ ability to clear posted interrupts. When an INT_CLRx register is read, any bits that are set indicates an interrupt has been posted for that ...
Page 54
Table 17-4. Interrupt Mask 3 (INT_MSK3) [0xDE] [R/W] Bit # 7 6 ENSWINT Field R/W – Read/Write 0 0 Default Bit 7: Enable Software Interrupt (ENSWINT) 0= Disable. Writing INT_CLRx register, when ENSWINT is cleared, causes the ...
Page 55
Table 17-6. Interrupt Mask 1 (INT_MSK1) [0xE1] [R/W] Bit # 7 6 TCAP0 Prog Interval Field Int Enable Timer Int Enable R/W R/W Read/Write 0 0 Default Bit 7: TCAP0 Interrupt Enable 0 = Mask TCAP0 interrupt 1 = Unmask ...
Page 56
Table 17-7. Interrupt Mask 0 (INT_MSK0) [0xE0] [R/W] Bit # 7 6 GPIO Port 1 Sleep Timer Field Int Enable Int Enable R/W R/W Read/Write 0 0 Default Bit 7: GPIO Port 1 Interrupt Enable 0 = Mask GPIO Port ...
Page 57
Regulator Output 18.1 VREG Control Table 18-1. VREG Control Register (VREGCR) [0x73] [R/W] Bit # 7 6 Field – – Read/Write 0 0 Default Bit [7:2]: Reserved Bit 1: Keep Alive Keep Alive, when set, allows the voltage regulator ...
Page 58
USB/PS2 Transceiver Although the USB transceiver has features to assist in interfacing to PS/2, these features are not controlled using these registers. The registers only control the USB interfacing features. PS/2 interfacing options are controlled by the D+ and ...
Page 59
USB Device 21.1 USB Device Address Table 21-1. USB Device Address (USBCR) [0x40] [R/W] Bit # 7 6 USB Enable Field R/W R/W Read/Write 0 0 Default Bit 7: USB Enable This bit must be enabled by firmware before ...
Page 60
Endpoint 0 Mode Because both firmware and the SIE are allowed to write to the Endpoint 0 Mode and Count Registers, the SIE provides an interlocking mechanism to prevent accidental overwriting of data. When the SIE writes to these ...
Page 61
Endpoint 1 and 2 Mode Table 21-4. Endpoint 1 and 2 Mode (EP1MODE – EP2MODE) [0x45, 0x46] [R/W] Bit # 7 6 Stall Reserved Field R/W R/W Read/Write 0 0 Default Bit 7: Stall When this bit is set ...
Page 62
Table 21-7. Endpoint 2 Data (EP2DATA) [0x60-0x67] [R/W] Bit # 7 6 Field R/W R/W Read/Write Unknown Unknown Default The Endpoint 2 buffer is comprised of 8 bytes located at address 0x60 to 0x67. The three data buffers are used ...
Page 63
SETUP, IN, and OUT Columns Depending on the mode specified in the 'Encoding' column, the 'SETUP', 'IN', and 'OUT' columns contain the SIE's responses when the endpoint receives SETUP, IN, and OUT tokens, respectively. A 'Check' in the Out ...
Page 64
Details of Mode for Differing Traffic Conditions Control Endpoint SIE Bus Event Mode Token Count Dval D0/1 Response S 0010 OUT <=10, <>2 valid x 0010 OUT 2 valid 0 0010 OUT 2 valid 1 ACK_OUT_STATUS_IN 1011 SETUP >10 ...
Page 65
Details of Mode for Differing Traffic Conditions Control Endpoint SIE Bus Event Mode Token Count Dval D0/1 1101 NAK IN 1100 OUT 1100 24. Register Summary The XIO ...
Page 66
Register Summary (continued) The XIO bit in the CPU Flags Register must be set to access the extended register space for all registers above 0xFF. Addr Name TMRCR First Edge 8-bit capture Prescale Hold 2B TCAPINTE ...
Page 67
Register Summary (continued) The XIO bit in the CPU Flags Register must be set to access the extended register space for all registers above 0xFF. Addr Name INT_MSK0 GPIO Port Sleep 1 Timer Int Enable Int ...
Page 68
Voltage Vs CPU Frequency Characteristics Figure 25-1. Voltage vs CPU Frequency Characteristics 5.50 4.75 4.00 Running the CPU at 24 MHz requires a minimum voltage of 4.75 V. This applies to any CPU speed above 12 MHz, so using ...
Page 69
Absolute Maximum Ratings Exceeding maximum ratings may shorten the useful life of the device. User guidelines are not tested. Storage Temperature ................................. –40 °C to +90 °C Ambient Temperature with Power Applied... –0 °C to +70 °C Supply Voltage ...
Page 70
DC Characteristics (continued) Description Parameter General V Differential input sensitivity DI V Differential input common mode range CM V Single ended receiver threshold SE C Transceiver capacitance IN I Hi-Z state data line leakage IO PS/2 Interface V Static ...
Page 71
AC Characteristics (continued) Parameter Description USB Driver T Transition rise time R1 T Transition rise time R2 T Transition fall time F1 T Transition fall time F2 T Rise/fall time matching R V Output signal crossover voltage CRS USB ...
Page 72
CLOCK 90% GPIO Pin Output Voltage 10 crs − T PERIOD Differential Data Lines Document 38-08035 Rev. *N Figure 28-1. Clock Timing T CYC Figure 28-2. GPIO ...
Page 73
Figure 28-5. Differential to EOP Transition Skew and EOP Width T PERIOD Differential Data Lines T PERIOD Differential Data Lines Document 38-08035 Rev. *N Crossover Point Extended Crossover Point Diff. Data to SE0 Skew PERIOD ...
Page 74
SS SCK (CPOL=0) T SCKH SCK (CPOL=1) T MDO MOSI MSB MISO T MSU SS T SSS SCK (CPOL=0) T SCKH SCK (CPOL=1) MOSI T T SDO MISO Document 38-08035 Rev. *N Figure 28-7. SPI Master Timing, CPHA = 1 ...
Page 75
SS SCK (CPOL=0) T SCKH SCK (CPOL=1) T MDO1 MOSI MSB MISO MSB T T MHD MSU SS T SSS SCK (CPOL=0) T SCKH SCK (CPOL=1) MSB MOSI T T SSU SHD T SDO1 MISO MSB Document 38-08035 Rev. *N ...
Page 76
... Ordering Information Ordering Code FLASH Size CY7C63310-SXC CY7C63801-SXC CY7C63803-SXC CY7C63803-SXCT CY7C63813-PXC CY7C63813-SXC CY7C63823-QXC CY7C63823-SXC CY7C63823-SXCT CY7C63803-LQXC CY7C63823-XC CY7C63823-3XW14C CY7C63833-LTXC CY7C63833-LTXCT 29.1 Ordering Code Definitions XXXXX 30. Package Handling Some IC packages require baking before they are soldered onto a PCB to remove moisture that may have been absorbed after leaving the factory ...
Page 77
Package Diagrams Document 38-08035 Rev. *N Figure 31-1. 16-Pin (300-Mil) Molded DIP P1 Figure 31-2. 16-Pin (150-Mil) SOIC S16.15 CY7C63310, CY7C638xx 51-85009 *B 51-85068 *C Page [+] Feedback ...
Page 78
Document 38-08035 Rev. *N Figure 31-3. 18-Pin (300-Mil) Molded DIP P3 Figure 31-4. 18-Pin (300-Mil) Molded SOIC S3 CY7C63310, CY7C638xx 51-85010 *C 51-85023 *C Page [+] Feedback ...
Page 79
S Document 38-08035 Rev. *N Figure 31-5. 24-Pin (300-Mil) SOIC S13 Figure 31-6. 24-Pin QSOP O241 CY7C63310, CY7C638xx 51-85025 *E 51-85055 *C Page [+] Feedback ...
Page 80
Figure 31-7. 24-Pin QFN 4X4X0.55 mm LQ24 A 2.65X2.65X EPAD (Sawn) Document 38-08035 Rev. *N Figure 31-8. 32-Pin QFN Package CY7C63310, CY7C638xx 001-13937 *C 51-85188 *D Page [+] Feedback ...
Page 81
Document 38-08035 Rev. *N Figure 31-9. 32-Pin Sawn QFN Package CY7C63310, CY7C638xx 001-30999 *C Page [+] Feedback ...
Page 82
Acronyms Acronym Description CMOS complementary metal oxide semiconductor CE chip enable I/O input/output OE output enable SRAM static random access memory TSOP thin small outline package WE write enable Document 38-08035 Rev. *N CY7C63310, CY7C638xx 33. Document Conventions Units ...
Page 83
... AC Characteristics on page 70 MDO1 Phase to 0. Pinouts on page 5: Removed the VREG from the CY7C63310 and CY7C63801 Removed SCLK and SDATA. Created a separate pinout diagram for the CY7C63813. Added the GPIO Block Diagram (Figure 14-1 on page Table 10-4 on page 24: Changed the Sleep Timer Clock unit from 32 kHz count to Hz ...
Page 84
Document History Page Document Title: CY7C63310, CY7C638xx enCoRe™ II Low Speed USB Peripheral Controller Document Number: 38-08035 Orig. of Submis- Revision ECN No. Change sion Date *G 424790 TYJ See ECN *H 491711 TYJ See ECN *I 504691 TYJ ...
Page 85
... Added partnumber CY7C63803-LQXC to the ordering information table and added package diagram (spec 001-13937) Removed inactive parts from ordering information table. CY7C63310-PXC CY7C63801-PXC CY7C63833-LFXC Updated package diagrams. Added Ordering Code Definition, Acronyms, and Document Conventions. Added part CY7C63823-3XW14C to the ordering information table. ...
Page 86
... Cypress against all charges. Any Source Code (software and/or firmware) is owned by Cypress Semiconductor Corporation (Cypress) and is protected by and subject to worldwide patent protection (United States and foreign), United States copyright laws and international treaty provisions. Cypress hereby grants to licensee a personal, non-exclusive, non-transferable license to copy, use, modify, create derivative works of, and compile the Cypress Source Code and derivative works for the sole purpose of creating custom software and or firmware in support of licensee product to be used only in conjunction with a Cypress integrated circuit as specified in the applicable agreement ...