LPC661AIM National Semiconductor, LPC661AIM Datasheet - Page 8
LPC661AIM
Manufacturer Part Number
LPC661AIM
Description
IC OP AMP LOW PWR CMOS 8-SOIC
Manufacturer
National Semiconductor
Datasheet
1.LPC661IMNOPB.pdf
(15 pages)
Specifications of LPC661AIM
Amplifier Type
General Purpose
Number Of Circuits
1
Output Type
Rail-to-Rail
Slew Rate
0.11 V/µs
Gain Bandwidth Product
350kHz
Current - Input Bias
0.002pA
Voltage - Input Offset
1000µV
Current - Supply
58µA
Current - Output / Channel
40mA
Voltage - Supply, Single/dual (±)
4.75 V ~ 15.5 V, ±2.38 V ~ 7.75 V
Operating Temperature
-40°C ~ 85°C
Mounting Type
Surface Mount
Package / Case
8-SOIC (3.9mm Width)
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Contains lead / RoHS non-compliant
-3db Bandwidth
-
Other names
*LPC661AIM
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Part Number:
LPC661AIMX
Manufacturer:
NS/国半
Quantity:
20 000
www.national.com
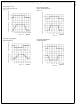
Typical Performance Characteristics
Stability vs Capacitive Load
Note: Avoid resistive loads of less than 500 , as they may cause
instability.
Application Hints
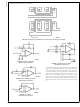
AMPLIFIER TOPOLOGY
The topology chosen for the LPC661 is unconventional
(compared to general-purpose op amps) in that the tradi-
tional unity-gain buffer output stage is not used; instead, the
output is taken directly from the output of the integrator, to al-
low rail-to-rail output swing. Since the buffer traditionally de-
livers the power to the load, while maintaining high op amp
gain and stability, and must withstand shorts to either rail,
these tasks now fall to the integrator.
As a result of these demands, the integrator is a compound
affair with an embedded gain stage that is doubly fed forward
(via C
driver. In addition, the output portion of the integrator is a
push-pull configuration for delivering heavy loads. While
sinking current the whole amplifier path consists of three
gain stages with one stage fed forward, whereas while
sourcing the path contains four gain stages with two fed
forward.
The large signal voltage gain while sourcing is comparable
to traditional bipolar op amps, for load resistance of at least
5 k . The gain while sinking is higher than most CMOS op
amps, due to the additional gain stage; however, when driv-
f
and C
FIGURE 1. LPC661 Circuit Topology
ff
) by a dedicated unity-gain compensation
DS011227-6
DS011227-4
V
Stability vs Capacitive Load
8
S
=
ing load resistance of 5 k
as indicated in the Electrical Characteristics. The op amp
can drive load resistance as low as 500
COMPENSATING INPUT CAPACITANCE
Refer to the LMC660 or LMC662 datasheets to determine
whether or not a feedback capacitor will be necessary for
compensation and what the value of that capacitor would be.
CAPACITIVE LOAD TOLERANCE
Like many other op amps, the LPC661 may oscillate when
its applied load appears capacitive. The threshold of oscilla-
tion varies both with load and circuit gain. The configuration
most sensitive to oscillation is a unity-gain follower. See the
Typical Performance Characteristics.
The load capacitance interacts with the op amp’s output re-
sistance to create an additional pole. If this pole frequency is
sufficiently low, it will degrade the op amp’s phase margin so
that the amplifier is no longer stable at low gains. The addi-
tion of a small resistor (50
amp’s output, and a capacitor (5 pF to 10 pF) from inverting
input to output pins, returns the phase margin to a safe value
without interfering with lower-frequency circuit operation.
Thus, larger values of capacitance can be tolerated without
oscillation. Note that in all cases, the output will ring heavily
when the load capacitance is near the threshold for
oscillation.
±
7.5V, T
A
= 25˚C unless otherwise specified (Continued)
or less, the gain will be reduced
to 100 ) in series with the op
without instability.
DS011227-5