LTC1799CS5 Linear Technology, LTC1799CS5 Datasheet - Page 7

LTC1799CS5
Manufacturer Part Number
LTC1799CS5
Description
Manufacturer
Linear Technology
Type
Silicon Oscillatorr
Datasheet
1.LTC1799CS5.pdf
(12 pages)
Specifications of LTC1799CS5
Mounting Style
Surface Mount
Screening Level
Commercial
Product Length (mm)
2.9mm
Product Depth (mm)
1.75mm
Product Height (mm)
0.9mm
Package / Case
TSOT-23
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Not Compliant
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Company:
Part Number:
LTC1799CS5
Manufacturer:
LINEAR
Quantity:
380
Company:
Part Number:
LTC1799CS5#PBF/H
Manufacturer:
LT
Quantity:
6
Company:
Part Number:
LTC1799CS5#TRMPBF
Manufacturer:
LT
Quantity:
1 505
Part Number:
LTC1799CS5#TRMPBF
Manufacturer:
LINEAR/凌特
Quantity:
20 000
Company:
Part Number:
LTC1799CS5TR
Manufacturer:
LT
Quantity:
6 610
APPLICATIO S I FOR ATIO
SELECTING THE DIVIDER SETTING AND RESISTOR
The LTC1799’s master oscillator has a frequency range
spanning 0.1MHz to 33MHz. However, accuracy may
suffer if the master oscillator is operated at greater than
10MHz with a supply voltage lower than 4V. A program-
mable divider extends the frequency range to greater than
three decades. Table 1 describes the recommended fre-
quencies for each divider setting. Note that the ranges
overlap; at some frequencies there are two divider/resistor
combinations that result in the desired frequency.
In general, any given oscillator frequency (f
obtained using the lowest master oscillator frequency.
Lower master oscillator frequencies use less power and
are more accurate. For instance, f
obtained by either R
= 10MHz or R
The R
accuracy.
Table 1. Frequency Range vs Divider Setting
DIVIDER SETTING
÷1
÷10
÷100 ⇒
*
LTC1799 may suffer reduced accuracy with a supply voltage less than 4V.
After choosing the proper divider setting, determine the
correct frequency-setting resistor. Because of the linear
correspondence between oscillation period and resis-
tance, a simple equation relates resistance with frequency.
Any resistor, R
oscillator, f
At master oscillator frequencies greater than 10MHz (R
(R
R
R
SETMAX
SET
SETMIN
⇒
⇒
SET
=
= 100k is preferred for lower power and better
DIV (Pin 4) = GND
DIV (Pin 4) = Floating
DIV (Pin 4) = V
10
OSC
= 1M)
= 3k (5V Supply), 5k (3V Supply),
SET
k
SET
.
•
⎛
⎜
⎝
= 100k, N = 10, master oscillator = 1MHz.
, tolerance adds to the inaccuracy of the
N f
10
U
•
SET
MHz
OSC
+
= 10k, N = 100, master oscillator
U
⎞
⎟
⎠
, N =
⎧
⎪
⎨
⎩ ⎪
W
OSC
100
10
1
FREQUENCY RANGE
= 100kHz can be
50kHz to 1MHz
> 500kHz
OSC
< 100kHz
SET
< 10kΩ), the
) should be
U
*
ALTERNATIVE METHODS OF SETTING THE OUTPUT
FREQUENCY OF THE LTC1799
The oscillator may be programmed by any method that
sources a current into the SET pin (Pin 3). The circuit in
Figure 3 sets the oscillator frequency using a program-
mable current source and in the expression for f
resistor R
already explained in the “Theory of Operation,” the voltage
difference between V
therefore, the Figure 3 circuit is less accurate than if a
resistor controls the oscillator frequency.
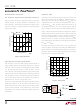
Figure 4 shows the LTC1799 configured as a VCO. A
voltage source is connected in series with an external 10k
resistor. The output frequency, f
V
V
relationship between the input current and the voltage
between V
degraded. The oscillator frequency, however, will mono-
tonically increase with decreasing V
5µA TO 200µA
CONTROL
0V TO 1.13V
+
V
and the SET pin. Again, this circuit decouples the
I
CONTROL
CONTROL
SET
, that is the voltage source connected between
V
+
V
–
+
+
Figure 4. Voltage Controlled Oscillator
+
Figure 3. Current Controlled Oscillator
is replaced by the ratio of 1.13V/I
0.1µF
R
and SET; the frequency accuracy will be
0.1µF
10k
SET
ƒ
OSC
ƒ
I
CONTROL
OSC
≅
10MHz
≅
+
1
2
3
1
2
3
10MHz
N
and SET is approximately 1.13V,
EXPRESSED IN (A)
N
V
GND
SET
V
GND
SET
LTC1799
+
LTC1799
+
•
R
10k
•
SET
10kΩ
1.13V
OUT
1799 F04
OUT
1799 F03
DIV
DIV
• 1 –
(APPROXIMATE, SEE TEXT)
(
5
4
5
4
• I
400kHz TO 21MHz
V
CONTROL
CONTROL
N = 1
1.13V
N = 1
OSC
CONTROL
LTC1799
, will vary with
)
.
CONTROL
sn1799 1799fbs
OSC
, the
7
. As