LTC1799CS5 Linear Technology, LTC1799CS5 Datasheet - Page 9

LTC1799CS5
Manufacturer Part Number
LTC1799CS5
Description
Manufacturer
Linear Technology
Type
Silicon Oscillatorr
Datasheet
1.LTC1799CS5.pdf
(12 pages)
Specifications of LTC1799CS5
Mounting Style
Surface Mount
Screening Level
Commercial
Product Length (mm)
2.9mm
Product Depth (mm)
1.75mm
Product Height (mm)
0.9mm
Package / Case
TSOT-23
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Not Compliant
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Company:
Part Number:
LTC1799CS5
Manufacturer:
LINEAR
Quantity:
380
Company:
Part Number:
LTC1799CS5#PBF/H
Manufacturer:
LT
Quantity:
6
Company:
Part Number:
LTC1799CS5#TRMPBF
Manufacturer:
LT
Quantity:
1 505
Part Number:
LTC1799CS5#TRMPBF
Manufacturer:
LINEAR/凌特
Quantity:
20 000
Company:
Part Number:
LTC1799CS5TR
Manufacturer:
LT
Quantity:
6 610
APPLICATIO S I FOR ATIO
Jitter
The typical jitter is listed in the Electrical Characteristics
and shown in the Typical Performance Characteristics.
These specifications assume that the capacitance on SET
(Pin 3) is limited to less than 10pF, as suggested in the Pin
Functions description. If this requirement is not met, the
jitter will increase. For more information, contact Linear
Technology Applications group.
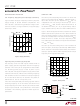
A Ground Referenced Voltage Controlled Oscillator
The LTC1799 output frequency can also be programmed
by steering current in or out of the SET pin, as conceptually
shown in Figure 8. This technique can degrade accuracy as
the ratio of (V
dependent of the value of R
Block Diagram. This loss of accuracy will become notice-
able when the magnitude of I
The frequency variation of the LTC1799 is still monotonic.
Figure 9 shows how to implement the concept shown in
Figure 8 by connecting a second resistor, R
SET pin and a ground referenced voltage source, V
For a given power supply voltage in Figure 9, the output
frequency of the LTC1799 is a function of V
and (V
f
⎡
⎢
⎢
⎢
⎢
⎣
OSC
1
Figure 8. Concept for Programming via Current Steering
+
+
(
=
– V
V
V
+
I
R
IN
PR
10
V
SET
SET
RES
−
MHz
N
V
) = V
0.1µF
+
+
)
– V
I
RES
•
•
U
RES
R R
⎛
⎜
⎜
⎜
⎝
IN
SET
1
10
:
+
1
2
3
) / I
R
k
U
1
V
GND
SET
SET
R
LTC1799
+
SET
SET
IN
PROG
RES
, as shown in the LTC1799
•
OUT
DIV
⎞
⎟
⎟
⎟
⎠
⎤
⎥
⎥
⎥
⎥
⎦
is no longer uniquely
5
4
is comparable to I
W
÷100
÷1
5V
÷10
IN
, between the
IN
OPEN
1799 F08
, R
U
IN
, R
IN
RES
.
SET
(1)
.
When V
assumes the highest value and it is set by the parallel
combination of R
quency, f
V
When V
proaches the ground potential, the oscillator frequency,
f
by the change of V
by ±8%, assuming the variation of V
perature coefficient of V
By manipulating the algebraic relation for f
simple algorithm can be derived to set the values of
external resistors R
1. Choose the desired value of the maximum oscillator
2. Set the desired value of the minimum oscillator fre-
3. Choose V
R
(
OSC
R
SET
V
SET
IN MAX
frequency, f
age V
quency, f
V
from the following:
IN
, assumes its lowest value and its accuracy is affected
IN(MIN)
Figure 9. Implementation of Concept Shown in Figure 8
(
) so the accuracy of f
=
+
–
IN
IN
IN(MAX)
V
)
OSC
IN
−
is less than V
= V
≥ 0.
V
R
OSC(MIN)
RES
+
IN
V
V
, is independent of the value of V
V
RES
RES
+
OSC(MAX)
+
–
+
)
, the output frequency of the LTC1799
≤ V
= 1.1 and calculate the ratio of R
−
IN
⎡
⎢
⎢
⎣
0.1µF
R
RES
(
SET
⎛
⎜
⎝
+
SET
, occurring at minimum input voltage
f
and R
f
.
OSC MAX
f
OSC MIN
f
OSC MAX
OSC MIN
= (V
, occurring at maximum input volt-
and R
RES
(
OSC
(
(
+
(
, and especially when V
SET
1
2
3
+
is within the data sheet limits.
– V
is 0.02%/°C.
)
V
GND
SET
)
IN
)
. Also note, the output fre-
LTC1799
)
+
)
⎞
⎟
⎠
, as shown in Figure 9.
−
SET
(
V
1
OUT
DIV
IN MIN
⎤
⎥
⎥
⎦
). At 25°C V
(
+
5
4
is ±5%. The tem-
÷100
LTC1799
f
)
OSC
÷1
−
5V
V
OSC
÷10
+
RES
)
RES
sn1799 1799fbs
OPEN
above, a
−
1799 F09
IN
= (V
1
IN
varies
/R
9
ap-
SET
+
(2)
–