LM1084IS-ADJ National Semiconductor, LM1084IS-ADJ Datasheet - Page 9
LM1084IS-ADJ
Manufacturer Part Number
LM1084IS-ADJ
Description
Linear Voltage Regulator IC
Manufacturer
National Semiconductor
Datasheet
1.LM1084IS-ADJ.pdf
(13 pages)
Specifications of LM1084IS-ADJ
No. Of Pins
3
Output Current
1.5A
Termination Type
Through Hole
Mounting Type
Through Hole
Output Voltage Min
1.25V
Voltage Regulator Type
LDO Linear
Peak Reflow Compatible (260 C)
No
Lead Free Status / RoHS Status
Contains lead / RoHS non-compliant
Available stocks
Company
Part Number
Manufacturer
Quantity
Price
Part Number:
LM1084IS-ADJ
Manufacturer:
NS/国半
Quantity:
20 000
Company:
Part Number:
LM1084IS-ADJ
Manufacturer:
NSTI
Quantity:
5 823
Part Number:
LM1084IS-ADJ/NOPB
Manufacturer:
TI/德州仪器
Quantity:
20 000
Application Note
must be added, one for case to heat-sink (θ
heatsink to ambient (θ
predicted as follows:
T
T
P
consumption is calculated as follows:
Once the devices power is determined, the maximum allow-
able (θ
θ
The LM1084 has different temperature specifications for two
different sections of the IC: the control section and the output
section. The Electrical Characteristics table shows the junc-
tion to case thermal resistances for each of these sections,
while the maximum junction temperatures (T
section is listed in the Absolute Maximum section of the
datasheet. T
T
θ
follows:
θ
θ
The required heat sink is determined by calculating its re-
quired thermal resistance (θ
JA (max)
JA (max)
JA
JA
J
J
J(max)
D
= T
is junction temperature, T
is the power consumption of the device. Device power
(max, CONTROL SECTION) = (125˚C - T
(max, OUTPUT SECTION) = (150˚C - T
A
JA (max)
is 150˚C for the output section.
+ P
should be calculated separately for each section as
= T
D
R(max)
J(max)
(θ
) is calculated as:
JC
/P
+ θ
is 125˚C for the control section, while
D
CH
HA
= T
). The junction temperature can be
+ θ
J(max)
HA (max)
HA
A
(Continued)
) = T
is ambient temperature, and
− T
A(max)
).
A
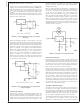
FIGURE 7. Heat sink thermal Resistance vs Area
+ P
/P
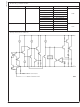
D
FIGURE 6. Power Dissipation Diagram
D
θ
CH
A(max)
JA
J(max)
A(max)
) and one for
) for each
)/P
)/P
D
D
9
Figure 6 shows the voltages and currents which are present
in the circuit.
θ
(θ
(θ
TROL SECTION) + θ
(θ
SECTION) + θ
If thermal compound is used, θ
C/W. If the case is soldered to the heat sink, then a θ
be estimated as 0 C/W.
After, θ
lower of the two θ
ate heat sink.
If PC board copper is going to be used as a heat sink, then
Figure 7 can be used to determine the appropriate area
(size) of copper foil required.
HA (max)
HA (max)
HA (max)
HA (max)
I
P
IN
D
HA (max)
= I
= (V
= θ
) should also be calculated twice as follows:
) = θ
) = θ
L
10094664
+ I
IN
JA (max)
JA
−V
JA
G
CH
(max, OUTPUT SECTION) - (θ
is calculated for each section, choose the
OUT
(max, CONTROL SECTION) - (θ
)
10094616
HA (max)
− (θ
) I
CH
L
)
+ V
JC
values to determine the appropri-
+ θ
IN
I
G
CH
CH
)
can be estimated at 0.2
JC
www.national.com
(OUTPUT
JC
CH
(CON-
can